

Bank Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Bank Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their banks.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating a bank business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write a bank business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your bank as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan
If you’re looking to start a bank or grow your existing bank, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your bank to improve your chances of success. Your bank business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Banks
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a bank are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for banks.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a bank.
If you want to start a bank or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your bank business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of bank you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a bank that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of banks?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the bank industry.
- Discuss the type of bank you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of bank you are operating.
For example, you might specialize in one of the following types of banks:
- Commercial bank : this type of bank tends to concentrate on supporting businesses. Both large corporations and small businesses can turn to commercial banks if they need to open a checking or savings account, borrow money, obtain access to credit or transfer funds to companies in foreign markets.
- Credit union: this type of bank operates much like a traditional bank (issues loans, provides checking and savings accounts, etc.) but banks are for-profit whereas credit unions are not. Credit unions fall under the direction of their own members. They tend to serve people affiliated with a particular group, such as people living in the same area, low-income members of a community or armed service members. They also tend to charge lower fees and offer lower loan rates.
- Retail bank: retail banks can be traditional, brick-and-mortar brands that customers can access in-person, online, or through their mobile phones. They also offer general public financial products and services such as bank accounts, loans, credit cards, and insurance.
- Investment bank: this type of bank manages the trading of stocks, bonds, and other securities between companies and investors. They also advise individuals and corporations who need financial guidance, reorganize companies through mergers and acquisitions, manage investment portfolios or raise money for certain businesses and the federal government.
In addition to explaining the type of bank you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of clients served, the number of clients with positive reviews, reaching X number of clients served, etc.
- Your legal business Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the bank industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the bank industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your bank business plan:
- How big is the bank industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your bank? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your bank business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, small businesses, families, and corporations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of bank you operate. Clearly, corporations would respond to different marketing promotions than individuals, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Bank Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other banks.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes trust accounts, investment companies, or the stock market. You need to mention such competition as well.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of bank are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide loans and retirement savings accounts?
- Will you offer products or services that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a bank business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of bank company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide savings accounts, auto loans, mortgage loans, or financial advice?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your plan, you are presenting the products and/or services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your bank. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your bank located in a busy retail district, a business district, a standalone office, or purely online? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your bank marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to websites
- Distribute flyers
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your bank, including reconciling accounts, customer service, accounting, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to sign up your Xth customer, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your bank to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your bank’s potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing banks. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing a bank or successfully running a small financial advisory firm.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you see 5 clients per day, and/or offer sign up bonuses? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your bank, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a bank:
- Cost of furniture and office supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your bank location lease or a list of accounts and loans you plan to offer.
Writing a business plan for your bank is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will understand the bank industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful bank.
Bank Business Plan Template FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my bank business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily write your bank business plan.
How Do You Start a Bank Business?
Starting a bank business is easy with these 14 steps:
- Choose the Name for Your Bank Business
- Create Your Bank Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your Bank Business
- Secure Startup Funding for Your Bank Business (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your Bank Business with the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your Bank Business
- Buy or Lease the Right Bank Business Equipment
- Develop Your Bank Business Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Bank Business
- Open for Business
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Bank business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how a Growthink business plan consultant can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


How To Write a Business Plan for Commercial Banking in 9 Steps: Checklist
By alex ryzhkov, resources on commercial banking.
- Financial Model
- Business Plan
- Value Proposition
- One-Page Business Plan
- SWOT Analysis
- Business Model
- Marketing Plan
Welcome to our blog post on how to write a business plan for commercial banking in 9 steps! As the financial industry continues to evolve, it is important for commercial banks to adapt and stay competitive. In this blog post, we will guide you through the key steps to creating a comprehensive business plan that will enable your bank to thrive in today's market.
Before we dive into the steps, let's take a moment to explore the current state of the commercial banking industry in the US. According to recent statistics, the sector has experienced steady growth over the past few years, with total assets reaching [statistical information about industry growth] .
Now, let's move on to the first step in writing a business plan for commercial banking: conducting market research. This crucial step involves gaining a deep understanding of the current market trends, customer preferences, and potential opportunities for growth. By thoroughly researching the market landscape, you will be better equipped to identify your target market and customer segments.
Once you have identified your target market, it's time to analyze your competitors and industry trends. This step will help you understand the competitive landscape and allow you to position your bank effectively.
Next, you need to define your business objectives and goals. This step will provide clarity on what you want to achieve and will guide the rest of your business plan.
After defining your objectives, conducting a SWOT analysis is crucial. This analysis will help you identify your bank's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, allowing you to develop strategies to capitalize on strengths and address weaknesses.
To ensure the financial feasibility and viability of your business plan, you must determine the financial aspects of your bank. This includes assessing your projected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
Identifying the resources and skills required to execute your business plan is another critical step. Knowing what you need in terms of infrastructure, technology, and human resources will help you plan and allocate resources effectively.
Developing a strong marketing strategy is essential to attract and retain customers. This step involves creating a comprehensive plan to promote your bank's products and services and differentiate yourself from competitors.
Lastly, establishing a timeline and milestones will enable you to track your progress and ensure that you are on track to achieve your goals. This step provides a roadmap for implementation and helps you stay focused on executing your business plan.
By following these nine steps, you will be well-equipped to create a thorough and effective business plan for commercial banking. Stay tuned as we dive deeper into each step in our upcoming blog posts!
Conduct Market Research
Market research is a crucial step in the process of writing a business plan for commercial banking. It allows you to gather essential information about the market and industry in which you plan to operate. By conducting thorough market research, you can identify key trends, understand customer needs and preferences, and gain insights into your competitors' strategies.
Here are some important steps to consider when conducting market research:
- Identify the target market and customer segments: Determine the specific group of customers you want to serve and understand their characteristics, preferences, and behaviors. This will help you tailor your banking services to meet their needs.
- Analyze competitors and industry trends: Study your competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and strategies. Identify any emerging trends or changes in the industry that may impact your business. This knowledge will help you position your bank effectively.
- Explore customer needs and pain points: Conduct surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gather insights into what customers want and what problems they are facing. This will allow you to develop products and services that address their needs.
- Stay updated with regulatory requirements: Understand the legal and regulatory framework in the banking industry. Ensure that your business plan aligns with the necessary compliance standards.
Market Research Tips:
- Use a combination of primary and secondary research methods: Primary research includes direct interaction with customers through surveys or interviews, while secondary research involves analyzing existing data and reports.
- Seek professional assistance if needed: If you are new to market research or lack the necessary expertise, consider hiring a market research firm or consultant to help you gather and analyze the data.
- Continuously update your market research: Market trends and customer preferences can change rapidly. Regularly revisit your market research to ensure you stay ahead of the curve and remain responsive to customer needs.
Identify Target Market And Customer Segments
Identifying your target market and customer segments is a crucial step in developing a successful business plan for commercial banking. It involves clearly understanding the needs and preferences of your potential customers and tailoring your products and services to meet those needs. Here are some key points to consider when identifying your target market and customer segments:
- Demographics: Start by examining the demographic characteristics of your potential customers, such as age, gender, income level, and location. This information will help you create targeted marketing campaigns and determine the best ways to reach your target market.
- Industry-specific needs: Depending on the nature of your business, you may want to focus on specific industries or sectors that are more likely to require commercial banking services. Analyze the needs and challenges faced by these industries and tailor your offerings accordingly.
- Behavior patterns: Understanding the behavior patterns of your target market can provide valuable insights into their preferences and decision-making processes. Consider factors such as their banking habits, preferences for digital or in-person banking, and likelihood to use additional services like investment advice.
- Unique selling proposition: Identify what sets your commercial banking services apart from competitors and how it aligns with the needs of your target market. Highlighting your unique selling proposition will help you attract and retain customers in a competitive market.
- Conduct surveys or interviews with potential customers to gain insights into their banking preferences and expectations.
- Segment your target market into more specific groups based on their characteristics and needs. This will allow you to tailor your messaging and offerings more effectively.
- Regularly monitor market trends and changes in customer preferences to ensure you stay relevant and adaptable in an evolving commercial banking industry.
By identifying your target market and customer segments, you can refine your business strategy and develop products and services that meet their specific needs. This customer-centric approach will increase the likelihood of attracting and retaining loyal customers, driving the growth and success of your commercial banking business.
Analyze Competitors And Industry Trends
Conducting a thorough analysis of competitors and industry trends is crucial for developing a successful business plan for commercial banking. This step will provide valuable insights into the current market landscape, competition, and potential opportunities. Here are key aspects to consider when conducting this analysis:
- Identify key competitors: Research and identify the main players in the commercial banking industry. This includes both traditional banks and online banking platforms. Analyze their market share, product offerings, customer base, and financial performance.
- Assess competitive advantage: Determine what sets your bank apart from competitors. This could be innovative technology, exceptional customer service, or specialized financial products. Understanding your competitive advantage is crucial for attracting and retaining customers.
- Analyze industry trends: Stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends and developments. This includes changes in customer preferences, advancements in technology, regulatory updates, and emerging market opportunities. Adapt your business plan to align with these trends to stay competitive.
- Examine customer satisfaction: Investigate customer satisfaction levels with current banking services. Look for areas where competitors may be falling short and strive to excel in those aspects. Providing a superior customer experience can be a significant competitive advantage.
Tips for Analyzing Competitors and Industry Trends:
- Consider conducting surveys or focus groups to gather feedback from potential customers about their banking needs and preferences.
- Stay updated on industry publications, reports, and conferences to stay informed about emerging trends.
- Monitor social media channels and online forums to gain insights into customer opinions and experiences with competitors.
- Regularly review competitor websites and promotional materials to understand their marketing strategies and product offerings.
Define Business Objectives And Goals
Defining clear and specific business objectives and goals is essential for any commercial banking venture. These objectives serve as a guidepost, helping you stay focused and aligned with your overall vision. Here are a few key steps to help you establish your business objectives and goals:
- Identify your mission: Define the purpose and mission of your commercial banking venture. What value do you aim to provide to your customers and the industry as a whole?
- Set measurable goals: Determine the specific outcomes you want to achieve and ensure they are measurable. This could include targets for loan portfolio growth, deposit growth, customer acquisition, or profitability.
- Consider market trends: Take into account current market trends and customer demands while setting your goals. Stay informed about industry developments and anticipate future shifts that could impact your business.
- Align with customer needs: Ensure that your objectives and goals align with the needs and preferences of your target market. Consider conducting market research or engaging with potential customers to better understand their requirements.
- Be realistic: While it's important to set ambitious goals, it's equally crucial to be realistic. Consider the financial and operational resources available to you and set achievable targets accordingly.
- Stay adaptable: As the banking industry continues to evolve, it's crucial to have flexibility in your objectives and goals. Be open to adjusting and refining them as market conditions change.
Additional Tips:
- Involve key stakeholders, such as senior management and relevant team members, in the process of defining business objectives and goals. This ensures buy-in and a shared vision.
- Regularly review and evaluate your progress towards achieving your objectives. This will allow you to make necessary adjustments and measure your success along the way.
- Communicate your objectives and goals internally to align your entire organization around a common purpose. This fosters a sense of unity and clarity among your employees.
By clearly defining your business objectives and goals, you can create a roadmap for success in the competitive landscape of commercial banking. This step sets the stage for the subsequent development of strategies and tactics to achieve your desired outcomes.
Conduct a SWOT Analysis
Performing a SWOT analysis is a crucial step in developing a comprehensive business plan for commercial banking. SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This analysis helps you gain a deeper understanding of your bank's internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats in the market.
Strengths: Begin by identifying the unique strengths of your bank. These could be factors such as a strong customer base, a well-established brand, a diverse portfolio of services, or a talented team. By recognizing these strengths, you can leverage them to gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Weaknesses: Acknowledge the areas where your bank may be falling short. These could include limited branch network, outdated technology, or a lack of expertise in certain financial areas. Pinpointing weaknesses allows you to develop strategies to improve upon them and address any potential vulnerabilities.
Opportunities: Assess the external factors that could present new opportunities for your bank. Are there emerging markets or segments that you can tap into? Are there any regulatory changes that could benefit your banking operations? Identifying opportunities enables you to position your bank proactively and capitalize on favorable conditions.
Threats: Evaluate the potential threats that your bank may face in the market. Consider factors such as increasing competition, economic uncertainty, changing consumer preferences, or regulatory hurdles. Understanding these threats helps you devise contingency plans and adapt your strategies accordingly.
Tips for Conducting a SWOT Analysis:
- Foster open and honest discussions among your team to gain diverse perspectives.
- Research and analyze market trends, industry reports, and customer feedback to gather relevant data for your analysis.
- Focus on actionable insights rather than vague observations.
- Regularly revisit and update your SWOT analysis to stay aligned with changing market dynamics.
A SWOT analysis serves as a valuable tool for business planning in commercial banking. It helps you identify areas for improvement, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate potential risks. By conducting a thorough SWOT analysis, you can develop a sound strategy that positions your bank for long-term success in the ever-evolving banking industry.
Determine The Financial Feasibility And Viability
One of the most crucial steps in developing a business plan for commercial banking is determining the financial feasibility and viability of your venture. This step involves evaluating the potential profitability and sustainability of your business model.
The following are key factors to consider when determining the financial feasibility and viability of your commercial banking business:
- Market demand: Evaluate the demand for banking services in your target market. Are there enough potential customers to sustain your business?
- Competition: Analyze the competitive landscape. Understand the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and identify ways to differentiate your bank.
- Profitability: Assess the potential profitability of your banking model. Calculate the projected revenue from lending activities, fees, and other revenue streams. Consider the associated costs, such as overhead expenses and regulatory compliance.
- Risk assessment: Identify and analyze the potential risks associated with your banking business. This includes credit risk, interest rate risk, operational risk, and regulatory risk. Develop risk mitigation strategies to minimize those risks.
- Capital requirements: Determine the amount of capital needed to start and operate your commercial bank. Consider the initial investments required for technology infrastructure, talent acquisition, and marketing efforts.
- Financial projections: Develop detailed financial projections, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These projections should cover at least the first three to five years of your business.
- Consult with financial experts and industry professionals to ensure accurate evaluation of financial feasibility.
- Stay updated with the latest industry trends and regulatory changes that may impact the financial viability of your venture.
- Consider creating different financial scenarios to assess the potential outcomes under various market conditions and risk scenarios.
Determining the financial feasibility and viability of your commercial banking business is essential for attracting investors, securing loans, and making informed strategic decisions. By carefully evaluating the market demand, competition, profitability, risks, capital requirements, and financial projections, you can build a solid case for the success of your business venture.
Identify Resources and Skills Required
Identifying the resources and skills required for your commercial banking business plan is crucial for ensuring its success. By understanding the specific resources and skills needed, you can adequately prepare and allocate the necessary assets to drive your business forward.
To identify the resources required for your commercial banking venture, consider the following:
- Financial Capital: Determine the amount of capital required to commence operations and sustain the business in the initial phase. This includes calculating the funds needed to secure office space, hire employees, invest in technology and security systems, and cover other operational expenses.
- Human Capital: Assess the skills and expertise required to run a commercial banking business. This includes hiring professionals with experience in lending, credit analysis, risk management, customer service, compliance, and other relevant areas. Additionally, consider the number of employees needed to handle the projected workload and ensure efficient operations.
- Technological Infrastructure: Identify the necessary technology and systems required for your banking operations. This may include secure servers, online banking platforms, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and other tools that enable efficient and secure banking transactions.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that you have a thorough understanding of the legal and regulatory requirements applicable to the commercial banking industry. This includes obtaining appropriate licenses and permits, complying with anti-money laundering regulations, and adhering to consumer protection laws.
- Consider outsourcing certain functions, such as IT support or marketing, to experienced third-party service providers. This can help reduce costs and enhance efficiency.
- Stay updated with industry trends and advancements in technology to ensure that your banking operations remain competitive and relevant.
- Invest in continuous training and development programs to enable your employees to stay abreast of the latest banking practices and regulations.
By identifying the necessary resources and skills, you can effectively plan and allocate your business's resources to enhance its viability and success in the commercial banking industry. Remember, a well-prepared and properly allocated resource plan is vital for achieving your business objectives and serving your customers effectively.
Develop A Marketing Strategy
Once you have conducted market research, identified your target market and customer segments, analyzed competitors and industry trends, defined your business objectives and goals, and conducted a SWOT analysis, it is time to develop a marketing strategy. This will be crucial in attracting and retaining customers, as well as creating brand awareness and positioning your bank in the market.
Here are some important steps to consider when developing your marketing strategy:
- 1. Identify your Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Determine what sets your bank apart from competitors and highlight your unique features and benefits. This will help you differentiate and position your bank in the market.
- 2. Define your target audience: Now that you have identified your target market and customer segments, it is important to create buyer personas to understand their characteristics, needs, and preferences. This will allow you to tailor your marketing efforts and messages accordingly.
- 3. Set marketing objectives: Determine specific and measurable objectives for your marketing efforts. Examples could include increasing customer acquisition, boosting brand awareness, or promoting specific financial products or services.
- 4. Choose marketing channels: Consider which marketing channels will be most effective in reaching your target audience. Traditional channels like television, radio, and print advertisements may still be relevant, but also explore digital channels such as social media, email marketing, content marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO).
- 5. Craft compelling messages and offers: Develop compelling messaging that communicates your USP and resonates with your target audience. Create offers or promotions that incentivize potential customers to choose your bank over competitors.
- Ensure your marketing messages align with your bank's brand identity and values.
- Regularly analyze and adapt your marketing strategy based on performance metrics and customer feedback.
- Consider utilizing partnerships or collaborations with other businesses or organizations to expand your reach.
By developing a well-thought-out marketing strategy, you can effectively communicate your bank's value proposition and attract customers in a competitive market. It is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to stay relevant and successful.
Establish A Timeline And Milestones
Once you have defined your business objectives and goals in your business plan, it is crucial to establish a timeline and milestones to track your progress. This will not only keep you organized but also help you stay motivated and ensure that you are making measurable progress towards your goals. Here are some important steps to consider when establishing a timeline and milestones for your commercial banking business:
- Break down your objectives into achievable milestones: Start by breaking down your long-term objectives into smaller, more manageable milestones. This will make your goals seem less daunting and allow you to measure your progress more effectively. For example, if your objective is to acquire a certain number of customers within a year, you can set quarterly milestones to track your customer acquisition progress.
- Set realistic deadlines: It is important to set realistic deadlines for each milestone based on your market research, analysis of competitors, and available resources. Avoid setting overly ambitious deadlines that may put undue pressure on you and your team. Instead, create a timeline that gives you a realistic timeframe to complete each milestone while considering any potential challenges or obstacles you may encounter along the way.
- Assign responsibilities and roles: Clearly define responsibilities and roles for each milestone to ensure that everyone on your team is aware of their tasks and accountabilities. This will help streamline the execution of your business plan and minimize any confusion or potential delays that may arise from overlapping responsibilities.
- Monitor and track progress: Regularly monitor and track your progress against the established timeline and milestones. This will allow you to identify any delays or deviations from the original plan and take appropriate actions to address them. Consider setting up key performance indicators (KPIs) or metrics to measure the success of each milestone and keep a record of your achievements and challenges along the way.
- Stay flexible and adaptable: While it is important to stick to your timeline and milestones, it is equally important to remain flexible and adaptable in the face of unexpected developments or changing market conditions. Be prepared to adjust your timeline or revise your milestones if necessary to stay aligned with your overall business objectives.
- Use project management tools or software to help you visualize and manage your timeline and milestones effectively.
- Regularly communicate with your team to ensure everyone is aware of the progress and any changes in the timeline or milestones.
- Celebrate your achievements when you reach a milestone to boost morale and motivation among your team members.
In conclusion, writing a business plan for commercial banking involves several important steps that will guide your strategy and help you navigate the competitive landscape. By conducting thorough market research, identifying target markets and segments, and analyzing competitors and industry trends, you can develop a solid foundation for your business. Additionally, defining clear business objectives, conducting a SWOT analysis, and determining the financial feasibility and viability of your plan are crucial for success. It is also important to identify the necessary resources and skills, develop a marketing strategy, and establish a timeline and milestones to track your progress.
With a well-structured and comprehensive business plan, you can demonstrate your understanding of the industry, set achievable goals, and attract the necessary funding and support. Remember that the commercial banking industry may be evolving with the rise of online platforms, but the core principles of deposit and lending remain the foundation of success. By following these steps and adapting to the changing landscape, you can position your commercial banking business for long-term growth and profitability. Good luck!

