B.Sc. Chemistry First Semester (I) Class Notes

Inorganic Chemistry Notes :
Organic Chemistry Notes:
Physical Chemistry Notes:

Post a Comment
Contact form.

Atomic Structure B.Sc. 1st Semester
Atomic structure mcqs, 2nd semester(session: 2023-2027) batch start: 20th december 2023 @ 7.30am, atomic structure, bohr's theory.
Postulates of Bohr's Model of an Atom
Limitations of Bohr's Theory
Atomic spectrum of hydrogen atom.
Rydberg Formula
de-Broglie Wave Equation
Find the de broglie wavelength for an electron moving at the speed of 5.0×10 6 m/s (mass of an electron is 9.1×10 −31 kg ), heisenberg uncertainty principle, significance of the heisenberg uncertainty principle, a particle is moving with constant momentum. the uncertainty in the momentum of the particle is 3.3 x 10 -2 kg ms -1 . calculate the uncertainty position., heisenberg uncertainty principles has no significance in our everyday life. explain., quantum number, significance of quantum numbers, which of the following is a possible set of quantum numbers that describes an electron a. n = 3, ℓ = 2, m = −3, s = −1⁄2 b. n = 0, ℓ = 0, m = 0, s = +1⁄2 c. n = 4, ℓ = 2, m = −1, s = 0 d. n = 3, ℓ = 1, m = −1, s = +1⁄2 e. n = 4, ℓ = −3, m = −1, s = +1, schrödinger wave equation, physical significance of wave function, normalization of the wave function, orthogonalization of the wave function, sign of wave functions --> radial and angular wave functions for hydrogen atom, radial wave function, r (r), angular wave function, ψ (θ, ɸ), radial and angular distribution curves or functions.
Shapes of s, p, d and f Orbitals
Contour Boundary and Probability Diagrams --> Radial Nodes
Angular Nodes or Nodal Planes
Total Number of Nodes
Pauli's exclusions principle, applications of pauli's exclusion principle, hund's rule of maximum multiplicity.
Multiplicity
Aufbau's principle.
Limitations of Aufbau's Principle
Variations of orbital energy with atomic number, factors affecting the energy of orbitals, social profiles, recent updates, class timing, most viewed pages, board / university mcqs, about author.

- NEWS GALLERY
- NTA IIT-JEE
- NTA Conducted Exams

- UNDER GRADUATE
- POST GRADUATE
- VIDEO LECTURES
- Bihar Board
- Jharkhand Board
- CSIR: NET/JRF
B.Sc. 1st Year Chemistry Notes
Syllabus: First Part Honours (BRABU Muzaffarpur)
Nine questions to be set. Five questions to be answered. Short answer type questions are recommended. There may be several parts in a question and different units may be mixed in questions. While setting questions the entire syllabus may be covered as far as practicable. Two questions to be answered from group 'A' and three questions to be answered from group 'B'
B.Sc. First Part Chemistry MCQs
Social profiles, recent updates, most viewed pages, medicinal chemistry synthesis of drug, new updates, temperature converter.
Fahrenheit:
Class Timing: 6 AM Topic: Physical Chemistry
NEET & IIT-JEE
M.sc. 1st semester, b.sc. (1st part), b.sc. (2nd part), b.sc. (3rd part), neet & iit-jee, class: 22.7.2023, time: 4pm-5.30pm, course duration: 8 months, complete course, revisition, dpp, test, assignments, practice mcq tests, about author.
Dr. Rakesh Srivastava M.Sc., DCE, CGSET, MPSET, Ph.D. About 15+ Years teaching experience of 11th, 12th, UG, PG, Biochemistry, IIT-JEE, NEET and Others. Specialization in Organic Chemistry. Intersted in Spectroscopy, Biochemistry, Natural Products and Environmental Chemistry. At present writing an Organic Chemistry Book
- Top Colleges
- Top Courses
- Entrance Exams
- Admission 2024
- Study Abroad
- Study in Canada
- Study in UK
- Study in USA
- Study in Australia
- Study in Germany
- IELTS Material
- Scholarships
- Sarkari Exam
- Visual Stories
- Write a review
- Login/ Register
- Login / Register
BSc Physics 1st Year Syllabus: Subjects List, Electives & Practicals