$169.00 $99.00 Get Template
Related Blogs
- Starting a Business
- KPI Metrics
- Running Expenses
- Startup Costs
- Pitch Deck Example
- Increasing Profitability
- Sales Strategy
- Rising Capital
- Valuing a Business
- How Much Makes
- Sell a Business
- Business Idea
- How To Avoid Mistakes
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published
- ATM locations
- ATM locator
Estás ingresando al nuevo sitio web de U.S. Bank en español.
How to get started creating your business plan, a successful business plan can help you focus your goals and take actionable steps toward achieving them. here’s what to consider as you develop your plan..
Regardless of whether or not you’re pitching to investors and lenders, starting a business requires a plan. A business plan gives you direction, helps you qualify your ideas and clarifies the path you intend to take toward your goal.
Four important reasons to write a business plan:
- Decision-making: Business plans help you eliminate any gray area by writing specific information down in black and white. Making tough decisions is often one of the hardest and most useful parts of writing a business plan.
- A reality check: The first real challenge after deciding to launch a new venture may be writing the business plan. Through the process, you may realize your business idea is a bit flawed or not yet fully developed. This may feel like extra work, but the effort you put into improving your idea during this step can bolster your chance of future success.
- New ideas: Discovering new ideas, different approaches and fresh perspectives are invaluable parts of the business planning process. Working closely with your concept can lead to unexpected insights, shifting your business in the right direction.
- Developing an action plan: Your business plan is a tool that will help you outline action items, next steps and future activities. This living, breathing document shows where you are and where you want to be, with the framework you need to get there.
Business plan guide: How to get started
Use this exercise to gather some of the most important information. When you're ready to put an outline together, follow our standard business plan template (PDF) and use this business plan example to use as a guide as you fill in your outline. Once your outline is finalized, you can share it with business partners, investors or banks as a tool to promote your concept.
- Vision: Your vision statement sets the stage for everything you hope your business will accomplish going forward. Let yourself dream, pinpointing the ideas that will keep you inspired and motivated when you hit a bump in the road.
- Mission: A mission statement clarifies the purpose of your business and guides your plan, ultimately answering the question, "Why do you exist?"
- Objectives: Use your business objectives to define your goals and priorities. What are you going to accomplish with your business, and in what timeframe? These touchstones will drive your actions and help you stay focused.
- Strategies: Your objectives describe what you’re going to do, while your strategies describe how you’re going to do it. Consider your goals here, and identify the different ways you’ll work to reach them.
- Startup capital: Determine what your startup expenses will be. Having a clear idea will allow you to figure out where the money is coming from and help you spend what you have in the right areas.
- Monthly expenses: What do you estimate your business’ ongoing monthly expenses will be? This may change significantly over time — consider what your expenditure could be immediately after launch, in three months, in six months and in one year.
- Monthly income: In order to cover your expenses (and hopefully make a profit), you will need to estimate your income. What are your revenue streams? It's always wise to diversify your income. That way, you won’t be tied to one stream that might not be lucrative as quickly as you need it to be.
- Goal-setting and creating an action plan: Once you have all the specifics outlined, it's time to set up the step-by-step action items explained in the companion guide, a standard business plan outline. This process will utilize the hard work you've already done, breaking each step down in a way that you can follow.
A business plan isn’t necessarily a static document that you create once and then forget about. You can use it as a powerful tool by referencing it to adjust your priorities, stay on track and keep your goals in sight.
Business plan: An outline
Use this exercise to gather important information about your business.
Answer these questions to start your planning process. Your responses will provide important information about your business, which you can use as an overview to develop your plan further.
- What is your dream?
- What do you feel inspired to do or create?
- What keeps you motivated, even in the face of uncertainty?
- Why does this business exist?
- What purpose(s) or need(s) does it fulfill for customers?
Objectives
- List the goals of your company, then number them in order of importance.
- What will the business accomplish when it’s fully established and successful?
- How much time will it take to reach this point?
- For each goal or objective listed above, write one or more actions required to complete it.
Startup capital
- List any and all startup expenses that come to mind.
- Next to each:
- Estimate the cost of any expenses you can.
- List the most likely source of the funding.
- Circle the high-priority expenses.
- Assess whether your available capital is going toward the high-priority items. If not, reconsider the way you will allocate funds.
Monthly expenses
- If you can, estimate your business’ ongoing monthly expenses immediately after launch, in three months, in six months and in one year.
- If you can’t, what information will you need in order to estimate your expenses?
Monthly income
- What are your revenue streams? Estimate your monthly income accordingly.
- Which revenue sources deliver fast or slow returns? Are there other sources you could consider to diversify assets?
- After completing your outline, reference your responses as you work through a traditional business plan guide. This next step will allow you to expand and add more detailed information to your plan.
- When you’re ready to make your formal plan, reference this companion guide, a standard business plan outline (PDF). We've also included a business plan example to help as you fill in your outline.
Learn how U.S. Bank can support you and your business needs at usbank.com/small-business.
Learn about U.S. Bank
Related content

7 tips to help grow your business after launch

Mapping out success for a small-business owner

Unexpected expenses: 5 small business costs to know and how to finance them

How to identify what technology is needed for your small business

Key considerations for online ordering systems

Staying organized when taking payments

Tools that can streamline staffing and employee management

How increased supply chain visibility can combat disruptors

How one organization is funding equity in the Chicago area

Making the leap from employee to owner

Starting a business with a friend: How to talk about it

How to fund your business without using 401(k) savings

How to choose the right business savings account

5 tips to help you land a small business loan

7 uncommon recruiting strategies that you may not have tried yet

Checklist: What you’ll need for your first retail pop-up shop

4 restaurant models that aren’t dine-in

Streamline operations with all-in-one small business financial support

Planning for restaurant startup costs and when to expect them

The moment I knew I’d made it: The Cheesecakery

Business tips and advice for Black entrepreneurs

Make your business legit

How a bright idea became a successful business (in Charlotte, North Carolina)

Starting a business? Follow these steps

How to establish your business credit score

Talent acquisition 101: Building a small business dream team

What is needed to apply for an SBA loan
How does an electronic point of sale help your business keep track of every dime.

Opening a business on a budget during COVID-19

Refinancing your practice loans: What to know

How I did it: Grew my business by branching out

6 common financial mistakes made by dentists (and how to avoid them)

How I did it: Turned my side hustle into a full-time job

Quit your job to start a business: How to save enough

How a 13-year-old created a clothing line that reflects her passions

How to test new business ideas

How running a business that aligns with core values is paying off

Meet the Milwaukee businessman behind Funky Fresh Spring Rolls

From LLC to S-corp: Choosing a small business entity

Costs to consider when starting a business

The different types of startup financing
Making a ‘workout’ work out as a business

How mobile point of sale (mPOS) can benefit your side gig
Disclosures.
Loan approval is subject to credit approval and program guidelines. Not all loan programs are available in all states for all loan amounts. Interest rates and program terms are subject to change without notice. Mortgage, home equity and credit products are offered by U.S. Bank National Association. Deposit products are offered by U.S. Bank National Association. Member FDIC.
Free Financial Templates for a Business Plan
By Andy Marker | July 29, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up expert-tested financial templates for your business plan, all of which are free to download in Excel, Google Sheets, and PDF formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find the essential financial statement templates, including income statement templates , cash flow statement templates , and balance sheet templates . Plus, we cover the key elements of the financial section of a business plan .
Financial Plan Templates
Download and prepare these financial plan templates to include in your business plan. Use historical data and future projections to produce an overview of the financial health of your organization to support your business plan and gain buy-in from stakeholders
Business Financial Plan Template
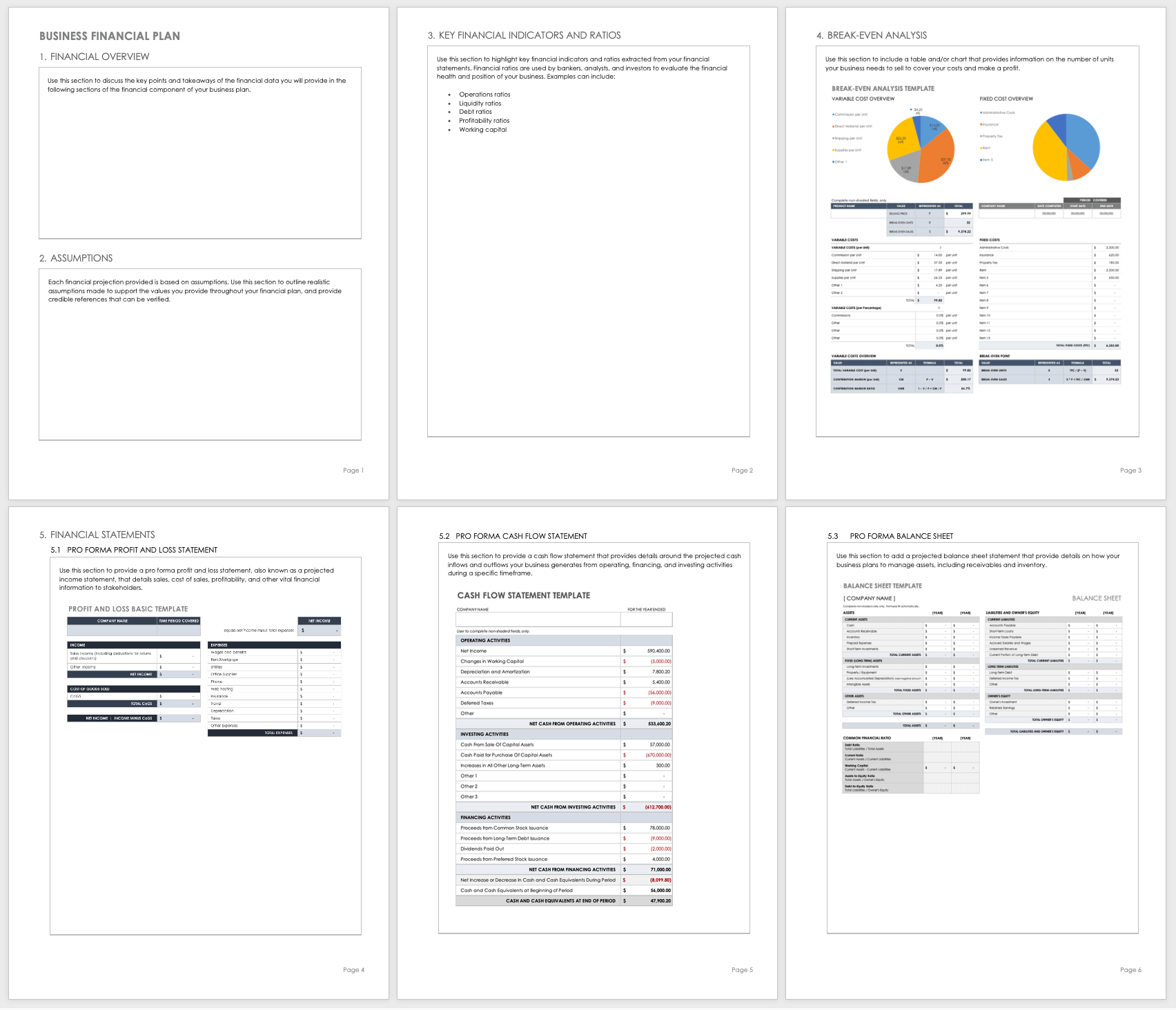
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors.
Download Financial Plan Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Financial Plan Projections Template for Startups
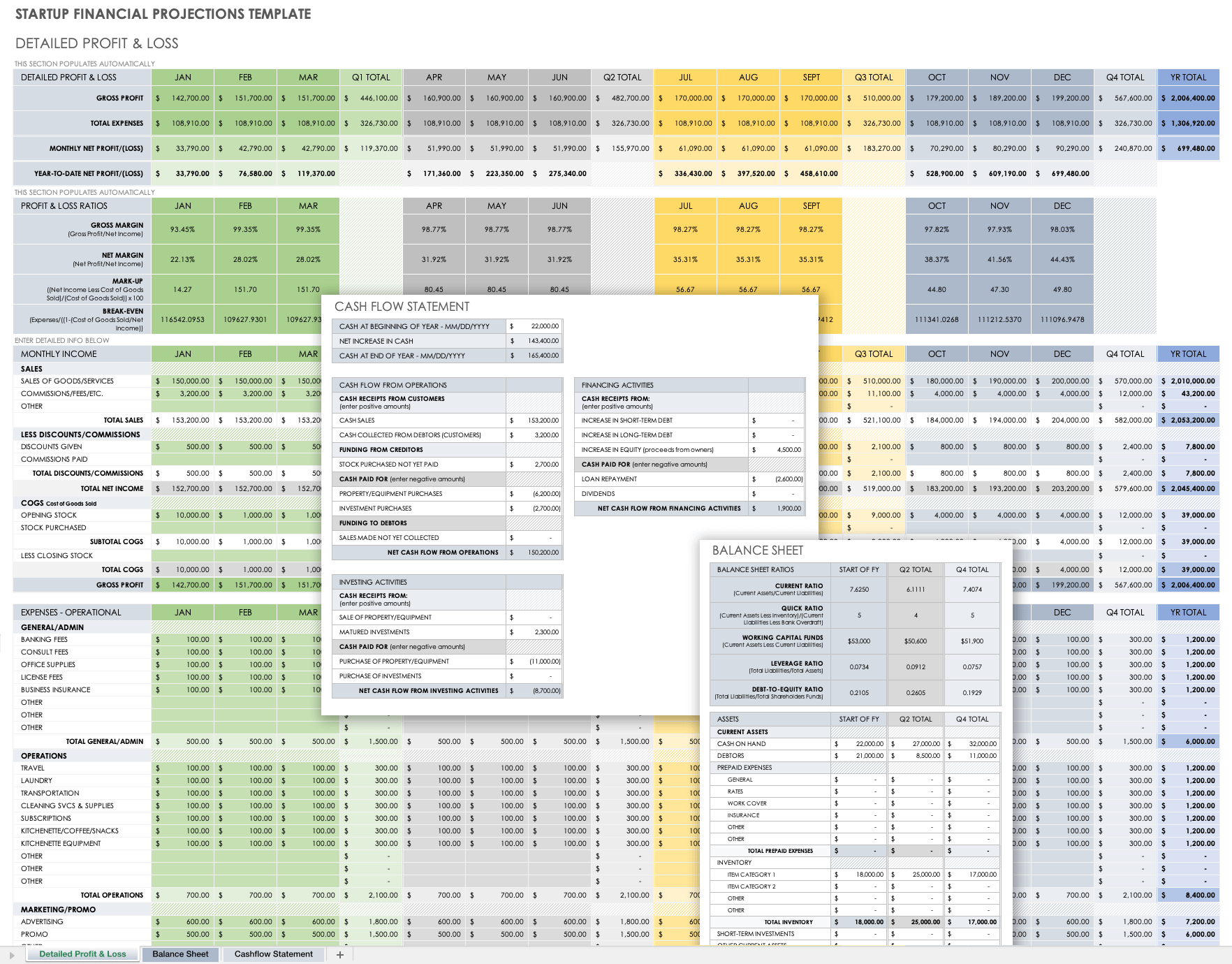
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business.
Download Startup Financial Projections Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Income Statement Templates for Business Plan
Also called profit and loss statements , these income statement templates will empower you to make critical business decisions by providing insight into your company, as well as illustrating the projected profitability associated with business activities. The numbers prepared in your income statement directly influence the cash flow and balance sheet forecasts.
Pro Forma Income Statement/Profit and Loss Sample
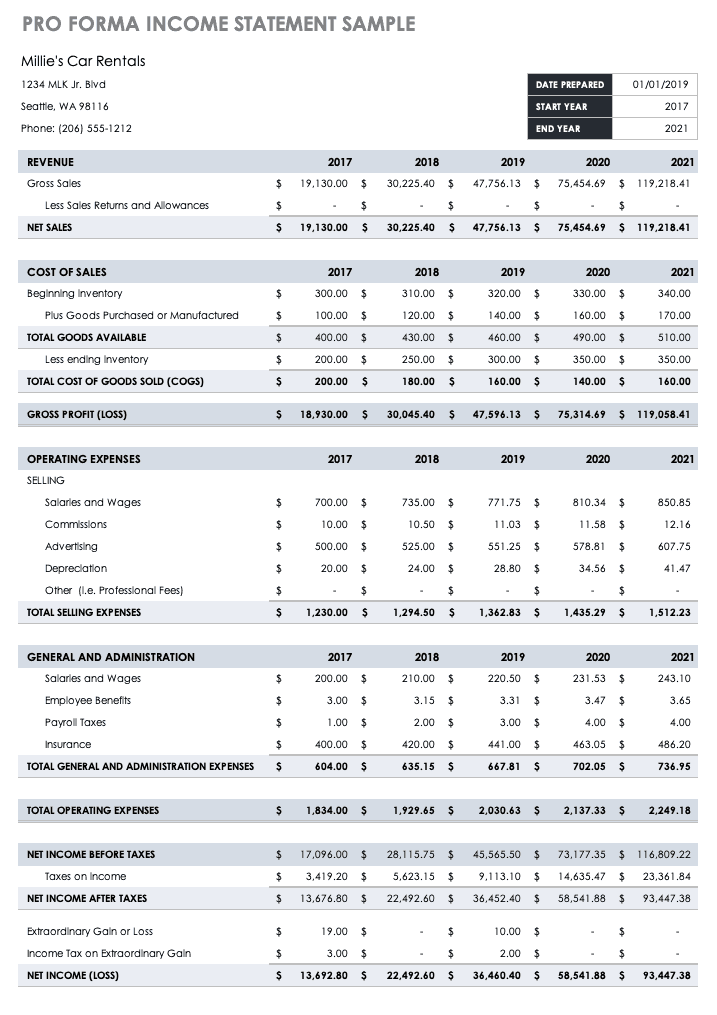
Use this pro forma income statement template to project income and expenses over a three-year time period. Pro forma income statements consider historical or market analysis data to calculate the estimated sales, cost of sales, profits, and more.
Download Pro Forma Income Statement Sample - Excel
Small Business Profit and Loss Statement
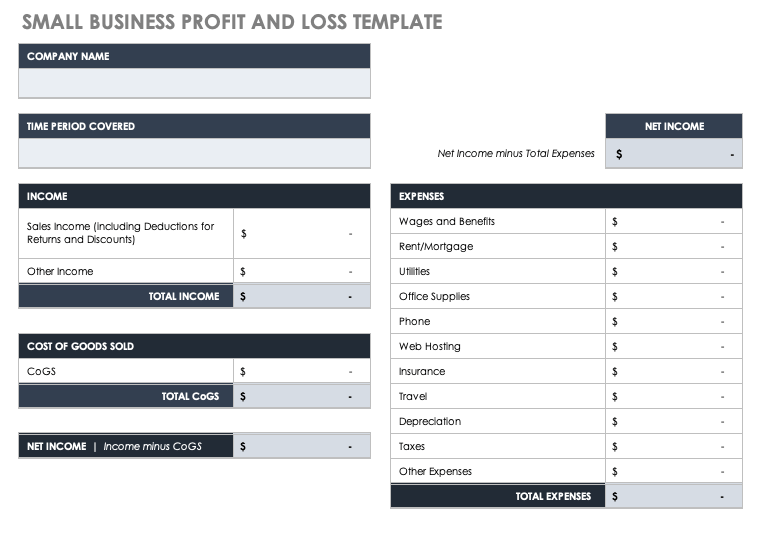
Small businesses can use this simple profit and loss statement template to project income and expenses for a specific time period. Enter expected income, cost of goods sold, and business expenses, and the built-in formulas will automatically calculate the net income.
Download Small Business Profit and Loss Template - Excel
3-Year Income Statement Template
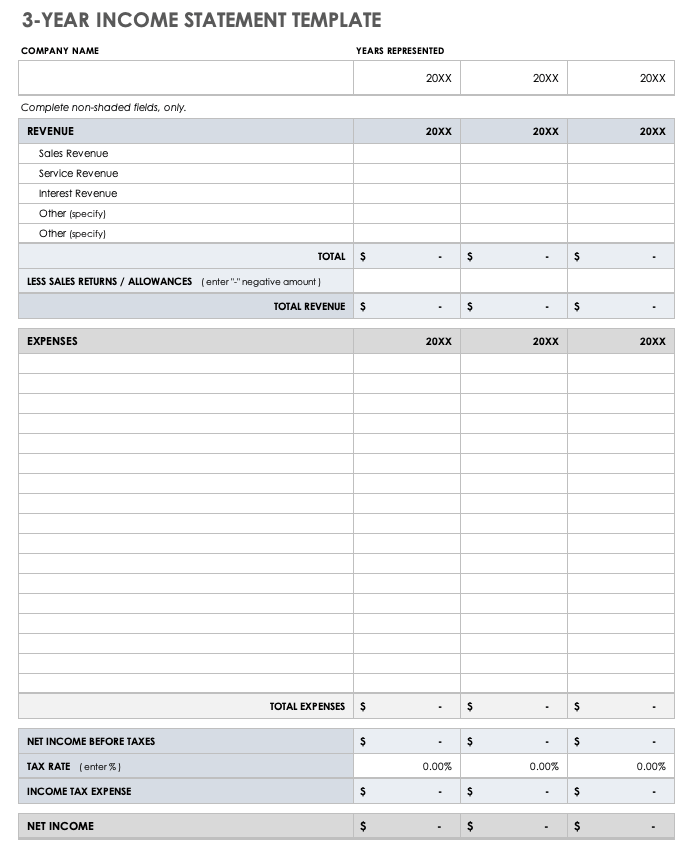
Use this income statement template to calculate and assess the profit and loss generated by your business over three years. This template provides room to enter revenue and expenses associated with operating your business and allows you to track performance over time.
Download 3-Year Income Statement Template
For additional resources, including how to use profit and loss statements, visit “ Download Free Profit and Loss Templates .”
Cash Flow Statement Templates for Business Plan
Use these free cash flow statement templates to convey how efficiently your company manages the inflow and outflow of money. Use a cash flow statement to analyze the availability of liquid assets and your company’s ability to grow and sustain itself long term.
Simple Cash Flow Template

Use this basic cash flow template to compare your business cash flows against different time periods. Enter the beginning balance of cash on hand, and then detail itemized cash receipts, payments, costs of goods sold, and expenses. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate total cash payments, net cash change, and the month ending cash position.
Download Simple Cash Flow Template
12-Month Cash Flow Forecast Template
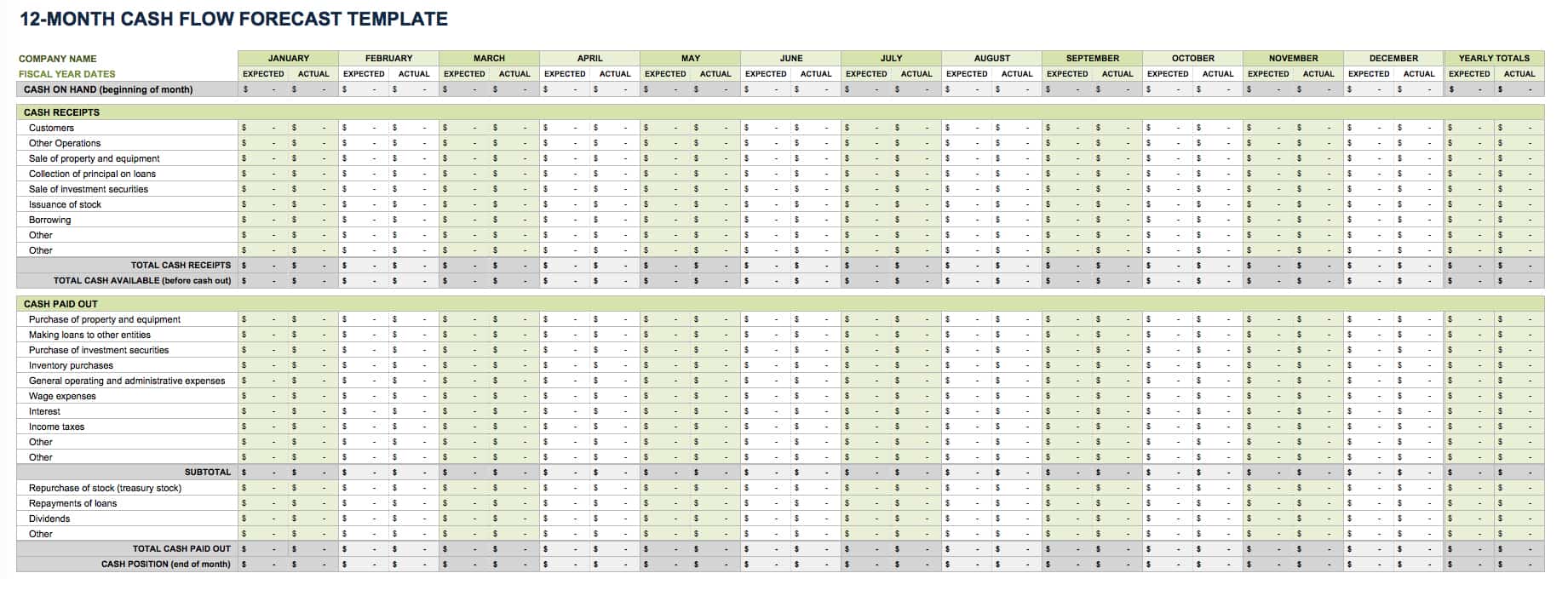
Use this cash flow forecast template, also called a pro forma cash flow template, to track and compare expected and actual cash flow outcomes on a monthly and yearly basis. Enter the cash on hand at the beginning of each month, and then add the cash receipts (from customers, issuance of stock, and other operations). Finally, add the cash paid out (purchases made, wage expenses, and other cash outflow). Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate your cash position for each month with.
Download 12-Month Cash Flow Forecast
3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template Set
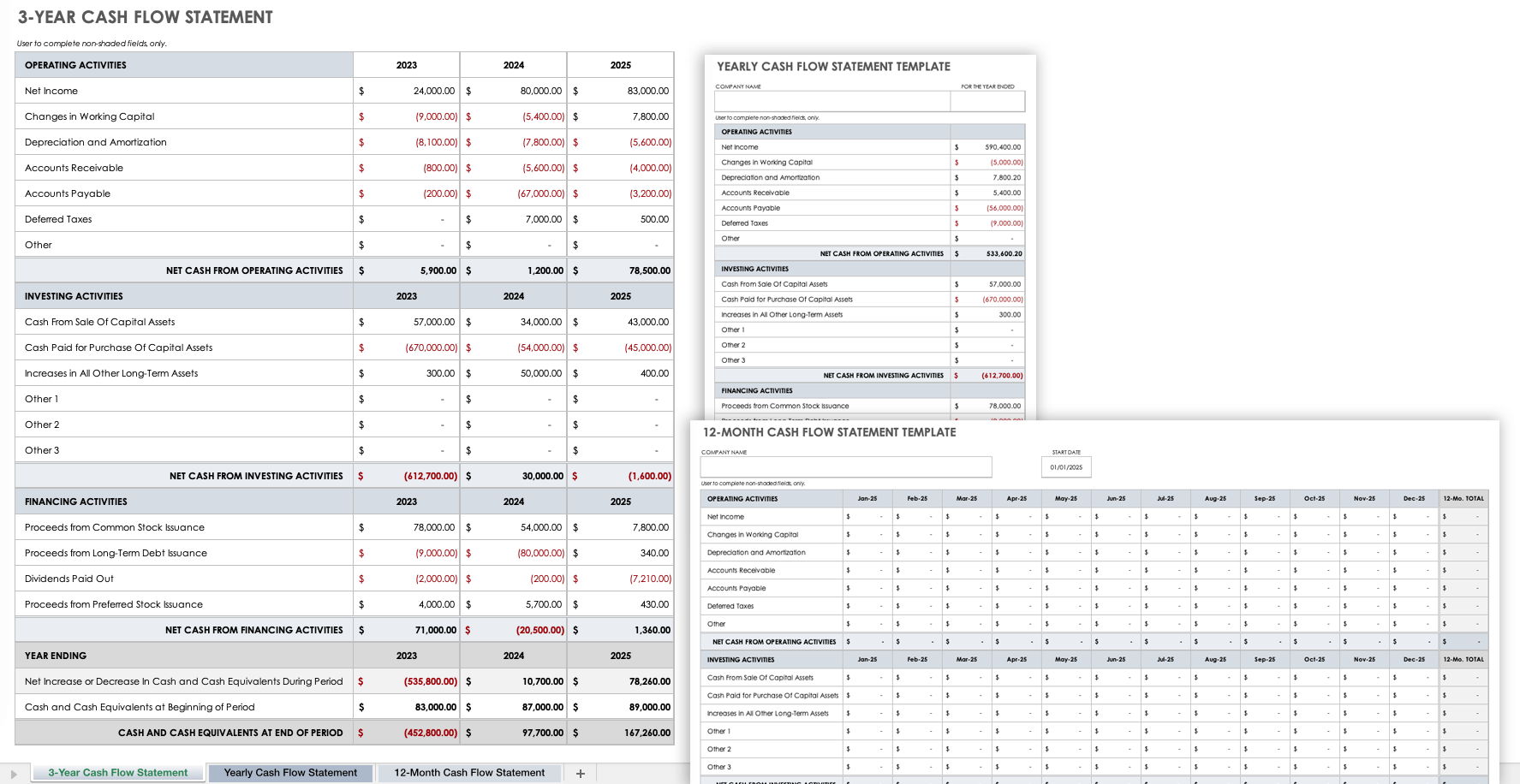
Use this cash flow statement template set to analyze the amount of cash your company has compared to its expenses and liabilities. This template set contains a tab to create a monthly cash flow statement, a yearly cash flow statement, and a three-year cash flow statement to track cash flow for the operating, investing, and financing activities of your business.
Download 3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template
For additional information on managing your cash flow, including how to create a cash flow forecast, visit “ Free Cash Flow Statement Templates .”
Balance Sheet Templates for a Business Plan
Use these free balance sheet templates to convey the financial position of your business during a specific time period to potential investors and stakeholders.
Small Business Pro Forma Balance Sheet
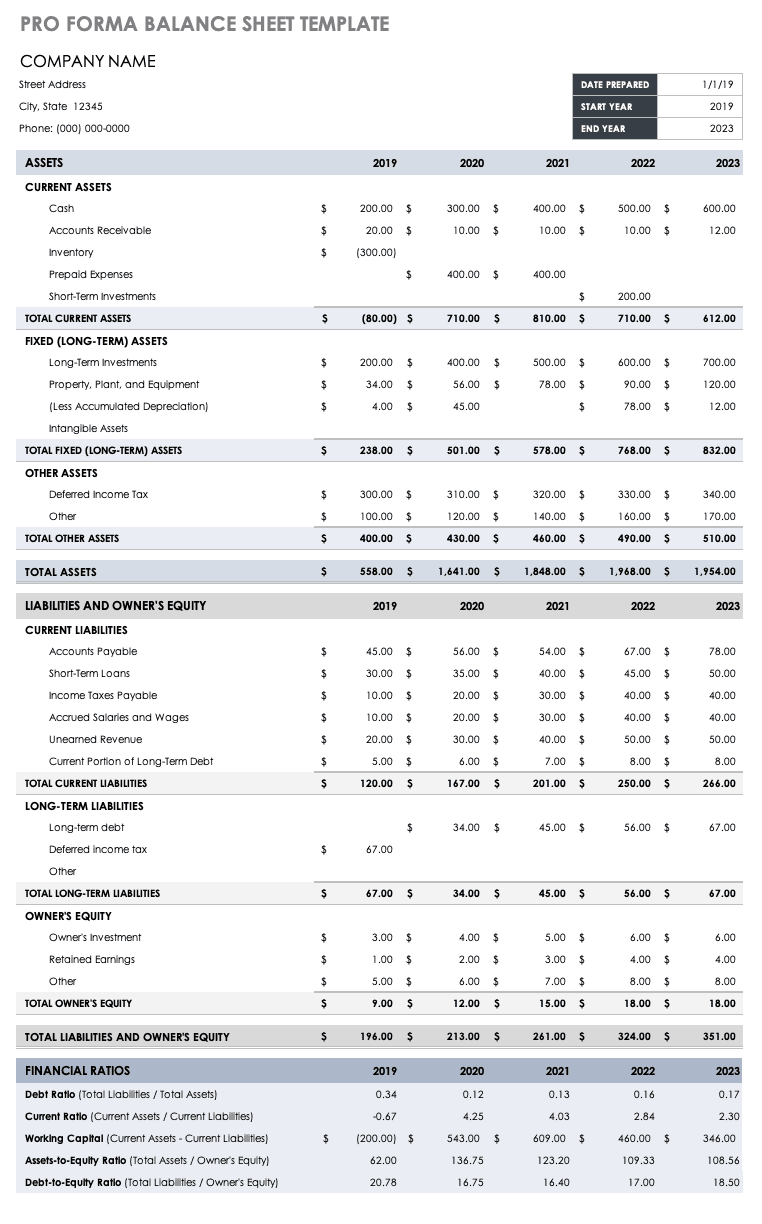
Small businesses can use this pro forma balance sheet template to project account balances for assets, liabilities, and equity for a designated period. Established businesses can use this template (and its built-in formulas) to calculate key financial ratios, including working capital.
Download Pro Forma Balance Sheet Template
Monthly and Quarterly Balance Sheet Template
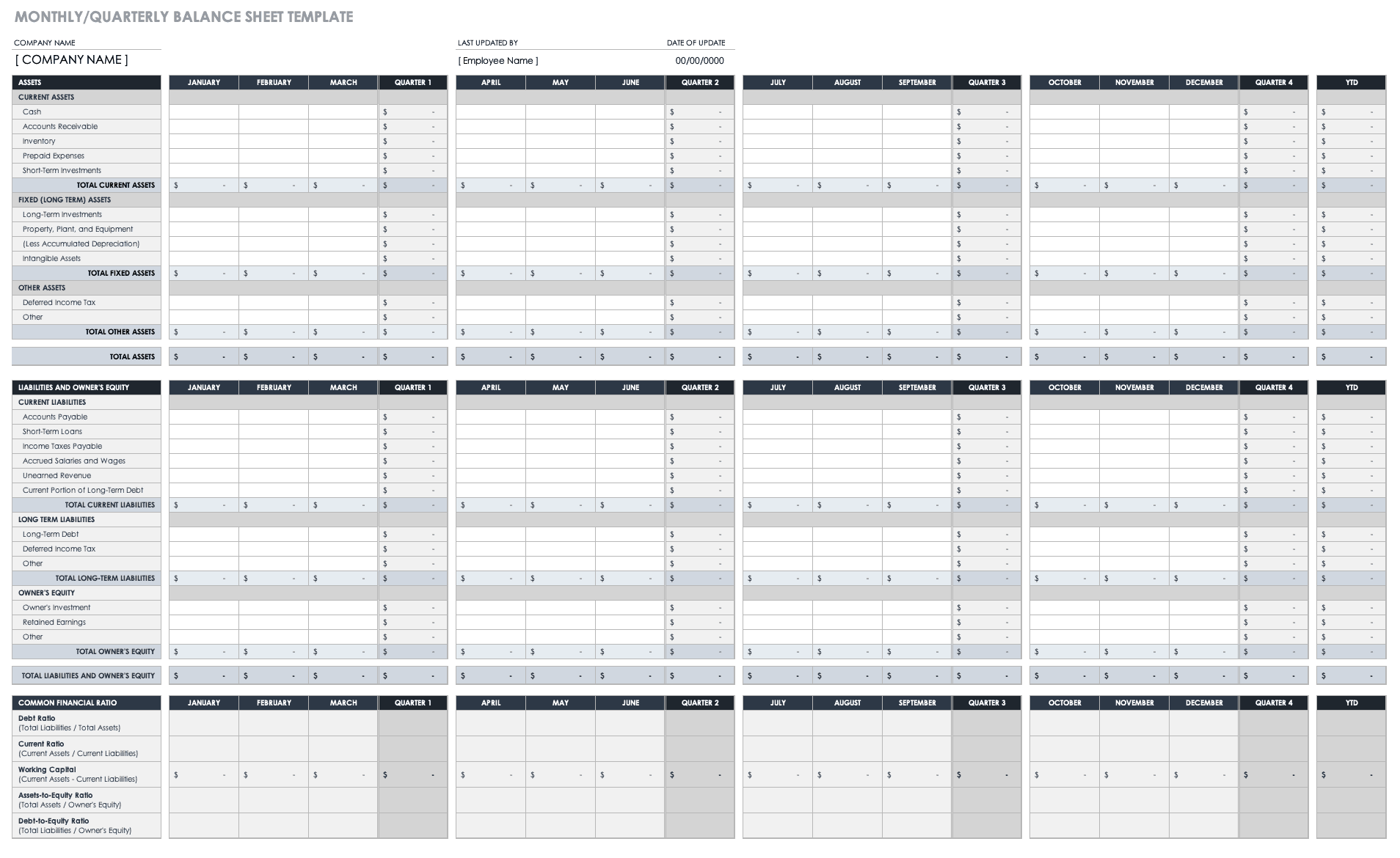
Use this balance sheet template to evaluate your company’s financial health on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. You can also use this template to project your financial position for a specified time in the future. Once you complete the balance sheet, you can compare and analyze your assets, liabilities, and equity on a quarter-over-quarter or year-over-year basis.
Download Monthly/Quarterly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
Yearly Balance Sheet Template
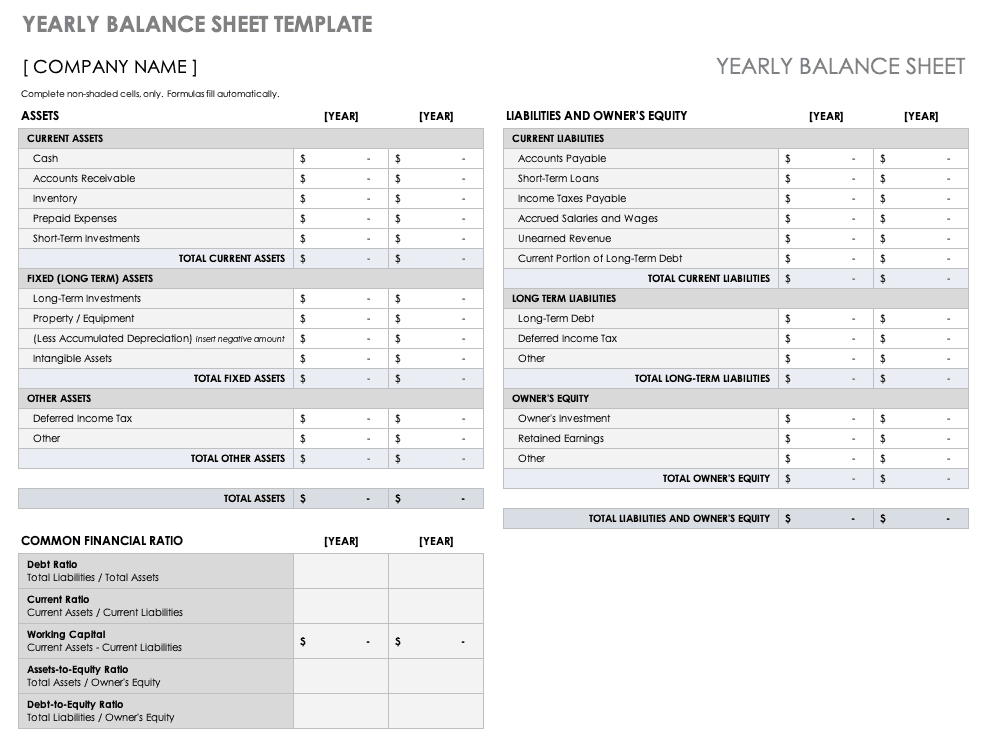
Use this balance sheet template to compare your company’s short and long-term assets, liabilities, and equity year-over-year. This template also provides calculations for common financial ratios with built-in formulas, so you can use it to evaluate account balances annually.
Download Yearly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
For more downloadable resources for a wide range of organizations, visit “ Free Balance Sheet Templates .”
Sales Forecast Templates for Business Plan
Sales projections are a fundamental part of a business plan, and should support all other components of your plan, including your market analysis, product offerings, and marketing plan . Use these sales forecast templates to estimate future sales, and ensure the numbers align with the sales numbers provided in your income statement.
Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
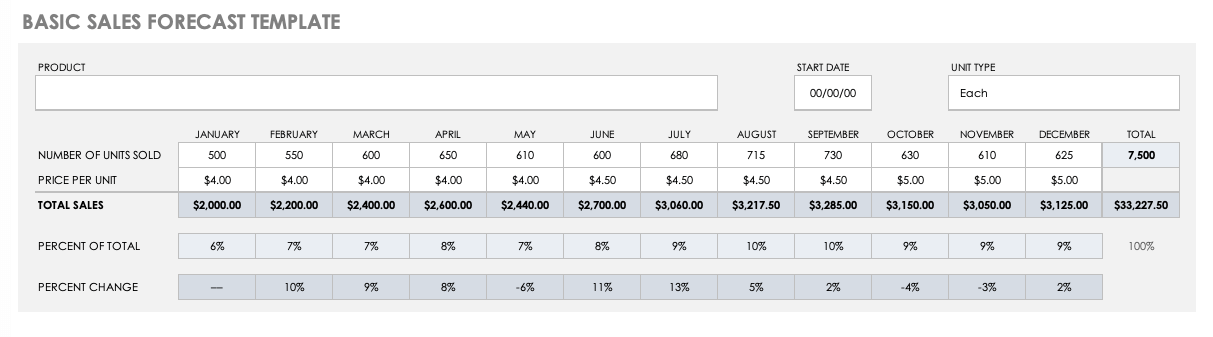
Use this basic forecast template to project the sales of a specific product. Gather historical and industry sales data to generate monthly and yearly estimates of the number of units sold and the price per unit. Then, the pre-built formulas will calculate percentages automatically. You’ll also find details about which months provide the highest sales percentage, and the percentage change in sales month-over-month.
Download Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
12-Month Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
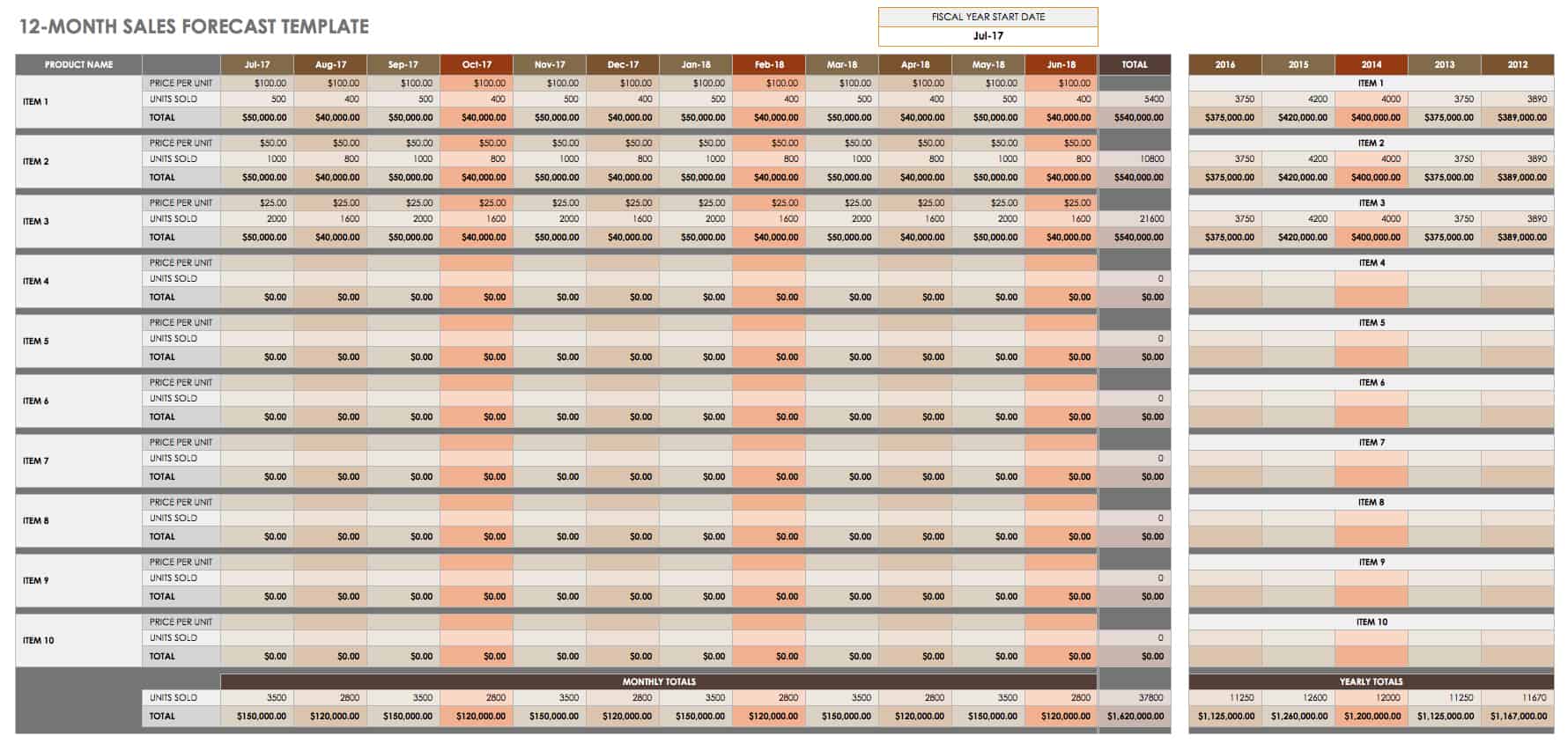
Use this sales forecast template to project the future sales of a business across multiple products or services over the course of a year. Enter your estimated monthly sales, and the built-in formulas will calculate annual totals. There is also space to record and track year-over-year sales, so you can pinpoint sales trends.
Download 12-Month Sales Forecasting Template for Multiple Products
3-Year Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
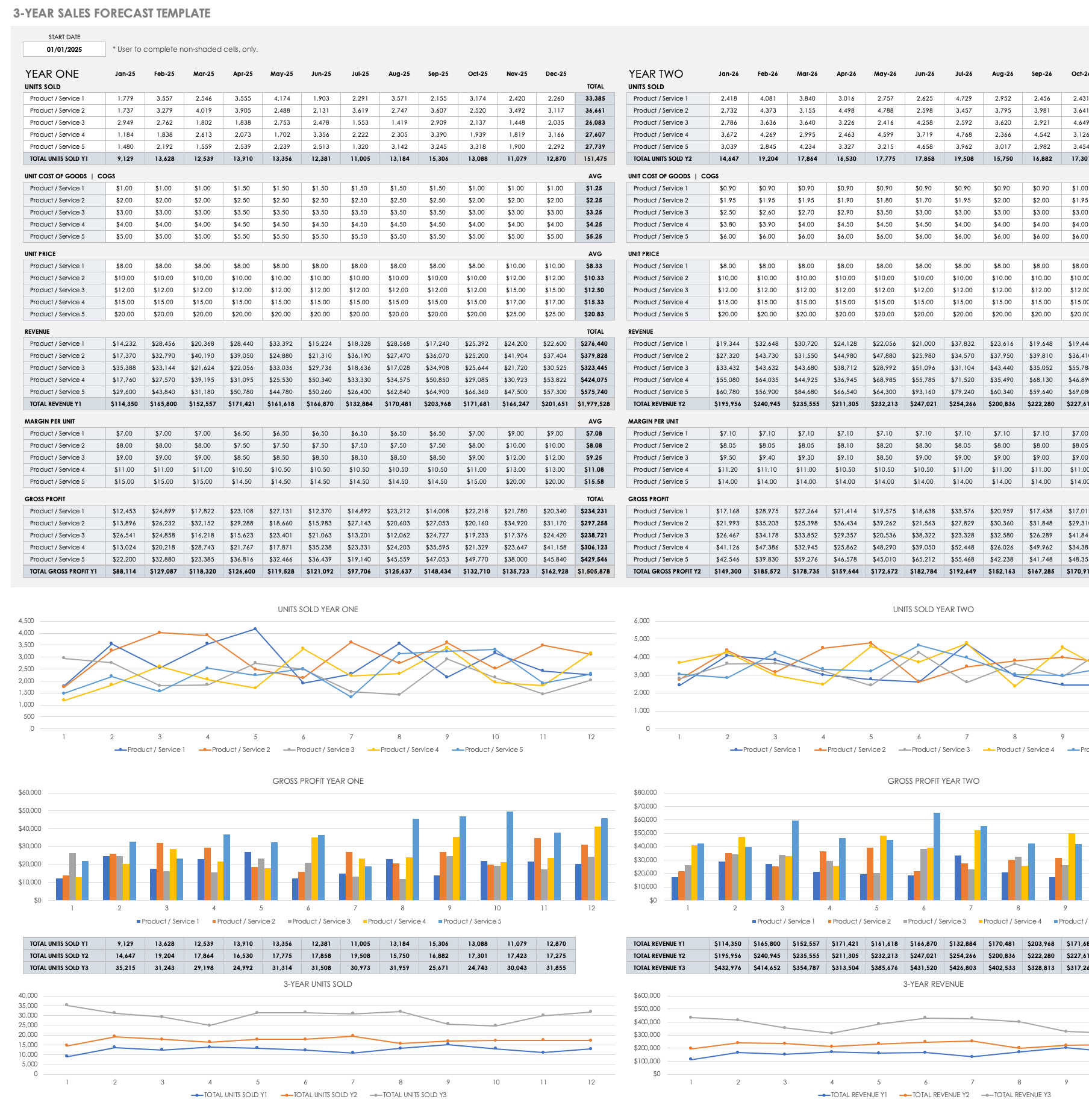
Use this sales forecast template to estimate the monthly and yearly sales for multiple products over a three-year period. Enter the monthly units sold, unit costs, and unit price. Once you enter those values, built-in formulas will automatically calculate revenue, margin per unit, and gross profit. This template also provides bar charts and line graphs to visually display sales and gross profit year over year.
Download 3-Year Sales Forecast Template - Excel
For a wider selection of resources to project your sales, visit “ Free Sales Forecasting Templates .”
Break-Even Analysis Template for Business Plan
A break-even analysis will help you ascertain the point at which a business, product, or service will become profitable. This analysis uses a calculation to pinpoint the number of service or unit sales you need to make to cover costs and make a profit.
Break-Even Analysis Template
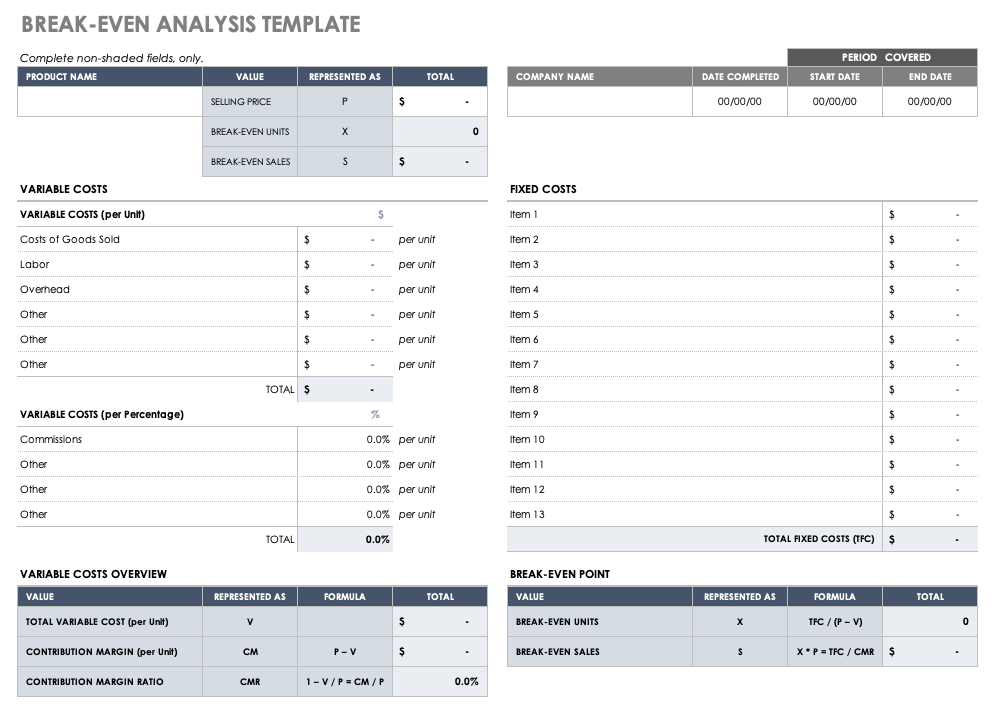
Use this break-even analysis template to calculate the number of sales needed to become profitable. Enter the product's selling price at the top of the template, and then add the fixed and variable costs. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate the total variable cost, the contribution margin, and break-even units and sales values.
Download Break-Even Analysis Template
For additional resources, visit, “ Free Financial Planning Templates .”
Business Budget Templates for Business Plan
These business budget templates will help you track costs (e.g., fixed and variable) and expenses (e.g., one-time and recurring) associated with starting and running a business. Having a detailed budget enables you to make sound strategic decisions, and should align with the expense values listed on your income statement.
Startup Budget Template
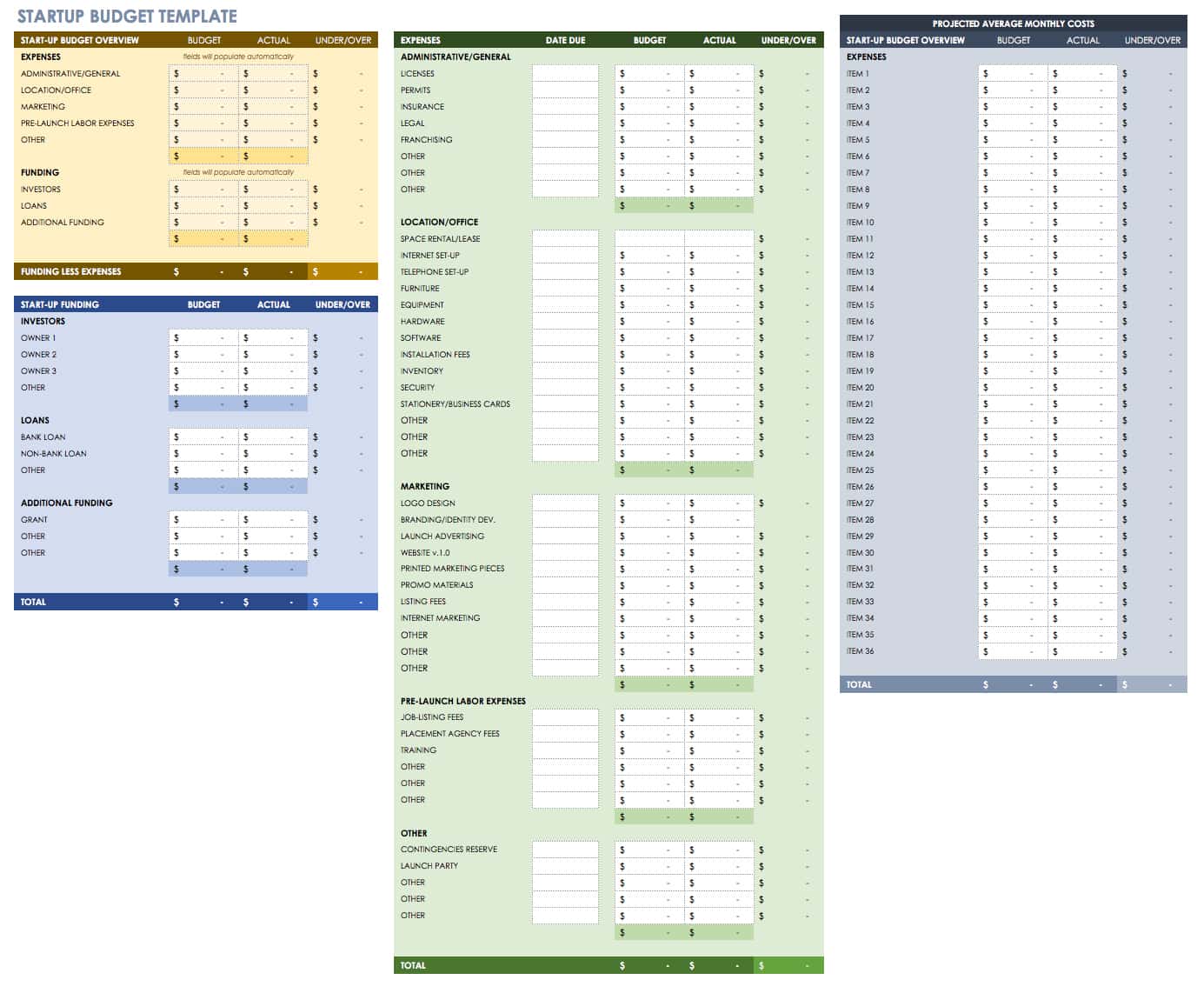
Use this startup budget template to track estimated and actual costs and expenses for various business categories, including administrative, marketing, labor, and other office costs. There is also room to provide funding estimates from investors, banks, and other sources to get a detailed view of the resources you need to start and operate your business.
Download Startup Budget Template
Small Business Budget Template
This business budget template is ideal for small businesses that want to record estimated revenue and expenditures on a monthly and yearly basis. This customizable template comes with a tab to list income, expenses, and a cash flow recording to track cash transactions and balances.
Download Small Business Budget Template
Professional Business Budget Template