Updated on - Feb 27, 2024
The BSc Physics 1st year syllabus is divided into two semesters consisting of both theory and practical subjects. BSc Physics 1st semester syllabus aims at imparting a strong foundation in physics with subjects such as Mechanics and Wave Motion, Circuit Fundamentals and Basic Electronics, Electricity, Magnetism, Electrostatics , etc., whereas the BSc Physics 2nd semester subjects include Kinetic Theory, Low-Temperature Physics, Waves and Oscillations, Applied Acoustics, etc.
In addition to the theory subjects, the BSc Physics syllabus covers practical topics such as Specific Heat by the Cooling-Graphical Method, Emissivity of Surface, Thermal Conductivity of Good Conductor by Searle’s Method, etc., for each semester.
Table of Contents
BSc Physics 1st Year Syllabus
Bsc physics subjects 1st year & topics covered.
- BSc Physics 1st Sem Subjects in Detail
- BSc Physics 2nd Sem Subjects in Detail
- B.Sc Physics 1st Year Syllabus Practical Subjects
BSc Physics 1st year syllabus focuses on equipping students with adequate knowledge and understanding of the foundation subjects such as Mechanics and properties of Matter, Heat, Thermodynamics, Wave, Oscillation, Radiation , etc.
Given below is the semester-wise breakdown of the B.Sc Physics 1st Year Syllabus:
BSc Physics 1st year subjects deal with subjects such as language, foundations, structure, and all the concepts related to basic physics. The topics in the BSc Physics first-year subjects include Electronics, Electromagnetics, Wave and Oscillation, etc. Listed below are the semester-wise BSc Physics subjects 1st year along with the topics covered:
BSc Physics 1st Semester Subjects
The topics covered in the BSc Physics 1st semester subjects include an introduction to diodes and transistors, their working and applications, Introduction to the world of digital electronics, use of basic logic gates, flip flops, registers and counters, Voltage and current sources; superposition theorem, etc.
Listed below are the BSc Physics 1st Semester subjects and topics covered:
BSc Physics 2nd Semester Subjects
BSc Physics 2nd Semester subjects deal with topics such as e lectrostatics and magnetostatics leading to the fundamental laws of electrodynamics, dynamics of a charged particle in electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields and its applications, etc.
Listed below are the BSc Physics 2nd Semester subjects along with the topics covered:
Also, Check :
B.Sc Physics 1st Year Practical Subjects
B Sc Physics syllabus 1st year consists of practical topics for each semester to enhance the understanding of concepts and to build confidence among students in applying the concepts in a practical context. BSc Physics course offers an industry-oriented syllabus that helps students to work in research centers, educational institutes, and other sectors.
Listed below are some of the B.Sc Physics syllabus 1st Year practical topics:
Also Check : Career Opportunities after BSc Physics in India
BSc Physics 1st Year Question Paper Marking Scheme
The students pursuing BSc Physics are evaluated based on their practical marks, end-semester marks, and mid-semester marks. For subjects with practical topics, the theory paper will be for 75 marks with 25 marks allotted for the mid-semester examination. Listed below is the semester-wise marking scheme for BSc Physics 1st Year Syllabus:
BSc Physics 1st Semester Question Paper Marking Scheme
Given below is the marking scheme for BSc Physics 1st Semester Syllabus Question Paper:
BSc Physics 2nd Semester Question Paper Marking Scheme
Given below is the marking scheme for B.Sc Physics 2nd sem syllabus Question Paper:
BSc Physics Books 1st Year
Students can refer to books by famous scholars and professionals in the field of physics to gain in-depth knowledge about the topics covered in the syllabus and beyond such as thermodynamics, electromagnetics, optics, Newton's laws, kinetic theory, etc. Given below are some of the BSc physics books for 1st year:
Top BSc Physics Colleges