Established organizations will appreciate this customizable business budget template, which contains a separate tab to track projected business expenses, actual business expenses, variances, and an expense analysis. Once you enter projected and actual expenses, the built-in formulas will automatically calculate expense variances and populate the included visual charts.
Download Professional Business Budget Template
For additional resources to plan and track your business costs and expenses, visit “ Free Business Budget Templates for Any Company .”
Other Financial Templates for Business Plan
In this section, you’ll find additional financial templates that you may want to include as part of your larger business plan.
Startup Funding Requirements Template
This simple startup funding requirements template is useful for startups and small businesses that require funding to get business off the ground. The numbers generated in this template should align with those in your financial projections, and should detail the allocation of acquired capital to various startup expenses.
Download Startup Funding Requirements Template - Excel
Personnel Plan Template
Use this customizable personnel plan template to map out the current and future staff needed to get — and keep — the business running. This information belongs in the personnel section of a business plan, and details the job title, amount of pay, and hiring timeline for each position. This template calculates the monthly and yearly expenses associated with each role using built-in formulas. Additionally, you can add an organizational chart to provide a visual overview of the company’s structure.
Download Personnel Plan Template - Excel
Elements of the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Whether your organization is a startup, a small business, or an enterprise, the financial plan is the cornerstone of any business plan. The financial section should demonstrate the feasibility and profitability of your idea and should support all other aspects of the business plan.
Below, you’ll find a quick overview of the components of a solid financial plan.
- Financial Overview: This section provides a brief summary of the financial section, and includes key takeaways of the financial statements. If you prefer, you can also add a brief description of each statement in the respective statement’s section.
- Key Assumptions: This component details the basis for your financial projections, including tax and interest rates, economic climate, and other critical, underlying factors.
- Break-Even Analysis: This calculation helps establish the selling price of a product or service, and determines when a product or service should become profitable.
- Pro Forma Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement, this section details the sales, cost of sales, profitability, and other vital financial information to stakeholders.
- Pro Forma Cash Flow Statement: This area outlines the projected cash inflows and outflows the business expects to generate from operating, financing, and investing activities during a specific timeframe.
- Pro Forma Balance Sheet: This document conveys how your business plans to manage assets, including receivables and inventory.
- Key Financial Indicators and Ratios: In this section, highlight key financial indicators and ratios extracted from financial statements that bankers, analysts, and investors can use to evaluate the financial health and position of your business.
Need help putting together the rest of your business plan? Check out our free simple business plan templates to get started. You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy. If you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering startup business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Discover a Better Way to Manage Business Plan Financials and Finance Operations
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Business plan
How to write an effective business plan in 11 steps (with workbook)
February 28, 2024 | 14 minute read
Writing a business plan is a powerful way to position your small business for success as you set out to meet your goals. Landmark studies suggest that business founders who write one are 16% more likely to build viable businesses than those who don’t and that entrepreneurs focused on high growth are 7% more likely to have written a business plan. HBR. July 14, 2017. Available online at https://hbr.org/2017/07/research-writing-a-business-plan-makes-your-startup-more-likely-to-succeed" data-footnote="sevenpercent" aria-label="Footnote 1" data-options="{"interstitialType":"leaving-site","targetAction":"new-tab"}" class="spa-ui-layer-link spa-fn spa-ui-layer-interstitial"> Footnote [1] Even better, other research shows that owners who complete business plans are twice as likely to grow their business successfully or obtain capital compared with those who don’t. Footnote [2]
The best time to write a business plan is typically after you have vetted and researched your business idea. (See How to start a business in 15 steps .) If conditions change later, you can rewrite the plan, much like how your GPS reroutes you if there is traffic ahead. When you update your plan regularly, everyone on your team, including outside stakeholders such as investors, will know where you are headed.
What is a business plan?
Typically 15-20 pages long, a business plan is a document that explains what your business does, what you want to achieve in the business and the strategy you plan to use to get there. It details the opportunities you are going after, what resources you will need to achieve your goals and how you will define success.
Why are business plans important?
Business plans help you think through barriers and discover opportunities you may have recognized subconsciously but have not yet articulated. A business plan can also help you to attract potential lenders, investors and partners by providing them with evidence that your business has all of the ingredients necessary for success.
What questions should a business plan answer?
Your business plan should explain how your business will grow and succeed. A great plan will provide detailed answers to questions that a banker or investor will have before putting money into the business, such as:
- What products or services do you provide?
- Who is your target customer?
- What are the benefits of your product and service for customers?
- How much will you charge?
- What is the size of the market?
- What are your marketing plans?
- How much competition does the business face in penetrating that market?
- How much experience does the management team have in running businesses like it?
- How do you plan to measure success?
- What do you expect the business’s revenue, costs and profit to be for the first few years?
- How much will it cost to achieve the goals stated in the business plan?
- What is the long-term growth potential of the business? Is the business scalable?
- How will you enable investors to reap the rewards of backing the business? Do you plan to sell the business to a bigger company eventually or take it public as your “exit strategy”?
How to write a business plan in 11 steps
This step-by-step outline will make it easier to write an effective business plan, even if you’re managing the day-to-day demands of starting a new business. Creating a table of contents that lists key sections of the plan with page numbers will make it easy for readers to flip to the sections that interest them most.
Use our editable workbook to capture notes and organize your thoughts as you review these critical steps. Note: To avoid losing your work, please remember to save this PDF to your desktop before you begin.
1. Executive summary
The executive summary is your opportunity to make a great first impression on investors and bankers. It should be just as engaging as the enthusiastic elevator pitch you might give if you bumped into a potential backer in an elevator.
In three to five paragraphs, you’ll want to explain what your business does, why it will succeed and where it will be in five years. The executive summary should include short descriptions of the following:
- Business concept. What will your business do?
- Goals and vision. What do you expect the business to achieve, both financially and for other key stakeholders, such as the community?
- Product or service. What does your product or service do — and how is it different from those of competitors?
- Target market. Who do you expect to buy your product or service?
- Marketing strategy. How will you tell people about your product or service?
- Current revenue and profits. If your business is pre-revenue, offer sales projections.
- Projected revenue and profits. Provide a realistic look at the next year, as well as the next three years, ideally.
- Financial resources needed. How much money do you need to borrow or raise to fund your plan?
- Management team. Who are the company’s leaders and what relevant experience will they contribute?
2. Business overview
Here is where you provide a brief history of the business and describe the product(s) or service(s) it offers. Make sure you describe the problem you are attempting to solve, for whom you will solve it (your customers) and how you will solve it. Be sure to describe your business model (such as direct-to-consumer sales through an online store) so readers can envision how you will make sales. Also mention your business structure (such as a sole proprietorship , general partnership, limited partnership or corporation) and why it is advantageous for the business. And be sure to provide context on the state of your industry and where your business will fit into it.
3. Business goals and vision
Explain what you hope to achieve in the business (your vision) as well as its mission and value proposition. Most founders judge success by the size to which they grow the business using measures such as revenue or number of employees. Your goals may not be solely financial. You may also wish to provide jobs or solve a societal problem. If that’s the case, mention those goals as well.
If you are seeking outside funding, explain why you need the money, how you will put it to work to grow the business and how you expect to achieve the goals you have set for the business. Also explain your exit strategy—that is, how you would enable investors to cash out, whether that means selling the business or taking it public.
4. Management and organization
Many investors say they bet on the team behind a business more than the business idea, trusting that talented and experienced people will be capable of bringing sound business concepts to life. With that in mind, make sure to provide short bios of the key members of your management team (including yourself) that emphasize the relevant experience each individual brings, along with their special talents and industry recognition. Many business plans include headshots of the management team with the bios.
Also describe more about how your organization will be structured. Your company may be a sole proprietorship, a limited liability company (LLC) or a corporation in one or more states.
If you will need to hire people for specific roles, this is the place to mention those plans. And if you will rely on outside consultants for certain roles — such as an outsourced CFO — be sure to make a note of it here. Outside backers want to know if you’ve anticipated the staffing you need.
5. Service or product line
A business will only succeed if it sells something people want or need to buy. As you describe the products or services you will offer, make sure to explain what benefits they will provide to your target customers, how they will differ from competing offerings and what the buying cycle will likely be so it is clear that you can actually sell what you are offering. If you have plans to protect your intellectual property through a copyright or patent filing, be sure to mention that. Also explain any research and development work that is underway to show investors the potential for additional revenue streams.
6. Market/industry analysis
Anyone interested in providing financial backing to your business will want to know how big your company can potentially grow so they have an idea of what kind of returns they can expect. In this section, you’ll be able to convey that by explaining to whom you will be selling and how much opportunity there is to reach them. Key details to include are market size; a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis ; a competitive analysis; and customer segmentation. Make it clear how you developed any projections you’ve made by citing interviews or research.
Also describe the current state of the industry. Where is there room for improvement? Are most companies using antiquated processes and technology? If your business is a local one, what is the market in your area like? Do most of the restaurants where you plan to open your café serve mediocre food? What will you do better?
In this section, also list competitors, including their names, websites and social media handles. Describe each source of competition and how your business will address it.
7. Sales and marketing
Explain how you will spread the word to potential customers about what you sell. Will you be using paid online search advertising, social media promotions, traditional direct mail, print advertising in local publications, sponsorship of a local radio or TV show, your own YouTube content or some other method entirely? List all of the methods you will use.
Make sure readers know exactly what the path to a sale will be and why that approach will resonate with customers in your ideal target markets as well as existing customer segments. If you have already begun using the methods you’ve outlined, include data on the results so readers know whether they have been effective.
8. Financials
In a new business, you may not have any past financial data or financial statements to include, but that doesn’t mean you have nothing to share. Preparing a budget and financial plan will help show investors or bankers that you have developed a clear understanding of the financial aspects of running your business. (The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) has prepared a guide you can use; SCORE , a nonprofit organization that partners with the SBA, offers a financial projections template to help you look ahead.) For an existing business, you will want to include income statements, profit and loss statements, cash flow statements and balance sheets, ideally going back three years.
Make a list of the specific steps you plan to take to achieve the financial results you have outlined. The steps are generally the most detailed for the first year, given that you may need to revise your plan later as you gather feedback from the marketplace.
Include interactive spreadsheets that contain a detailed financial analysis showing how much it costs your business to produce the goods and services you provide, the profits you will generate, any planned investments and the taxes you will pay. See our startup costs calculator to get started.
9. Financial projections
Creating a detailed sales forecast can help you get outside backers excited about supporting you. A sales forecast is typically a table or simple line graph that shows the projected sales of the company over time with monthly or quarterly details for the next 12 months and a broader projection as much as five years into the future. If you haven’t yet launched the company, turn to your market research to develop estimates. For more information, see “ How to create a sales forecast for your small business .”
10. Funding request
If you are seeking outside financing such as a loan or equity investment, your potential backers will want to know how much money you need and how you will spend it. Describe the amount you are trying to raise, how you arrived at that number and what type of funding you are seeking (such as debt, equity or a combination of both). If you are contributing some of your own funds, it is worth noting this, as it shows that you have skin in the game.
11. Appendix
This should include any information and supporting documents that will help investors and bankers gain a greater understanding of the potential of your business. Depending on your industry, you might include local permits, licenses, deeds and other legal documents; professional certifications and licenses; media clips; information on patents and other intellectual property; key customer contracts and purchase orders; and other relevant documents.
Some business owners find it helpful to develop a list of key concepts, such as the names of the company’s products and industry terms. This can be helpful if you do business in an industry that may not be familiar to the readers of the business plan.
Tips for creating an effective business plan
Use clear, simple language. It’ll be easier to win people over if your plan is easy to read. Steer clear of industry jargon, and if you must use any phrases the average adult won’t know, be sure to define them.
Emphasize what makes your business unique. Investors and bankers want to know how you will solve a problem or gap in the marketplace differently from anyone else. Make sure you’re conveying your differentiating factors.
Nail the details. An ideal business plan will be detailed and accurate. Make sure that any financial projections you make are realistic and grounded in solid market research. (If you need help in making your calculations, you can get free advice at SCORE.) Seasoned bankers and investors will quickly spot numbers that are overly optimistic.
Take time to polish it. Your final version of the plan should be neat and professional with an attractive layout and copy that has been carefully proofread.
Include professional photos. High-quality shots of your product or place of business can help make it clear why your business stands out.
Updating an existing business plan
Some business owners in rapidly growing businesses update their business plan quarterly. Others do so every six months or every year. When you update your plan make sure you consider these three things:
1. Are your goals still current? As you’ve tested your concept, your goals may have changed. The plan should reflect this.
2. Have you revised any strategies in response to feedback from the marketplace? You may have found that your offerings resonated with a different customer segment than you expected or that your advertising plan didn’t work and you need to try a different approach. Given that investors will want to see a marketing and advertising plan that works, keeping this section current will ensure you are always ready to meet with one who shows interest.
3. Have your staffing needs changed? If you set ambitious goals, you may need help from team members or outside consultants you did not anticipate when you first started the business. Take stock now so you can plan accordingly.
Final thoughts
Most business owners don’t follow their business plans exactly. But writing one will get you off to a much better start than simply opening your doors and hoping for the best, and it will be easier to analyze any aspects of your business that aren’t working later so you can course-correct. Ultimately, it may be one of the best investments you can make in the future of your business.
Business plan FAQs
The biggest mistake you can make when writing a business plan is creating one before the idea has been properly researched and tested. Not every idea is meant to become a business. Other common mistakes include:
- Not describing your management team in a way that is appealing to investors. Simply cutting and pasting someone’s professional bio into the management section won’t do the trick. You’ll want to highlight the credentials of each team member in a way that is relevant to this business.
- Failing to include financial projections — or including overly optimistic ones. Investors look at a lot of business plans and can tell quickly whether your numbers are accurate or pie in the sky. Have a good small business accountant review your numbers to make sure they are realistic.
- Lack of a clear exit strategy for investors. Investors may want the option to cash out eventually and would want to know how they can go about doing that.
- Slapdash presentation. Make sure to fact-check any industry statistics you cite and that any charts, graphs or images are carefully prepared and easy to read.
There are a variety of styles of business plans. Here are three major types:
Traditional business plan. This is a formal document for pitching to investors based on the outline in this article. If your business is a complicated one, the plan may exceed the typical length and stretch to as many as 50 pages.
One-page business plan. This is a simplified version of a formal business plan designed to fit on one page. Typically, each section will be described in bullet points or in a chart format rather than in the narrative style of an executive summary. It can be helpful as a summary document to give to investors — or for internal use. Another variation on the one-page theme is the business model canvas .
Lean plan. This methodology for creating a business plan is ideal for a business that is evolving quickly. It is designed in a way that makes it easy to update on a regular basis. Lean business plans are usually about one page long. The SBA has provided an example of what this type of plan includes on its website.
Many elements of a business plan for a nonprofit are similar to those of a for-profit business. However, because the goal of a nonprofit is achieving its mission — rather than turning a profit — the business plan should emphasize its specific goals on that front and how it will achieve them. Many nonprofits set key performance indicators (KPIs) — numbers that they track to show they are moving the needle on their goals.
Nonprofits will generally emphasize their fundraising strategies in their business plans rather than sales strategies. The funds they raise are the lifeblood of the programs they run.
A strategic plan is different from the type of business plan you’ve read about here in that it emphasizes the long-term goals of the business and how your business will achieve them over the long run. A strong business plan can function as both a business plan and a strategic plan.
A marketing plan is different from a business plan in that it is focused on four main areas of the business: product (what you are selling and how you will differentiate it), price (how much your products or services will cost and why), promotion (how you will get your ideal customer to notice and buy what you are selling) and place (where you will sell your products). A thorough business plan may cover these topics, doing double duty as both a business plan and a marketing plan.
The Small Business Community is now Small Business Resources .
Writing a Bank Business Plan
- Written By Dave Lavinsky