IISc Bangalore
Bangalore,Karnataka

Kanpur,Uttar Pradesh

IIT Kharagpur
Kharagpur,West Bengal

IIT Roorkee
Roorkee,Uttarakhand

Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham
Coimbatore,Tamil Nadu

Jadavpur University
Kolkata,West Bengal

University of Hyderabad (UOH)
Hyderabad,Telangana

Delhi University (DU)
Delhi,Delhi NCR
Top Science Entrance Exams

- Eligibility Criteria

Result Date: Mar 22, 2024

BSc Physics Fee Structure
What are the subjects in the B Sc 1st year Physics syllabus?
The B Sc Physics 1st year syllabus includes classical mechanics, mathematical physics, electricity and magnetism, thermodynamics, and an introduction to modern physics.
What are the topics covered in classical mechanics?
Topics include kinematics, Newton's laws, work and energy, rotational motion, and oscillations.
Do I need prior knowledge of physics to start BSc Physics 1st year?
While some basic understanding of physics and mathematics is beneficial, the first year is designed to provide foundational knowledge.
Do students have the option to choose elective courses in the BSc 1st year Physics syllabus?
The availability of elective courses varies, but in many programs, the first year is often structured with a fixed curriculum, offering core physics subjects and practical sessions.
What topics are covered in Electricity and Magnetism?
Electricity and Magnetism cover topics like Gauss's law, electric potential, capacitance, electric current, resistance, magnetic fields, Ampere's law, Faraday's law, etc.
How is the 1st-year Physics syllabus assessed?
1st BSc Physics syllabus, assessment criteria include written exams, practical experiments, assignments, viva, etc.
Get Free Scholarship worth 25000 INR
Atomic Structure & Chemical Bonding Notes pdf bsc 1st year
Atomic structure and chemical bonding notes pdf.
Free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf are provided here for Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding students so that they can prepare and score high marks in their Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding exam.
In these free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf, we will study the atom, which is a necessary pre-requisite in understanding the nature of chemical bonding in compounds. It provides basic knowledge about ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding and explains that chemical bonding is best regarded as a continuum between the three cases. It discusses the periodicity in properties with reference to the s and p block, which is necessary for understanding their group chemistry.
We have provided complete Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding handwritten notes pdf for any university student of BCA, MCA, B.Sc, B.Tech, M.Tech branch to enhance more knowledge about the subject and to score better marks in their Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding exam.
Free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf are very useful for Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding students in enhancing their preparation and improving their chances of success in Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding exam.
These free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding pdf notes will help students tremendously in their preparation for Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding exam. Please help your friends in scoring good marks by sharing these free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding handwritten notes pdf from below links:
Topics in our Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Notes PDF
The topics we will cover in these Atomic Structure & Chemical Bonding Notes PDF will be taken from the following list:
Atomic Structure: Recapitulation of Bohr’s theory, its limitations, and the atomic spectrum of hydrogen atom. Wave mechanics: de Broglie equation, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle, and its significance. Schrödinger’s wave equation, the significance of ψ and ψ2 . Quantum mechanical treatment of H- atom, Quantum numbers, and their significance. Normalized and orthogonal wave functions. Sign of wave functions. Radial and angular wave functions for hydrogen atom. Radial and angular distribution curves. Shapes of s , p , and d o rbitals, Relative energies of orbitals. Pauli’s Exclusion Principle, Hund’s rule of maximum spin multiplicity, Aufbau principle, and its limitations.
Periodicity of Elements: Brief discussion of the following properties of the elements, with reference to s- & p -block and the trends shown: (a) Effective nuclear charge, shielding or screening effect, Slater rules, variation of effective nuclear charge in periodic table. (b) Atomic and ionic radii (c) Ionization enthalpy, Successive ionization enthalpies, and factors affecting ionization enthalpy and trends in groups and periods. (d) Electron gain enthalpy and trends in groups and periods. (e) Electronegativity, Pauling’s/ Allred Rochow’s scales. Variation of electronegativity with bond order, partial charge, hybridization, group electronegativity.
Ionic bond: General characteristics, types of ions, size effects, radius ratio rule and its limitations. Packing of ions in crystals. Born-Landé equation with derivation and importance of Kapustinskii expression for lattice energy. Madelung constant, Born-Haber cycle and its application, Solvation energy. Covalent character in ionic compounds, polarizing power and polarizability. Fajan’s rules and consequences of polarization.
Covalent bond : Valence Bond theory ( Heitler-London approach). Energetics of hybridization, equivalent and non-equivalent hybrid orbitals. Bent’s rule, Resonance and resonance energy. Ionic character in covalent compounds: Bond moment and dipole moment. Percentage ionic character from dipole moment and electronegativity difference. Molecular orbital theory. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic and simple polyatomic molecules N2, O2, C2, B2, F2, CO, NO, and their ions; HCl (idea of s-p mixing and orbital interaction to be given).
VSEPR Theory : Lewis structure, Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR), shapes of the following simple molecules and ions containing lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons: H2O, NH3, PCl3, PCl5, SF6, ClF3, I3- , BrF2+ , PCl6- ,ICl2- ICl4- , and SO4 2-.
Metallic Bond: Qualitative idea of valence bond and band theories. Semiconductors and insulators, defects in solids.
Weak Chemical Forces: v an der Waals forces, ion-dipole forces, dipole-dipole interactions, induced dipole interaction, Hydrogen bonding (theories of hydrogen bonding, valence bond treatment). Effects of weak chemical forces, melting and boiling points, solubility, energetics of dissolution process.
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Notes PDF FREE Download
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding students can easily make use of all these complete Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf by downloading them from below links:

Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Notes pdf Source: nptel.ac.in

Atomic Structure Chemistry Notes pdf for b.sc 1st year Source: egyankosh.ac.in
Atomic Structure Chemistry Notes pdf for b.sc 1st year Source: nios.ac.in

Atomic structure bsc 1st year notes pdf Source: nptel.ac.in

Atomic structure notes pdf b.sc 1st year Source: vssdcollege.ac.in
atomic structure bsc 1st year notes pdf Source: bits-pilani.ac.in

Atomic structure and bonding bsc 1st year notes pdf Source: vssut.ac.in
How to Download FREE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Notes PDF?
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding students can easily download free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf by following the below steps:
- Visit TutorialsDuniya.com to download free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf
- Select ‘College Notes’ and then select ‘Chemistry Course’
- Select ‘Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Notes’
- Now, you can easily view or download free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding handwritten notes pdf
Benefits of FREE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Notes PDF
Free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf provide learners with a flexible and efficient way to study and reference Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding concepts. Benefits of these complete free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding pdf notes are given below:
- Accessibility: These free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding handwritten notes pdf files can be easily accessed on various devices that makes it convenient for students to study Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding wherever they are.
- Printable: These Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding free notes pdf can be printed that allows learners to have physical copies of their Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes for their reference and offline reading.
- Structured content: These free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf are well-organized with headings, bullet points and formatting that make complex topics easier to follow and understand.
- Self-Paced Learning: Free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding handwritten notes pdf offers many advantages for both beginners and experienced students that make it a valuable resource for self-paced learning and reference.
- Visual Elements: These free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding pdf notes include diagrams, charts and illustrations to help students visualize complex concepts in an easier way.
We hope our free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf has helped you and please share these Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding handwritten notes free pdf with your friends as well 🙏
Download FREE Study Material App for school and college students for FREE high-quality educational resources such as notes, books, tutorials, projects and question papers.
If you have any questions feel free to reach us at [email protected] and we will get back to you at the earliest.
TutorialsDuniya.com wishes you Happy Learning! 🙂
Chemistry Notes
- Analytical Clinical Biochemistry Notes
- Atomic Structure & Chemical Bonding Notes
- Basic Analytical Chemistry Notes
- Biomolecules Notes
- Business Skills for Chemists Notes
- Coordination Chemistry Notes
- Conductance & Chemical Kinetics Notes
- Chemical Thermodynamics and its Applications Notes
- Chemical Technology & Society Notes
- Cheminformatics Notes
- Chemistry of Cosmetics & Perfumes Notes
- Fuel Chemistry Notes
- Green Methods in Chemistry Notes
- Halogenated Hydrocarbons and Oxygen Containing Functional Groups Notes
- Intellectual Property Rights Notes
- IT Skills for Chemists Notes
- Organic Chemistry Basics and Hydrocarbons Notes
- Organometallic Chemistry & Bioinorganic Chemistry Notes
- Pesticide Chemistry Notes
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Notes
- Phase Equilibria and Electrochemical Cells Notes
- Polynuclear Hydrocarbons, Heterocyclic Chemistry, Alkaloids and Terpenes Notes
- Quantum Chemistry & Spectroscopy Notes
- S-block and P-block Elements Notes
- Spectroscopy & Applied Organic Chemistry Notes
- States of Matter & Ionic Equilibrium Notes
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Notes FAQs
Q: Where can I get complete Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Notes pdf FREE Download?
A: TutorialsDuniya.com have provided complete Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding free Notes pdf so that students can easily download and score good marks in your Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding exam.
Q: How to download Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf?
A: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding students can easily make use of all these complete free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding pdf notes by downloading them from TutorialsDuniya.com
Software Engineering Projects with Source & Documentation

You will always find the updated list of top and best free Software Engineering projects with source code in an easy and quick way. Our Free Software Engineering projects list has projects for beginners, intermediates as well as experts to learn in 2023.
URL: https://www.tutorialsduniya.com/software-engineering-projects-pdf/
Author: Delhi University

IGNOUHelp.in
A Leading Portal for IGNOU Students
IGNOU BSc Assignment 2024 (January & July)
IGNOU BSc Assignments 2024 - IGNOU BSc Assignment Question Paper has been uploaded by the university for its current session 2024. The students of the BSc program can now download the Assignment Questions from this page. Candidates have to compulsory download and submit these assignments with the solutions to the university to get permission for attending the Term End Exam of the IGNOU BSc Program.
We also inform all BSc students that the assignment questions for each of the courses of the IGNOU BSc program are available for download from here. You have to prepare each of BSc assignment separately so that IGNOU Evaluators can easily understand and identify the course code of each subject.
- IGNOU BSc Syllabus
- IGNOU BSc Study Material
List of IGNOU BSc Assignment 2024
- Download IGNOU BSc Assignments 2024
Each of the Assignment questions will have different marks and the same will be printed on each question. Candidates should write the solutions to all questions according to the instructions given in the IGNOU BSc Assignment Question Paper . The BSc students have to submit the Assignments for each course to IGNOU Study Centre in which they get registered. The candidates have to submit it before the due date to appear in Term End Exam conducted by IGNOU.
IGNOU BSc Assignment Submission Last Date for 2024
Here is the Last Date for Submission of the IGNOU BSc Assignment to appear in the Upcoming Term End Exam June 2024 or December 2024 .
Where to Submit IGNOU BSc Assignments?
If you have completely solved your assignment then you have to submit your IGNOU BSc Assignments to the coordinator of the study centre which is allotted to you at the time of admission. Don’t forget to get a receipt for the submission of BSc Assignments.
After preparing the solution for your BSc Assignment, you have to submit IGNOU Assignments to the coordinator of the study centre which was allotted to you at the time of taking admission. Moreover, Don't forget to get a receipt for the submission of BSc Assignments.
Related Posts:
- IGNOU CPF Assignment 2024 (January & July)
- IGNOU CHR Assignment 2024 (January & July)
- IGNOU CIG Assignment 2024 (January & July)
- IGNOU CIS Assignment 2024 (January & July)
- IGNOU BTS Assignment 2024 (January & July)
- IGNOU DTG Assignment 2024 (January & July)
104 thoughts on “IGNOU BSc Assignment 2024 (January & July)”
Any reference for assignment MTE 01 2 4 5 6
please inform if anyone is having solved PHE 09 (2019) assignment
Respected, I took admission in July 2019 Enrollment no. 197602950 and I’ve to submit my assignment in March so for that I’ll solve the question paper with validity date of December 19 or other assignment question paper will uploaded for us with validity date of December 2020