When it comes to seeking funding from a bank or other financial institution, one of the most important things you can do is have a well-written business plan . This document will not only give potential lenders and investors an idea of your company’s current position and future goals but will also provide them with a clear understanding of the risks involved in lending you money or investing in your business.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that provides a detailed description of a business, its products or services, its market, and its financial projections. It is used to secure funding from lenders or investors and to provide guidance for the business’s future operations.
Why Write a Business Plan
There are several reasons why you might want to write a plan for your business, even if you’re not looking for funding, they are:
- To clarify your company’s purpose and direction
- To better understand your industry and customers
- To develop a realistic financial plan and accurate projections
- To identify potential risks and opportunities
- To track your company’s progress over time
An effective and well-written plan is helpful for potential investors and clarifies the plans you have for any future business partners.

Sources of Business Funding for Banks
There are many sources of business funding available to banks, including:
- Equity financing: This is when you sell a portion of your business to investors in exchange for capital. This can be a good option if you need a large amount of money quickly, as it doesn’t require you to pay back the funds over time.
- Debt financing: This is when you borrow money from a lender, such as a bank, in exchange for repayment plus interest. This type of financing can be helpful if you need to keep your cash flow low in the early stages of your business.
- Grants: There are several different government and private grants available to businesses, which can often be used for start-up costs or expansion.
- Venture capital: This is when you receive funding from a venture capitalist in exchange for a portion of your company’s equity. Venture capitalists typically invest their own personal savings in high-growth businesses with a lot of potential.
Resources to Write a Bank Business Plan
To write a bank business plan, you’ll need access to a variety of resources, including:
Sample Plans for Your Business
A good place to start is by looking at some sample plans for businesses in your industry. This will give you a good idea of the types of information to include in your own plan.
Business planning software
There are a number of software programs that can help you create professional-looking plans for your business.
Market Research
When writing a business plan for a bank, it’s important to include a section on your company’s market research. This will include detailed information about your industry, your market, and your competition.
Industry Analysis
In order to accurately describe your industry and the market for your products or services, you’ll need to conduct an industry analysis. This should include information about the size and growth of the industry, the key players in the industry, and any major trends or changes that are taking place.
Target Market Analysis
To effectively market your products or services, you need to understand who your target market is. This should include information about the demographics of your target customers (age, gender, income, etc.), psychographics (lifestyle preferences, interests, etc.), and geographic (location, region).
Competition Analysis
In order to differentiate your business from the competition, you’ll need to know what they’re offering and how they’re positioning themselves in the market. This should include a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) of your competitors.
Customer Segments
A customer segment is a group of customers who share common characteristics, such as age, income, location, or lifestyle preferences. When creating business plans for a bank, it’s important to identify and target your key customer segments. This will help you focus your marketing efforts and create products and services that appeal to your target market.
There are a variety of ways to segment customers, including:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income, location, etc.
- Psychographics: Lifestyle preferences, interests, etc.
- Behavior: How they interact with your brand, what channels they use to purchase products or services, etc.
- Usage: How often they purchase your product or service, how much they spend, etc.
- Value: How much they’re willing to pay for your product or service, how much they value customer service, etc.
Once you’ve identified your customers, you can create buyer personas. These are fictional characters that represent your ideal customer within each segment. Creating buyer personas will help you better understand your target market and create more effective marketing campaigns.
Financial templates
If you’re not familiar with financial terminology or calculations, use a financial template to help you develop your business’s financial projections as well as including an income statement and balance sheets.
Accounting and Legal Advice
It’s important to seek out accounting and legal advice from professionals who can help ensure that your business plan is accurate and complete.
Bank Business Plan Template
While there is no one-size-fits-all template for writing a business plan, there are some key elements that should be included. Here is a brief overview of what should be included:
Executive Summary
This is a high-level overview of your company, its products or services, and its financial situation. Be sure to include information on your target market, your competitive advantage, and your plans for growth.
Company Description
This section provides more detail on your company, including its history, structure, and management team. Be sure to include information on your company’s mission and vision, as well as its values and goals.
Products and Services
Here you will describe your company’s products or services in detail, including information on your target market and your competitive advantage.
Market Analysis
In this section, you will provide an overview of your market, including demographic information and information on current and future trends. This is also a good section to add the marketing plan you have developed to appeal to potential customers.
Sales and Marketing
This section will detail your sales and marketing strategy, including information on your pricing, your distribution channels, and your promotion plans.
Financial projections
This is perhaps the most important section of your business plan, as it will provide lenders and investors with an idea of your company’s financial health. Be sure to include detailed information on your past financial performance, as well as your projections for future revenue and expenses. This is also a good section to include your cash flow statements, income statements, and information about any bank accounts opened for your business.
This is where you will include any supporting documents, such as your financial statements, marketing materials, or product data sheets.
While this is not an exhaustive list of everything that should be included in your bank business plan, it covers the most important elements. By taking the time to write a well-thought-out and detailed business plan, you will increase your chances of securing the funding you need to grow your business.
Opening a bank is a detailed and complex process, but it can be enormously rewarding both professionally and financially. The best way to increase your chances of success is to write a business plan that outlines all aspects of opening and running a bank. This document should include market analysis, organizational structure, financial projections, and more. Our team has extensive experience helping entrepreneurs open banks. We have created a comprehensive business plan template that covers all the key points you need to consider when writing your own business plan. By following our template, you can be sure that you haven’t missed any essential elements in your planning process. Investing in professional help when writing your business plan gives you the best chance for success when opening a new bank.
Bank Business Plan Template FAQs
Do i need to use a business plan template.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. If you are seeking funding from a lender or investor, they may have specific requirements for the format and content of your business plan. In other cases, using a template can be helpful in ensuring that you include all of the important information in your plan.
Where can I find a business plan template?
There are a number of resources that offer business plan templates, including the Small Business Administration (SBA) and the U.S. Chamber of Commerce. Additionally, many software programs that offer business planning tools also include templates.
How long should my business plan be?
Again, there is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. The length of your business plan will depend on the complexity of your business and the amount of detail you need to include. In general, however, most business plans range from 20 to 50 pages.
Do I need to hire a professional to help me write my business plan?
While you are not required to hire a professional to write your business plan, it may be helpful to do so. A professional can help you ensure that your plan is well-written and free of errors. Additionally, they can offer advice on how to best structure your plan and make it more likely to succeed.
Recent Posts

How to Start A Car Rental Business

How to Start A Staffing Agency

Business Plan Outline and Example
Blog categories.
- Business Planning
- Venture Funding
Please turn on JavaScript in your browser
It appears your web browser is not using JavaScript. Without it, some pages won't work properly. Please adjust the settings in your browser to make sure JavaScript is turned on.
What Is a Business Plan and How to Write One
Start writing your business plan today and find out how Chase for Business can help you be successful. Presented by Chase for Business.

If you're planning on starting a business, one of your first steps should be writing a business plan.
The objectives of a business plan are guided by the goals of your business and should leave room for flexibility and future restructuring. Use these tips to help you get started.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a guide for your company to follow as it scales in size and complexity. Business plans include basic information about your company's operational, financial and marketing goals. Writing a business plan will include several key sections:
- Executive summary: A summary of your business model, your target market, your products and services and basic financial information.
- Company overview: An overview of your business’ mission, location, legal structure and history.
- Products and services: An explanation of the products and services your business offers. This section should cover the problems you solve for customers, intended audiences, and use cases and pricing.
- Market analysis: An analysis of your value proposition, how you plan to reach your target market and where you fit into the competitive landscape.
- Financial plan: An outline of the fiscal details of your business including a balance sheet, cash flow statement and sales forecast. This section should include a profit and loss statement, as well.
- Contact Directory: An introduction of all key team members and an explanation of their roles. If applicable, list the chief executive officer (CEO), chief financial officer (CFO), chief operations officer (COO) and other key management roles.
Why is a business plan important?
The specific steps in writing a business plan can help your company build a strategy for long-term success. When starting a business, you should consider some items including:
- Research your market
- Develop a strategy
- Record existing financial data
- Organize your goals into a cohesive vision
If you're seeking financing or applying for a business loan , a business plan is essential. Banks, private investors and venture capital firms all need to see a business plan to make funding decisions. These institutions want to know how your business plan will achieve its goals and make their investments worthwhile.
Your company doesn't have to follow the same plan in perpetuity — you can and should revise your model as necessary. Reference your business plan in relation to other major goals and strategy throughout the year.
Types of business plans
Different business plans work for different business cases. Two of the most common business plan types include:
- Traditional business plan: This plan tends to be long and detailed. It includes all of the sections above as well as information on the specific funding and human resources goals you hope to achieve. Traditional investors tend to request traditional business plans.
- Lean business plan: This type of business plan is much shorter and includes only essential information. It should include partnerships, activities, resources, market, value proposition and distribution channels. A lean business plan may also include your cost structure and revenue streams. Lean business plans are ideal for internal use.
5 ways companies use business plans
The following are five ways that companies typically use a business plan to aid in their development and growth.
1. Assess feasibility
Business plans can be used to help examine the feasibility of a business or product idea. As you research your market, create a financial plan and crunch the numbers. By doing this, you’ll develop a better sense of what is needed in order to make a profit.
You should share your business plan with other people for feedback — such as mentors, potential partners or prospective employees. If you can demonstrate you have a plan to succeed, prospective clients or investors may be more confident in working with you.
2. Understand the market
Understanding your customers and marketplace dynamics is key to running a successful business. The market analysis section of your business plan positions your company within the industry and among your competitors. For example, your business plan might explain how you intend to solve a persistent problem in a way that your competitors cannot.
To help know your market better, you should conduct a SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. By digging deep into your business goals, you can discover who your customers are and how you can best serve them. You can also assess where your business is likely to thrive and manage any perceived opportunities upfront.
3. Create milestones
It can be challenging to keep your eye on the big strategic picture while also managing a business. Writing a business plan forces you to set aside your daily tasks and consider your goals. In turn, setting milestones will help guide your business and give it a greater purpose.
The milestones you create should be unique to your business. For example, your milestones might include reaching $1 million in revenue, expanding to a new region, or selling your business to a larger company.
4. Seek funding
Some companies have all the capital they need to launch while others need outside financing. If you request funding from a bank or a private investor, you will need a clear business plan that allows investors to assess how your company will make money and grow.
Consider these business plan tips for common financial projections:
- Cash-flow statement
- Profit and loss statement
- Break-even projection
- Sales forecast
Reposition the business
Few companies follow the same path the entire time they're in business. Issues like market changes, new technology, and economic growth can force a change in direction.
When you need to reposition your company, referring to your original business plan is essential. This will encourage you to analyze the market, consider different operational models and experiment with new strategies.
Even as you continue to evolve your business strategies and objectives, your business plan can guide your company through major changes and improve your chances for profitability.
Once your business plan is in motion, meet with your local business banker to manage your available finances or see how a Chase business checking account might help.
What to read next
Manage your business how to help protect your business from check fraud.

Think writing checks is a safe way to pay vendors? Think again. Learn about five common scams and how to help prevent them.
START YOUR BUSINESS 10 tips before starting your new businesses
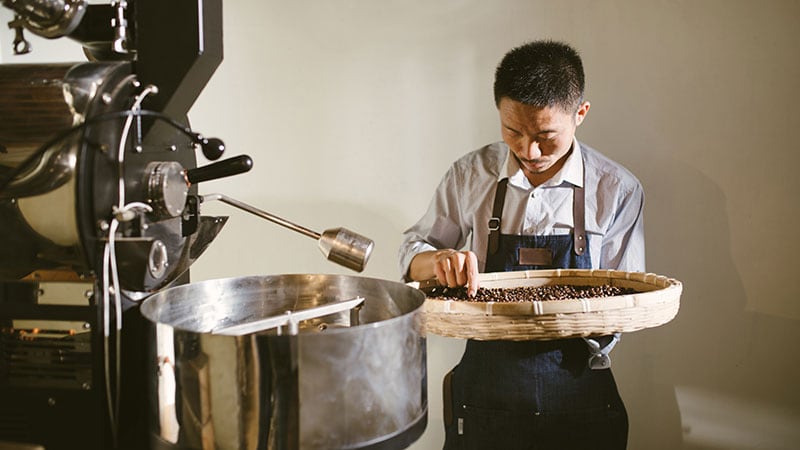

Thinking about starting a business? Check these 10 items off your list.
MANAGE YOUR BUSINESS Inventory management can help maintain cash flow

Inventory can eat up a lot of cash. Here are a few ways to manage inventory with cash flow in mind.
MANAGE YOUR BUSINESS Banking tips for cash businesses

Learn how to keep your cash business safe, secure and compliant.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Why Do I Need a Business Plan?
Sections of a business plan, the bottom line.
- Small Business
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
How to secure business financing
Matt Webber is an experienced personal finance writer, researcher, and editor. He has published widely on personal finance, marketing, and the impact of technology on contemporary arts and culture.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/smda1_crop-f0c167dd2b2144f68f352c63d17f7db5.jpg)
A business plan is a document that explains what a company’s objectives are and how it will achieve them. It contains a road map for the company from a marketing, financial, and operational standpoint. Some business plans are more detailed than others, but they are used by all types of businesses, from large, established companies to small startups.
If you are applying for a business loan , your lender may want to see your business plan. Your plan can prove that you understand your market and your business model and that you are realistic about your goals. Even if you don’t need a business plan to apply for a loan, writing one can improve your chances of securing finance.
Key Takeaways
- Many lenders will require you to write a business plan to support your loan application.
- Though every business plan is different, there are a number of sections that appear in every business plan.
- A good business plan will define your company’s strategic priorities for the coming years and explain how you will try to achieve growth.
- Lenders will assess your plan against the “five Cs”: character, capacity, capital, conditions, and collateral.
There are many reasons why all businesses should have a business plan . A business plan can improve the way that your company operates, but a well-written plan is also invaluable for attracting investment.
On an operational level, a well-written business plan has several advantages. A good plan will explain how a company is going to develop over time and will lay out the risks and contingencies that it may encounter along the way.
A business plan can act as a valuable strategic guide, reminding executives of their long-term goals amid the chaos of day-to-day business. It also allows businesses to measure their own success—without a plan, it can be difficult to determine whether a business is moving in the right direction.
A business plan is also valuable when it comes to dealing with external organizations. Indeed, banks and venture capital firms often require a viable business plan before considering whether they’ll provide capital to new businesses.
Even if a business is well-established, lenders may want to see a solid business plan before providing financing. Lenders want to reduce their risk, so they want to see that a business has a serious and realistic plan in place to generate income and repay the loan.
Every business is different, and so is every business plan. Nevertheless, most business plans contain a number of generic sections. Common sections are: executive summary, company overview, products and services, market analysis, marketing and sales plan, operational plan, and management team. If you are applying for a loan, you should also include a funding request and financial statements.
Let’s look at each section in more detail.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is a summary of the information in the rest of your business plan, but it’s also where you can create interest in your business.
You should include basic information about your business, including what you do, where you are based, your products, and how long you’ve been in business. You can also mention what inspired you to start your business, your key successes so far, and your growth plans.
Company Overview
In this section, focus on the core strengths of your business, the problem you want to solve, and how you plan to address it.
Here, you should also mention any key advantages that your business has over your competitors, whether this is operating in a new market or a unique approach to an existing one. You should also include key statistics in this section, such as your annual turnover and number of employees.
Products and Services
In this section, provide some details of what you sell. A lender doesn’t need to know all the technical details of your products but will want to see that they are desirable.
You can also include information on how you make your products, or how you provide your services. This information will be useful to a lender if you are looking for financing to grow your business.
Market Analysis
A market analysis is a core section of your business plan. Here, you need to demonstrate that you understand the market you are operating in, and how you are different from your competitors. If you can find statistics on your market, and particularly on how it is projected to grow over the next few years, put them in this section.
Marketing and Sales Plan
Your marketing and sales plan gives details on what kind of new customers you are looking to attract, and how you are going to connect with them. This section should contain your sales goals and link these to marketing or advertising that you are planning.
If you are looking to expand into a new market, or to reach customers that you haven’t before, you should explain the risks and opportunities of doing so.
Operational Plan
This section explains the basic requirements of running your business on a day-to-day basis. Your exact requirements will vary depending on the type of business you run, but be as specific as possible.
If you need to rent office space, for example, you should include the cost in your operational plan. You should also include the cost of staff, equipment, and any raw materials required to run your business.
Management Team
The management team section is one of the most important sections in your business plan if you are applying for a loan. Your lender will want reassurance that you have a skilled, experienced, competent, and reliable senior management team in place.
Even if you have a small team, you should explain what makes each person qualified for their position. If you have a large team, you should include an organizational chart to explain how your team is structured.
Funding Request
If you are applying for a loan, you should add a funding request. This is where you explain how much money you are looking to borrow, and explain in detail how you are going to use it.
The most important part of the funding-request section is to explain how the loan you are asking for would improve the profitability of your business, and therefore allow you to repay your loan.
Financial Statements
Most lenders will also ask you to provide evidence of your business finances as part of your application. Graphs and charts are often a useful addition to this section, because they allow your lender to understand your finances at a glance.
The overall goal of providing financial statements is to show that your business is profitable and stable. Include three to five years of income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. It can also be useful to provide further analysis, as well as projections of how your business will grow in the coming years.
What Do Lenders Look for in a Business Plan?
Lenders want to see that your business is stable, that you understand the market you are operating in, and that you have realistic plans for growth.
Your lender will base their decision on what are known as the “five Cs.” These are:
- Character : You can stress your good character in your executive summary, company overview, and your management team section.
- Capacity : This is, essentially, your ability to repay the loan. Your lender will look at your growth plans, your funding request, and your financial statements in order to assess this.
- Capital : This is the amount of money you already have in your business. The larger and more established your business is, the more likely you are to be approved for finance, so highlight your capital throughout your business plan.
- Conditions : Conditions refer to market conditions. In your market analysis, you should be able to prove that your business is well-positioned in relation to your target market and competitors.
- Collateral : Depending on your loan, you may be asked to provide collateral , so you should provide information on the assets you own in your operational plan.
How Long Does It Take to Write a Business Plan?
The length of time it takes to write a business plan depends on your business, but you should take your time to ensure it is thorough and correct. A business plan has advantages beyond applying for a loan, providing a strategic focus for your business.
What Should You Avoid When Writing a Business Plan?
The most common mistake that business owners make when writing a business plan is to be unrealistic about their growth potential. Your lender is likely to spot overly optimistic growth projections, so try to keep it reasonable.
Should I Hire Someone to Write a Business Plan for My Business?
You can hire someone to write a business plan for your business, but it can often be better to write it yourself. You are likely to understand your business better than an external consultant.
Writing a business plan can benefit your business, whether you are applying for a loan or not. A good business plan can help you develop strategic priorities and stick to them. It describes how you are going to grow your business, which can be valuable to lenders, who will want to see that you are able to repay a loan that you are applying for.
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Fund Your Business .”
Navy Federal Credit Union. “ The 5 Cs of Credit .”
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
You are leaving the Hands on Banking website
You are leaving Hands on Banking.org and entering a website that the Hands on Banking program does not control. The Hands on Banking program has provided this link for your convenience, but does not endorse and is not responsible for the content, links, privacy policy, or security policy of this website.
Calculators
- Standard Calculator
Value of an Investment
- Cost of Loan
- Cost of Mortgage
- Retirement Savings
- Credit Calculator
Number of Years to Save
Total Amount*
* Daily compounding, with contributions made at the end of the time period.
Calculate Reset
Loan Term in Years
Monthly Payment
Total Cost of Loan
Mortgage Term in Years
Total Cost of Mortgage
Annual income needed from investments
Total amount you need to have invested
Months to Pay
Total Amount paid
Total Interest paid
Term in Years
Plan a Business
Consider entrepreneurship.
The reality, according to the U.S. Small Business Administration, is that less than 50 percent of all new businesses last more than two years. They also attribute 95 percent of all business failures to the business owner’s lack of experience and expertise.
Before launching a venture of your own, strongly consider gaining experience and expertise working for someone else, especially a successful leader in the field. People with a solid track record who have thoroughly thought through their new venture have a far greater chance of success than those who have not.
In addition to experience and expertise, many successful entrepreneurs share certain personal qualities. Although it’s a rare individual who excels in all of the traits listed below, reviewing this list may help you decide whether entrepreneurship is a career path you’d like to pursue.
Key attributes of successful entrepreneurs
- Takes initiative. A self-starter. Makes things happen rather than waiting and reacting. Self-directed. Independent. Doesn’t need a boss.
- Driven to achieve. Has desire and passion to succeed. Enjoys competition. Has energy and stamina. Willing to work more than forty hours a week. Willing to sacrifice to achieve goals and dreams.
- Positive mental attitude. Self-confident. Believes in self. Trusts own ideas, instincts, and abilities.
- Sets goals. Creates a vision of success. Works with focus and intention.
- Plans ahead. Creates plans and follows them. Updates plans periodically. Good at anticipating new developments.
- Resourceful. Creative problem-solver. Imaginative and innovative. Sees better ways of doing things. Uncovers new resources and opportunities. Finds a way.
- A leader. Takes responsibility and accepts accountability. Like to make decisions. Shows an attitude of respect for others. Motivates and inspires others. Gives others the opportunity to be great. Shares the credit for success. Gains the respect of peers.
- Good communicator. Likes people. Has great people skills. Good listener. Effective negotiator.
- Always learning. Open to new ideas. Learns from others.
- Leverages exceptional skills. Makes the most of personal strengths, but doesn’t try to be and do everything.
- Has technical knowledge. Understands both general business practices and the processes used to deliver goods and services.
- Organized. Able to prioritize. Good time manager. Gets things done on time.
- Objective. Able to evaluate risk. Willing to take calculated risks. Can make good decisions under pressure.
- Uses money well. Good money manager. Sees money as a tool for business success rather than an end in itself.
- Realistic. Accepts the ups and downs of business. Willing to face facts and change strategy or direction when needed.
- Persistent. Has determination and self-discipline. Follows through. Meets commitments. Will dedicate however much time it takes. Never gives up.
- Bounces back. Accepts rejection and failure without being defeated. Flexible. Adapts to changing conditions. Learns from experience and mistakes, creates new plans, and moves ahead.
As you review the items you checked, notice the items you didn’t. To succeed, you’ll need to find ways to fill your gaps.
Remember : there are millions of successful small businesses in our country, but there’s always room for one more. When you think about your future in the world of work, consider the option of starting a business of your own.