please upload the PHE8L assignment because it is not uploaded on the website and also BSHF101 also not uploaded
koi bataiga Anthropology Honours Paper …BANC-101,102,103,104….KAHAN MILEGA…ASSIGNMENT AND PREVIOUS PAPER..
Hello Plz koi btaye lse4L , Lse8L , and Phe8l ka assignment banta bhi Hain ya nhi??
nhi banta hai jitne bhi lab courses h unka assignment submit nhi hota
Sir i need your help please mujhe btao bscbch ka assignment exams kab hai maine june2020mai forms bhare the
Woh laboratory subject hai uska nhi hoga. Only theory subject ka assignment submit krna hoga.
आप को assignment mile h kya
BSCG assignment 2021 nhi mila hai.
Kya kisi ko pta h ki agr maine BSCG me july 2019 me admissn liya h aur is saal mujhe 1st year ka assignment submit krna h aur exam dena h bt agr main 2nd year ka bhi isi saal assignment submit kru to kis saal ka paper solve krna hoga???kuki 2nd year to 2020-2021 ka part h to paper 2019-2020 solve kru ya 2021-2022???
Bsc m kitne assignment bnane hai total
BSCG ka assignment ko kis pate per online bhejna hoga.mera study centre hai T.P.S.College Patna.568.
Please koe mere ko September 2021 ka assignment pdf send kre
Kaun sa topic mila hai apko
plz help me mene october mai ignou bscg mai admission liya i have no study material and no syllabus in fact i have no idea how i have to have test or exams in this course or how i have to submit assignment
i also registered in november. kya tumhe kuch pata chala schedule ke baare me?
Mera bhi same h kuch nahi pata isi July 2021 me admission lia bsc general me
Hello, Pooja Sharma enrollment no. 2005646759 m current session me hu mujhe pta nhi assignment kaise banane h or all subject bnanana h are koi btao
I also want PHE8 and CHE8 and CHE7
I didnt get the BSHF 101 assignment for june 2021
Solve assignment CHE-05 for year of 2021
Please koi batayie ki BHDA 101, BHDF101, BRPA 101, FHD 2 Ka assignment banta hai .
Sir bsc 1st year assignment ke answer
Sir/Madam, please provided 2021 solved assignment CHE-4,PHE-7, MTE-4,PHE-102,PHE-09
I Shiv kumar dwivedi my enrollment no is 171571119 and i am student of b come 3rd year in study center satna and regional center jabalpur m.p. I have not received AHE-01 Book in our study material and my exam cycle is january to december 2021. Assignment submission date is 30 september 21 and i call and email many time to mpdd site in ignou. how can i submit our assignment .
Sir mene admission july2020 ko liya tha ab me second year me hoon to muje konsi date ko assignment submit krna h 15th may Or 30th april
Mam i have a doubt i took admission in july 2022 in bscg whats my last date to submit assignments.
Where is AHE-01 assignments?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

BSc 1st Year Physics Notes PDF: Free Download Here (2024)
Are you looking for BSc Physics notes? Well if so, you are in the right place. In this post, we are going to share the download links to BSc 1st year physics notes in pdf format.
In the past few months, hundreds of BSc 1st year students have requested study material (notes & question bank ) in Physics. As a result, we are here with complete handwritten notes.
In our last few posts, we have also shared question banks & notes for chemistry 1st-year students.