write a business plan
- Key components
- Most important elements
The purpose of a business plan is to serve as a roadmap for the present and a vision of the future. It can also help to attract investors for your business. The SBA and Small Business Development Centers can help you to create a business plan. There are many books and Web sites on the subject. Here are key components of what the plan should include:
Executive summary – business concept, key success factors, and financial situation/needs
Company profile – inspirational vision statement describing the business you want to create, including who your customers will be, what and how you plan to sell to them; and, a mission statement describing why your business exists and why customers will buy your product or service. The best mission statements briefly but powerfully convey a company’s commitment to its customers.
Products and services – product/service description, positioning of products/services, and competitive evaluation of products/services
Competitive analysis – industry overview, competition, competitor products and services, opportunities; key strengths and weaknesses compared to your competitors,
Market analysis – market overview, market segments, and target market and customers. To show investors or lenders that you have researched the market and understand the challenges, include reasons why the venture could fail, and your strategies for addressing these risks.
Objectives – your highest priority goals in the key areas of your business, including finance marketing, and operations. What do you want to accomplish in the near-term future? Where will you focus your time and resources? The best objectives are clearly-stated, specific, and measurable.
Strategies – the general approaches you will take to achieve your goals. Strategies describe how you will go about making your business successful over time given the strengths and weaknesses inside your business and the opportunities and threats in the marketplace.
Plans – the specific action steps you will take to achieve your objectives. Effective plans clearly state “who will do what by when.”
Management qualifications and operations – key personnel, organizational structure, product/service delivery, customer service/support, facilities. To get bank financing or investors, management experience is a critical element of your plan because investors generally invest in people, not products. A lot of businesses have great product ideas, but not all have the skills and experience to succeed.
Financial information – assumptions and comments, starting balance sheet and projection, profit-and-loss projection, cash flow projection, ratios and analyses.
If you want to attract investors or get bank financing for your business, the experience of the management team is one of the most important elements of your plan. Your product or service is almost secondary, because, in general, investors invest in people, not products. A lot of businesses have great product ideas, but not all have the skills and experience to succeed.
Review your business plan twice a year to see if it still fits your company or if you need to make changes to your strategic direction.
a sample business plan
Find financing.
Almost every business needs at least some money to get started. Many seek additional funding at various times after the business is up and running. Where can you find the money you’ll need?
Common sources of start-up funding
If you haven’t saved all of the money you’ll need, you’ll need to combine your own investment with funds from other sources. A lender will have greater confidence in your commitment to succeed when they know you have your own personal investment in the business. Many lenders, including the SBA, often require this.
Your family and friends may believe in you and your business plan and may be willing to loan you funds. Be prepared to show them how and when you’ll be able to repay.
Loans and lines of credit from financial institutions can be a source of start-up funding. To borrow from a financial institution, you need to have good credit. Secured credit is ideal if you’re just starting out and want to build good credit history. Develop a good working relationship with your banker or lender. The more they know about you and your business, the better they can advise and assist you.
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) is an independent agency of the Federal Government. Its purpose is to help people get in business, stay in business, and grow. The SBA offers a tremendous number of resources to help you start, finance and manage your business, and find new business opportunities. It can help you write a business plan, obtain start-up capital, purchase real estate, and much more. The SBA has offices throughout the United States to assist you. Learn more by visiting the SBA Web site at www.sba.gov.
examples of sba services
Starting your business: Small Business Start-up Kit; training and counseling; business planning tutorial; special assistance programs for minorities, women, the disabled, veterans, and other groups; workshops; shareware.
Financing your business: Loan programs, including those that focus on: microloans (up to $50,000) for start-up, newly established, or growing small businesses; low and moderate income areas. Working capital lines of credit.
Client commitments to contracts Your customers (or future customers) may be willing to sign contracts, or even pre-pay, for products or services that you commit to deliver to them.

two types of business financing
There are two basic types of business financing, debt financing and equity financing. Here is a comparison of the two:

NEW BUSINESS CHECKLIST
The best place to start in building a business is to ask yourself some basic questions. You may not have all the answers you need right now, but exploring these questions is a good way to spark your thinking and identify the areas you need to research. As you gather the answers, start putting your plan down on paper.
- What products or services will I provide?
- Who will be my customers?
- How will my products and services meet my customers’ needs?
- What equipment or special skills will I need?
- How will I advertise or promote my business?
- Who will be my competitors?
- In the eyes of my customer, how will my business compare to what my competitors offer?
- Where will my business be located? Do I need to buy or rent space, or can I work from home?
- Will I operate my business alone (as a sole proprietor) or as a partnership or corporation?
- Will I need to hire employees?
- How will I find people to hire? How will I pay them?
- How much money will I need to start my business?
- How much money will I need to run the business day-to-day?
- Where will I get the money to get started? Do I qualify for a personal loan?
- How will I structure my company?
- What kinds of legal regulations will my business have to meet – for example, laws regarding employees, environmental protection or import/export?
- What kinds of insurance will I need?
Also, keep in mind that there are probably resources available in your own local community, such as business development centers, to help you create your plan. Check with your local library, university or college, and search online to see what’s available in your community.
Related Resources

Launch a Business

Manage a Business


How to Write a Successful Commercial Bank Business Plan (+ Template)

Creating a business plan is essential for any business, but it can be especially helpful for commercial bank businesses that want to improve their strategy or raise funding.
A well-crafted business plan not only outlines the vision for your company but also documents a step-by-step roadmap of how you will accomplish it. To create an effective business plan, you must first understand the components essential to its success.
This article provides an overview of the key elements that every commercial bank business owner should include in their business plan.
Download the Ultimate Business Plan Template
What is a Commercial Bank Business Plan?
A commercial bank business plan is a formal written document describing your company’s business strategy and feasibility. It documents the reasons you will be successful, your areas of competitive advantage, and it includes information about your team members. Your business plan is a key document that will convince investors and lenders (if needed) that you are positioned to become a successful venture.
Why Write a Commercial Bank Business Plan?
A commercial bank business plan is required for banks and investors. The document is a clear and concise guide to your business idea and the steps you will take to make it profitable.
Entrepreneurs can also use this as a roadmap when starting their new company or venture, especially if they are inexperienced in starting a business.
Writing an Effective Commercial Bank Business Plan
The following are the critical components of a successful commercial bank business plan:
Executive Summary
The executive summary of a commercial bank business plan is a one- to two-page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which will be presented in full in the rest of your business plan.
- Start with a one-line description of your commercial bank company
- Provide a summary of the key points in each section of your business plan, which includes information about your company’s management team, industry analysis, competitive analysis, and financial forecast, among others.
Company Description
This section should include a brief history of your company. Include a short description of how your company started and provide a timeline of milestones your company has achieved.
You may not have a long company history if you are just starting your commercial bank business. Instead, you can include information about your professional experience in this industry and how and why you conceived your new venture. If you have worked for a similar company or been involved in an entrepreneurial venture before starting your commercial bank firm, mention this.
You will also include information about your chosen commercial bank business model and how, if applicable, it is different from other companies in your industry.
Industry Analysis
The industry or market analysis is a crucial component of a commercial bank business plan. Conduct thorough market research to determine industry trends and document the size of your market.
Questions to answer include:
- What part of the commercial bank industry are you targeting?
- How big is the market?
- What trends are happening in the industry right now (and if applicable, how do these trends support your company’s success)?
You should also include sources for your information, such as published research reports and expert opinions.
Customer Analysis
This section should include a list of your target audience(s) with demographic and psychographic profiles (e.g., age, gender, income level, profession, job titles, interests). You will need to provide a profile of each customer segment separately, including their needs and wants.
For example, commercial bank customers may include small businesses, startups, and entrepreneurs.
You can include information about how your customers decide to buy from you as well as what keeps them buying from you.
Develop a strategy for targeting those customers who are most likely to buy from you, as well as those that might be influenced to buy your products or commercial bank services with the right marketing.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis helps you determine how your product or service will differ from competitors and what your unique selling proposition (USP) might be that will set you apart in this industry.
For each competitor, list their strengths and weaknesses. Next, determine your areas of competitive advantage; that is, in what ways are you different from and ideally better than your competitors.
Below are sample competitive advantages your commercial bank business may have:
- Proven industry experience
- Extensive knowledge of the market
- Robust and innovative products and services
- Strong financial position
- Excellent customer service
Marketing Plan
This part of the business plan is where you determine and document your marketing plan. . Your plan should be laid out, including the following 4 Ps.
- Product/Service : Detail your product/service offerings here. Document their features and benefits.
- Price : Document your pricing strategy here. In addition to stating the prices for your products/services, mention how your pricing compares to your competition.
- Place : Where will your customers find you? What channels of distribution (e.g., partnerships) will you use to reach them if applicable?
- Promotion : How will you reach your target customers? For example, you may use social media, write blog posts, create an email marketing campaign, use pay-per-click advertising, or launch a direct mail campaign. Or you may promote your commercial bank business via PR, by being quoted in the media, or by writing articles for industry publications.
Operations Plan
This part of your commercial bank business plan should include the following information:
- How will you deliver your product/service to customers? For example, will you do it in person or over the phone?
- What infrastructure, equipment, and resources are needed to operate successfully? How can you meet those requirements within budget constraints?
The operations plan is where you also need to include your company’s business policies. You will want to establish policies related to everything from customer service to pricing, to the overall brand image you are trying to present.
Finally, and most importantly, your Operations Plan will outline the milestones your company hopes to achieve within the next five years. Create a chart that shows the key milestone(s) you hope to achieve each quarter for the next four quarters, and then each year for the following four years. Examples of milestones for a commercial bank business include reaching $X in sales. Other examples include adding new products, entering new markets, or expanding your distribution channels.
Management Team
List your team members here, including their names and titles, as well as their expertise and experience relevant to your specific commercial bank industry. Include brief biography sketches for each team member.
Particularly if you are seeking funding, the goal of this section is to convince investors and lenders that your team has the expertise and experience to execute your plan. If you are missing key team members, document the roles and responsibilities you plan to hire for in the future.
Financial Plan
Here, you will include a summary of your complete and detailed financial plan (your full financial projections go in the Appendix).
This includes the following three financial statements:
Income Statement
Your income statement should include:
- Revenue : how much revenue you generate.
- Cost of Goods Sold : These are your direct costs associated with generating revenue. This includes labor costs, as well as the cost of any equipment and supplies used to deliver the product/service offering.
- Net Income (or loss) : Once expenses and revenue are totaled and deducted from each other, this is the net income or loss.
Sample Income Statement for a Startup Commercial Bank Firm
Balance sheet.
Include a balance sheet that shows your assets, liabilities, and equity. Your balance sheet should include:
- Assets : Everything you own (including cash).
- Liabilities : This is what you owe against your company’s assets, such as accounts payable or loans.
- Equity : The worth of your business after all liabilities and assets are totaled and deducted from each other.
Sample Balance Sheet for a Startup Commercial Bank Firm
Cash flow statement.
Include a cash flow statement showing how much cash comes in, how much cash goes out and a net cash flow for each year. The cash flow statement should include cash flow from:
- Investments
Below is a sample of a projected cash flow statement for a startup commercial bank business.
Sample Cash Flow Statement for a Startup Commercial Bank Firm
Finally, you will also want to include an appendix section including:
- Your complete financial projections
- A complete list of your company’s business policies and procedures related to the rest of the business plan (marketing, operations, etc.)
- Any other documentation which supports what you included in the body of your business plan.
Writing a good business plan gives you the advantage of being fully prepared to launch and grow your commercial bank company. It not only outlines your business vision but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it.
Now that you know how to write a business plan for your commercial bank, you can get started on putting together your own.
Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With our Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Microfinance Business Plan
NOV.05, 2023

Sample Business Plan for Microfinance
Microfinance is a banking service that provides financial assistance to low-income individuals or groups who do not have access to formal financial services. In the US, microfinancing refers to loans of $50,000 or less. Microfinance institutions (MFIs) offer loans, savings, insurance, and other products to help clients improve their livelihoods, reduce their vulnerability, and achieve their goals.
This microfinance business plan template is about a sample microfinance bank that operates in the USA. It will provide an overview of a microfinance bank’s business models, services, customer focus, management team, success factors, financial highlights, and plans. Refer to our financial advisor business plan for a detailed understanding.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
InnoLoan is a microfinance bank that provides affordable and accessible financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses in the USA. Our mission is to empower our customers to improve their livelihoods, create jobs, and contribute to the economic development of their communities.
InnoLoan microfinance bank offers a range of financial products and services to its clients, such as:
- Microloans – Tailored to the needs and capacities of our customers, with flexible repayment terms and competitive interest rates
- Savings products – Help our customers build assets and plan for the future
- Insurance products – Protect our customers from risks and uncertainties
- Money transfer – Enables our customers to send and receive money conveniently and securely
- Financial education program – Equips our customers with the skills and knowledge to manage their finances effectively
Customer Focus
Our target market comprises low-income individuals and small businesses excluded or underserved by the formal financial sector. We focus on women, youth, minorities, and rural populations facing multiple barriers to financial services. We segment our customers based on their demographic profile, income level, business activity, and financial needs.
Management Team
We have a strong management team with extensive experience and expertise in microfinance, banking, and social development. Our team is committed to delivering high-quality services to our customers and achieving social and financial impact. We also have a network of well-trained and motivated staff who work closely with our customers at the grassroots level.
Success Factors
Our success factors include:
- Clear vision and mission
- Customer-centric approach
- Diversified product portfolio
- Robust operational system
- Strong risk management framework
- Sound financial performance
- Positive social impact
Financial Highlights
Our financial highlights for the next five years are:
- Projected portfolio growth of 25% annually, reaching $50 million by 2026
- Projected customer base of 100,000 by 2026, with 60% women, 40% youth, 30% minorities, and 70% rural
- Projected revenue growth of 30% annually, reaching $15 million by 2026
- Projected net income growth of 35% annually, reaching $3 million by 2026
- Projected return on equity of 20% by 2026
- Projected operational self-sufficiency of 120% by 2026
Company Overview
Who is innoloan microfinance bank.
InnoLoan microfinance bank, established in 2020 in San Francisco, CA, is a US-registered and regulated bank that offers affordable and accessible financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses.
InnoLoan Micro Lending Company
InnoLoan micro-lending company, a branch of InnoLoan microfinance bank, gives small US businesses microloans from $500 to $10,000. It supports entrepreneurs with good business ideas or who need more capital.
Industry Analysis
The microfinance industry in the USA is a growing and dynamic sector that provides financial services to millions of low-income individuals and small businesses who are excluded or underserved by the formal financial sector.
According to the Global Microfinance Market Research Report 2023 , the global Microfinance market reached USD 218.31 billion in 2022. The market is expected to achieve USD 447.76 billion by 2028, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.72% during the forecast period.
Here are some more interesting insights on the microfinance industry:
- There are approximately 10,000 microfinance institutions throughout the world. ( Fit Small Business )
- Microfinance institutions worldwide serve more than 140 million borrowers and have a total loan portfolio estimated at $124 billion. ( Microfinance Barometer Report )
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Our target market consists of low-income individuals and small businesses excluded or underserved by the formal financial sector in the USA. We estimate that over 50 million potential customers in this market segment need financial services but lack access to them. We focus on women, youth, minorities, and rural populations facing multiple barriers to financial services.
Customer Segmentation
We segment our customers based on their demographic profile, income level, business activity, and financial needs. The following table shows the characteristics and size of our customer segments:
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
We face direct and indirect competition from various providers of financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses in the USA.
Some of the direct competitors include:
- MicroVest – A microfinance institution with over $50 million in loans to 100,000 customers. It gives microloans from $100 to $10,000 at 18% interest. It also provides 2% interest savings accounts and life and health insurance.
- MicroFlex – A microfinance institution with over $25 million in loans to 50,000 customers. It gives microloans from $50 to $5,000 at 15% interest. It also provides 1% interest savings accounts and a money transfer service with a 3% fee.
Some of the indirect competitors include:
- Payday lenders – Providers of short-term loans that charge high-interest rates and fees. They target customers who need urgent cash but have poor credit history or no collateral.
- Pawn shops – Providers of loans that require customers to pledge their personal belongings as collateral. They charge high-interest rates and fees and may sell the collateral if the customers fail to repay the loans.
- Credit unions – Non-profit financial cooperatives offering their members loans, savings, and other services. They charge lower interest rates and fees than other providers but have limited outreach and eligibility criteria.
Competitive Advantage
Our competitive advantage is based on the following factors:
Marketing Plan
Our marketing plan is designed to achieve the following objectives:
- To increase our brand awareness and recognition
- To attract new customers and retain existing ones
- To expand our market share and reach by entering new geographic areas
- To enhance our competitive position and reputation
Our marketing plan consists of the following strategies:
- Product strategy – We will continuously improve our products based on customer feedback and market research. We will also introduce new products in the future.
- Price strategy – We will offer competitive and affordable prices that reflect the value and quality of our services. We will also provide incentives and discounts for loyal customers and referrals.
- Place strategy – We will leverage our existing network of branches, agents, and partners to deliver our services to our customers.
- Promotion strategy – We will use traditional and digital media to communicate our value proposition and social impact to our target market and stakeholders.
Operations Plan
Operation function.
Our operations plan describes delivering customer services and managing our internal processes. Our operations plan consists of the following functions:
- Loan origination – We assess and approve microloan applicants using interviews, credit scores, collateral, and group lending, and assist them with the application process.
- Loan disbursement – We deliver the approved loan amount to our customers via cash, bank, mobile money, or prepaid cards, ensuring speed, ease, and safety.
- Loan collection – We collect the loan repayments from our customers as per agreement, using direct debit, mobile money, or cash collection, and monitor the loan performance and contact late customers to prevent defaults and losses.
- Savings mobilization – We offer and manage savings accounts for our customers who want to save money, with good interest rates and no minimum balance, and easy access and withdrawal options through branches, agents, mobile banking, or ATMs.
- Insurance provision – We offer insurance products that protect our customers from life, health, property, and business risks, working with good insurance companies to provide cheap and customized insurance plans, and handling the claims and payments for our customers in case of loss or damage.
- Money transfer service – We offer a money transfer service that allows our customers to send and receive money locally and internationally, working with reliable money transfer operators to provide fast and secure money transfer options, and charging low fees and offering good exchange rates.
- Financial education program – We run a financial education program for our customers who want to learn more, using workshops, seminars, online courses, or mobile apps, and measuring the impact of our program on customers’ financial behavior and well-being.
- January 2024 – Launch of our microfinance bank with all the necessary licenses, registrations, and approvals
- June 2024 – Opening of 10 branches in strategic locations across California
- December 2024 – Reaching 10,000 customers with a loan portfolio of $5 million
- March 2025 – Introduction of new products such as insurance, money transfer, and financial education
- June 2025 – Expansion to new states
- December 2025 – Reaching 50,000 customers with a loan portfolio of $25 million
- March 2026 – Adoption of digital technologies such as mobile banking, online platforms, and biometric identification
- December 2026 – Reaching 100,000 customers with a loan portfolio of $50 million
Financial Plan
Our financial plan provides an overview of our key revenue and costs, funding requirements and use of funds, key assumptions, and financial projections. Refer to our bookkeeping business plan here.
Key Revenue & Costs
Our key revenue sources are:
- Interest income – The income generated from charging interest on our microloans. We charge an average interest rate of 16% per annum on our microloans.
- Fee income – The income generated from charging fees for our services. We charge an average fee of 2% per transaction on our services.
- Other income – The income generated from other sources such as grants, donations, investments, etc. We expect to receive an average of $500,000 annually from other sources.
Our key cost drivers are:
- Operating expenses – The expenses incurred for running our operations, such as salaries, rent, utilities, travel, marketing, etc. Our operating expenses will be 40% of our total revenue.
- Loan loss provision – The provision made for potential losses due to loan default or delinquency. We estimate that our loan loss provision will be 5% of our total loan portfolio.
- Capital expenditure – The expenditure for acquiring or upgrading fixed assets such as equipment, software, vehicles, etc. Our capital expenditure will be 10% of our total revenue.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
We require a total funding of $10 million to launch and grow our microfinance bank in the next five years. We plan to raise this funding from various sources such as equity, debt, grants, etc. The following table shows the breakdown of our funding sources and amounts:
Key Assumptions
Our financial plan is based on the following key assumptions:
- Market share – We will capture 0.2% of our target market by 2026 (100,000 customers)
- Portfolio growth – Our loan portfolio will grow at an annual rate of 25% ($50 million by 2026)
- Revenue growth – Our revenue will grow at an annual rate of 30% ($15 million by 2026)
- Net income growth – Our net income will grow at an annual rate of 35% ($3 million by 2026)
- Return on equity – Our return on equity will be 20% by 2026
Income Statement

Balance Sheet

Cash Flow Statement

Hire OGSCapital for Your Microfinance Business Plan
Writing a microfinance business plan is hard and time-consuming. That’s why you should hire us, OGSCapital. We are a team of leading business plan experts, having helped over 5,000 clients attract over $2.7 billion in financing and achieve their business goals. We have a team of experienced and qualified business plan experts and SBA business plan consultants who have worked in various industries and sectors, including microfinance. We know how to create a compelling and customized five-year microfinance business plan that will meet the expectations of your target audience.
We will also provide strategic advice, market research, financial projections, and graphic design to make your micro loan business plan stand out. Contact us for a free consultation and quote for your microfinance business plan template.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much capital is required to start a microfinance company.
In the US, you may need a minimum capital of $5 million to register as a non-banking financial company (NBFC) microfinance institution. You should have a microfinance institution business plan showing your projected income and expenses for the next five years, or refer to our loan officer business plan .
Is the microfinance business profitable?
Microfinance business can be profitable in the US if you deliver high-quality services that meet the needs and preferences of your target market. You can also use digital technologies or a payday loan business plan to manage costs and risks and show your social and financial impact.
How do I start a microfinance business?
To start a microfinance business, you must identify your target market, choose a specialty of finance, create a business plan, and comply with state and federal regulations. You also need a strategic business plan for a microfinance bank that outlines your vision, mission, goals, and strategies.
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:


- Commercial Lending
- Community Banking
- Compliance and Risk
- Cybersecurity
- Human Resources
- Mutual Funds
- Retail and Marketing
- Tax and Accounting
- Wealth Management
- Magazine Archive
- Newsletter Archive
- Sponsored Archive
- Podcast Archive

FDIC unveils updated financial inclusion strategic plan

The FDIC first published a plan to guide its economic inclusion efforts in 2014. The plan was last updated five years ago. The 2024 update calls on the agency to help households achieve financial stability through the establishment of positive credit histories and the use of consumer credit from banks, along with insured savings accounts, Gruenberg said during a speech at an economic conference in Washington, D.C. As part of that effort, the plan identifies mortgages and small business lending from banks as important opportunities to build household wealth, he said. It also draws an “explicit connection” between the FDIC’s economic inclusion work and community development.
The agency will use a variety of tools to achieve the plan’s objectives, including outreach to bankers, financial education resources, communication to the public about the value of insured deposits and partnerships with community organizations, he said
Related Posts

ABA Data Bank: Farm banks exhibit solid farm loan growth in 2023
Total agricultural lending by farm banks increased 6.7% in 2023 to $110 billion, up from $103 billion the prior year.

ABA, associations urge lawmakers to bolster funding for CDFI Fund
ABA joined the Community Development Bankers Association, National Bankers Association and two other associations in urging members of the House...

Consumer credit increased 3.4% in February
Consumer credit increased at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 3.4% in February, the Federal Reserve reported.

ABA urges FinCEN to rethink currency transaction report requirements
A FinCEN proposal to renew without change its information collection requirements for currency transaction reports, or CTRs, severely underestimates the...

SEC pauses enforcement of climate disclosure rule
The SEC issued a stay on enforcement of its climate disclosure final rule while federal courts consider several challenges to...

Survey: Customer satisfaction higher when bank branches deliver ‘basic’ services
Customer satisfaction with retail bank branches is much higher than average when banks deliver the fundamentals of customer service, according...
SPONSORED CONTENT

ERM Model Risk and AI

The Federal Reserve’s Nick Stanescu shares what’s next for the FedNow® Service

AI Compliance and Regulation: What Financial Institutions Need to Know

Gain Efficiencies and Other Timely Benefits with Data Analytics
American Bankers Association 1333 New Hampshire Ave NW Washington, DC 20036 1-800-BANKERS (800-226-5377) www.aba.com About ABA Privacy Policy Contact ABA

© 2024 American Bankers Association. All rights reserved.
The Economic Times daily newspaper is available online now.
Outgoing bandhan bank chief chandra sekhar ghosh gives a peek into his next plan of action.
Chandra Shekhar Ghosh, set to resign as Bandhan Bank's CEO & MD, cites strong business momentum as reason and the rime being right. He plans to transition to a strategic role within the group's holding company. Speculation rises over his successor, with a search committee expected to be formed. Bandhan Bank shares see a significant drop.

Read More News on
Download The Economic Times News App to get Daily Market Updates & Live Business News.

Better returns than stock, gold? Rolex, the new asset class for investments that transcends time.

LTIMindtree: All eyes are on the next CEO, but investors need to reset expectations. Here’s why.

Many new mothers face this problem that plucks the joy out of giving birth.

TaMo boards Chennai express, reaches Hyundai’s backyard with an INR9,000 crore plant

Stock Radar: Time to buy? Cyient stock breaks out from falling trendline resistance

Big beneficiaries of government focus on sectors like power & railways: 4 PSU stocks with focus on sectoral lending
Find this comment offensive?
Choose your reason below and click on the Report button. This will alert our moderators to take action
Reason for reporting:
Your Reason has been Reported to the admin.

To post this comment you must
Log In/Connect with:
Fill in your details:
Will be displayed
Will not be displayed
Share this Comment:
Uh-oh this is an exclusive story available for selected readers only..
Worry not. You’re just a step away.

Prime Account Detected!
It seems like you're already an ETPrime member with
Login using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits
Log out of your current logged-in account and log in again using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits.
To read full story, subscribe to ET Prime
₹34 per week
Billed annually at ₹2499 ₹1749
Super Saver Sale - Flat 30% Off
On ET Prime Membership
Unlock this story and enjoy all members-only benefits.
Offer Exclusively For You
Save up to Rs. 700/-
ON ET PRIME MEMBERSHIP
Get 1 Year Free
With 1 and 2-Year ET prime membership
Get Flat 40% Off
Then ₹ 1749 for 1 year
ET Prime at ₹ 49 for 1 month
Stay Ahead in the New Financial Year
Get flat 20% off on ETPrime
90 Days Prime access worth Rs999 unlocked for you

Exclusive Economic Times Stories, Editorials & Expert opinion across 20+ sectors
Stock analysis. Market Research. Industry Trends on 4000+ Stocks
Get 1 Year Complimentary Subscription of TOI+ worth Rs.799/-
Stories you might be interested in
US bank regulator eyes scrutiny of asset manager stakes in banks

- BlackRock Inc Follow
- Bank of America Corp Follow
- Citigroup Inc Follow
Get a look at the day ahead in U.S. and global markets with the Morning Bid U.S. newsletter. Sign up here.
Reporting by Pete Schroeder in Washington and Niket Nishant in Bengaluru; additional reporting by Megan Davies; Editing by David Gregorio and Stephen Coates
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Covers financial regulation and policy out of the Reuters Washington bureau, with a specific focus on banking regulators. Has covered economic and financial policy in the U.S. capital for 15 years. Previous experience includes roles at The Hill newspaper and The Wall Street Journal. Received a Master's degree in journalism from Georgetown University, and an undergraduate degree from the University of Notre Dame.

Tesla's Musk predicts AI will be smarter than the smartest human next year
Tesla Chief Executive Elon Musk on Monday said artificial intelligence that was smarter than the smartest human probably would be developed next year, or possibly the next.

Recommended
Royal bank of canada fires finance boss over undisclosed relationship.
- View Author Archive
- Get author RSS feed
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
The Royal Bank of Canada fired its Chief Financial Officer Nadine Ahn after an internal probe revealed that she was in an undisclosed personal relationship with another employee that violated the bank’s code of conduct.
The investigation was launched after the bank became aware of “allegations” against Ahn in March.
An RBC spokesperson told The Post that the company “immediately” tapped outside legal counsel to investigate.
It was concluded that her relationship with a staffer — who remains anonymous — “led to preferential treatment of the employee including promotion and compensation increases.”

The investigation found no evidence of misconduct by the former CFO or the other employee in regards to the bank’s previously issued financial statements, RBC’s strategy or its financial or business performance, the bank said.
Both employees, however, had their employment terminated as a result on April 5, RBC noted in its statement issued Friday evening.
Ahn’s Facebook profile says she is married.
According to Ahn’s LinkedIn profile, she began her 12-year tenure at RBC as a senior manager, before being promoted to managing director, then vice president and senior vice president.
Ahn could not immediately be reached for comment.
She entered the Toronto-based bank’s C-suite in 2021. By 2023, she was bringing home roughly $3 million a year in annual compensation, including more than $475,000 in salary and upwards of $2.5 million in bonuses and stock awards, according to Bloomberg .
Ahn’s annual earnings last year were up 25% from the year prior.

Per the Royal Bank’s annual proxy circular issued earlier this month, top executives who are fired for cause aren’t owed severance. The employee could also be asked for forfeit bonus awards.
It wasn’t immediately clear if Ahn had to give back any of her hefty earnings from 2023.
A spokesperson fro RBC said in a statement to The Post: “As a matter of policy, we do not comment on specific matters relating to individual employees, past or present.”

Meanwhile, longtime RBC staffer Katherine Gibson was named interim CFO while the bank searches for a permanent replacement.
Gibson, who’s been with RBC for more than two decades, has held multiple senior positions during her tenure, including her most recent role as senior vice president of finance and controller.
With Post wires.
Share this article:

Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Marketing Plan. Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a bank business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of bank company that you documented in your company overview.
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
A successful bank business plan is critical for entrepreneurs. This article provides a step-by-step guide & template to help you write your own. ... Complete your business plan and financial model in hours. Sample Income Statement for a Startup Bank. Year 1: Year 2: Year 3: Year 4: Year 5: Revenues: Revenues: $ 336,090: $ 450,940: $ 605,000 ...
A well-crafted plan will continue to serve you throughout the life of your business. Expect to update your document regularly to ensure the information is current and aligns with the overall goals and growth of your organization. Instructions: Use this workbook to solidify and document the core components of your business plan.
This section is the most important for most businesses, as it can make or break a lender's confidence and willingness to extend credit. Always include the following documents in the financial ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
This step involves evaluating the potential profitability and sustainability of your business model. The following are key factors to consider when determining the financial feasibility and viability of your commercial banking business: Market demand: Evaluate the demand for banking services in your target market.
A business plan gives you direction, helps you qualify your ideas and clarifies the path you intend to take toward your goal. Four important reasons to write a business plan: Decision-making: Business plans help you eliminate any gray area by writing specific information down in black and white. Making tough decisions is often one of the ...
5. Make realistic projections. When writing a business plan, you're naturally going to be excited, and it may feel easy to think positively and overestimate how well your business will perform. Optimism may cause you future distress when investors or business partners expect more than your business is able to provide.
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business. . Download Startup Financial Projections Template.
The balance sheet portion of the financial plan aims to give an idea of what the business will be worth, considering all its assets and liabilities, at a future date. To do this, it uses figures from the income statement and cash flow statement. The essence of a balance sheet is found in the equation: Liabilities + Equity = Assets.
Bank Business Plan Checklist. A bank business plan is a document that describes the bank's goals, strategies, operations, and financial projections. It communicates the bank's vision and value proposition to potential investors, regulators, and stakeholders. A SBA business plan should be clear, concise, and realistic. It should also cover ...
Use the numbers that you put in your sales forecast, expense projections, and cash flow statement. "Sales, lest cost of sales, is gross margin," Berry says. "Gross margin, less expenses, interest ...
Traditional business plan. This is a formal document for pitching to investors based on the outline in this article. If your business is a complicated one, the plan may exceed the typical length and stretch to as many as 50 pages. One-page business plan. This is a simplified version of a formal business plan designed to fit on one page.
The best way to increase your chances of success is to write a business plan that outlines all aspects of opening and running a bank. This document should include market analysis, organizational structure, financial projections, and more. Our team has extensive experience helping entrepreneurs open banks.
6. Financials. The financial section of your business plan is critical, especially if you want to circulate the plan to investors or lenders. The purpose of this section is threefold: to 1) outline your business's financial plan, 2) demonstrate your profit potential, and 3) share your financing needs.
A business plan is a guide for your company to follow as it scales in size and complexity. Business plans include basic information about your company's operational, financial and marketing goals. Writing a business plan will include several key sections: Executive summary: A summary of your business model, your target market, your products and ...
Nevertheless, most business plans contain a number of generic sections. Common sections are: executive summary, company overview, products and services, market analysis, marketing and sales plan ...
Definition. Borrowing money that is to be repaid over a period of time, usually with interest. Debt financing can be either short-term (full repayment due in less than one year) or long-term (repayment due over more than one year). Definition. An exchange of money for a share of business ownership. Key Benefit.
3. Review Your Bank's Current Business Plan. Next, thoroughly examine your existing business plan. Evaluate its strengths and weaknesses, identifying any gaps between the business plan and your long-term goals. This will set the stage for future enhancements. 4. Analyze Market and Industry Trends.
Writing an Effective Commercial Bank Business Plan. The following are the critical components of a successful commercial bank business plan:. Executive Summary. The executive summary of a commercial bank business plan is a one- to two-page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which will be presented in full in the rest of your business plan.
1. Regular reviews and updates. Markets shift, consumer behavior changes, and your business will grow. Your plan must evolve with these factors, which makes regular reviews and updates a must-do ...
This microfinance business plan template is about a sample microfinance bank that operates in the USA. It will provide an overview of a microfinance bank's business models, services, customer focus, management team, success factors, financial highlights, and plans. Refer to our financial advisor business plan for a detailed understanding.
The FDIC has released an updated financial inclusion strategic plan that calls on the agency to take steps to encourage bank lending, investments and services that support healthy communities, including in low- and moderate-income neighborhoods and other underserved communities, FDIC Chairman Martin Gruenberg said today. The FDIC first published a plan to guide its economic inclusion efforts ...
Global bank messaging network SWIFT is planning a new platform in the next one to two years to connect the wave of central bank digital currencies now in development to the existing finance system ...
Chandra Shekhar Ghosh, set to resign as Bandhan Bank's CEO & MD, cites strong business momentum as reason and the rime being right. He plans to transition to a strategic role within the group's holding company. Speculation rises over his successor, with a search committee expected to be formed. Bandhan Bank shares see a significant drop.
JPMorgan said on Monday that an orderly CEO transition is the top priority for its board in the medium term, as Jamie Dimon completes 18 years at the helm of the largest U.S. bank by assets.
April 2 (Reuters) - A top U.S. banking regulator is considering a plan to ensure asset management giants BlackRock (BLK.N), opens new tab, Vanguard and State Street (STT.N), opens new tab stick to ...
Published April 8, 2024, 8:49 a.m. ET. The Royal Bank of Canada fired its Chief Financial Officer Nadine Ahn after an internal probe revealed that she was in an undisclosed personal relationship ...