BSc 1st Year Physics Notes: General Info & Download Links
Let us first share a little about the course/subject and then we will move to the study material downloading process.
About BSc Physics
BSc (Bachelors in Science) is an undergraduate 3-year degree program that is designed for 10+2 students who are interested in the Science stream.
It consists of the major subjects including: Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, Zoology, Botany, Computer Science, Biology, Biochemistry, EVS & Electronics.
Students can either opt for honors in specific subjects or for the plane course (where he/she will have to choose 3 subjects. e.g. BSc with PCM or BSc with ZBC).
Well, I think it’s enough about the course. Let’s discuss the syllabus of BSc 1st year Physics.
BSc 1st Year Physics Syllabus
Syllabus of degree 1st-year physics consists of the following books:
- Mechanics & General Properties of Matter
- Electricity & Magnetism
- Theory of Oscillations, Waves & Acoustics
For students with semester system the syllabus is as:
This is not the complete syllabus of physics. It just comprises of BSc books that you will have in your course. However, the complete syllabus of physics for BSc students is also available on our website.
As we don’t know which system your university follows (i.e. Semester system or Yearly Examination System), so the study material we have provided here consists of notes for both the 1st & 2nd semester. We’ve provided download links for notes of each chapter below.
Download Links: BSc 1st Year Physics Notes
Below are the download links of notes in pdf format for all chapters.
All you have to do is to simply click on the “Download Here” link after each subject and download the study material.
Book 1: Mechanics & General Properties of Matter
Book 2: Electricity & Magnetism
Book 3: Theory of Oscillations, Waves & Acoustics
Along with these notes, you should also practice important questions & numerical problems in physics.
How to Download?
Downloading BSc 1st year Physics notes is quick & easy. All you have to do is to follow the below steps:
Step 1: Click here to go to the download links.
Step 2: Click on the download links beside each subject & the pdf file will be downloaded in your system.
Step 3: For opening these pdf files, you should have proper application installed on your system. We recommend installing Adobe PDF reader on all your devices.
FAQ: I can’t download the pdf files using the download links? What to do?
Ans: If you are not able to download the study material, then these might be the issues:
- The speed of the Internet is too slow in your device.
- You might be using some adblocker which might be causing this.
- Data Saving mode is on in your browser.
If even after doing all this, you are still not able to download the pdf files. Simply reach out to us by either sending a message on WhatsApp or leaving an email at [email protected] .
Final Words
In this post, we have shared complete information regarding how to download BSc 1st year physics notes. If you face any difficulty during the download process, simply leave a comment below so that we can look after it.
Do you know? You can also download IGNOU study material for any subject for absolutely free (without being a student)
You are also welcome to write suggestions, ways of improvement & future recommendations in the comment box. If you like the post, appreciate our efforts by sharing it with your friends.
Fullonstudy
Related posts.

Basics of Calculus: Exploring Limits, Derivatives, & Integrals With Calculations

BA Psychology Syllabus 2024: Free Download (1st, 2nd & 3rd Year )

BSc 1st Year Zoology Books 2024: Free Download PDF

- _9th Class Chemistry Notes
- _10th Class Chemistry Notes
- _11th Class Chemistry Notes
- _12th Class Chemistry Notes
- _BSc Chemistry Notes
- _MSc Chemistry Notes
- _Spectroscopy
- 🛒 Shop 🛍️
- _Chemistry Podcast
- _Science & Chemistry Quiz
- _Symbol and Formula
- _Chemistry Infographics
- _Chemistry Videos
- _Chemistry Terms
- _Download PDF Notes
- _Chemistry and Pharma Jobs
- _Famous scientists and their inventions
- _Foods for Good Health
- _Chemistry Lab Experiments
- _Financial Education
- _Science & Chemistry Web Stories
- _Interesting Facts of Elements
BSc1Year Atomic Structure
Atomic structure, atomic structure in chemistry, philosopher scientists and their ideas about matter & atom, 1. democritus, 2. aristotle, 3. john dalton.
- In the nineteenth century John Dalton (1766–1844), marks the beginning of the progress of modern atomic theory.
- John Dalton challenges the Aristotelian theory. Dalton revived and revised Democritus’s ideas based on the results of scientific research he conducted.
- The ideas of Democritus’s and Dalton’s were similar. Dalton carried out a number of experiments that allowed him to refine and support his hypotheses.
- Dalton carried out numerous chemicals reactions where he was able to determine the mass ratios of different elements involves in the chemical reactions.
- The outcomes of his research are known as Dalton’s atomic theory, which he proposed in 1803.
- Based on Dalton’s atomic theory , John Dalton calculated the first relative weights of atoms.
- He assessed the atomic weights of some elements according to the mass ratios in which they combined; with the hydrogen atom taken as unity.

Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- Matter consists of atoms, which cannot be divided into simpler element. Therefore atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
- Atoms of one element cannot be transformed into other atoms of an element. In chemical reactions, the atoms of an element can combine with same or other atoms of an element to form new substances.
- Atoms of an element have mass, physical and chemical properties and are different from atoms of any other element.
- Compounds are formed from a chemical reaction of a specific ratio of atoms of different elements.
How the Theory Explains the Mass Laws
Mass conservation, definite composition, multiple proportions, nuclear atom model.
- In 1855, Sir William Crookes carried out a series on experiment to investigate the behavior of heated metals in a vacuum. The experiments showed that a heated cathode produced radiation, which could make substances to emit light.
- The radiation emitted from the cathode is called cathode rays.
- According to some research, it was known that cathode rays could be deflected by a magnetic field and electric field, and they carried a negative charge (the cathode is the negatively charged electrode and because the beam originated from the cathode, it must therefore be negatively charged).
- Subscribe Chemistry Notes Info for more chemistry notes related to atomic structure and follow us on Facebook Page of ChemistryNotesInfo .
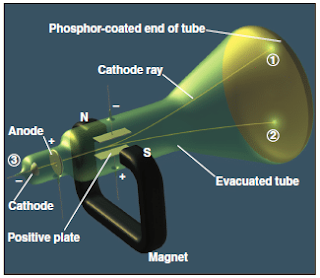
The cathode-ray tube
- In 1897, Joseph J. Thomson demonstrated that both the beam and the charged particles could be bent by an electrical field is applied perpendicular to the path of the beam, as shown in Figure 5 .
- Thomson used the cathode-ray tube to show the deflection of electron by an applied electric field.
- When the cathode is heated, cathode rays is produced which travel along the tube and hit the phosphor-coated end of the tube and emit a glowing spot of light (Figure 5).
- The rays produced at the negative electrode (cathode) and moved to the positive electrode (anode).
- It was concluded that cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles found in all matter.
- By varying the electric field strength and measuring the angle of deflection, Thomson was able to determine the charge-to-mass ( e / m ) ratio of the particles, which are known as electrons .
- Thomson measured the e / m ratio as −1.76 × 108 C/g.
- According to Thomson, the e / m ratio is larger than the one expected compared to the atomic weights of the lightest of atoms. Therefore this indicates that the negatively charged electrons must be much smaller in size than a typical atom.
- As a result of his experiment, Thomson proposed the plum pudding model of the atom, where the atom consisted of one or more of these tiny electrons distributed in a sea of positive charge.
Millikan’s oil-drop experiment for measuring an electron’s charge
Mass and charge of the electron.
- In 1897, the British physicist J. J. Thomson (1856–1940) measured the ratio of the mass of a cathode ray particle to its charge.
- By comparing this value with the mass/charge ratio for the lightest charged particle in solution, he estimated that the cathode ray particle weighed less than as much as hydrogen , the lightest atom.
- In 1909, the American researcher Robert Millikan designed an experiment that measured the charge on the electron.
- He did so by observing the movement of oil droplets in an apparatus that contained electrically charged plates and an x-ray source as shown in Figure 6 .
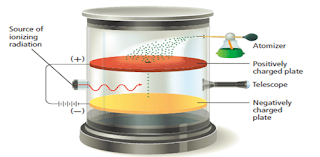
- This experiment also enabled the calculation of the mass of the electron based from its mass: charge ration obtained from J.J Thomson experiment.
- Millikan measured the charge on a great number of tiny oil drops which had been charged.
- An x-ray radiation is used to remove electrons from the gas molecules present in the chamber.
- The oil drops pick up the electrons present in the chamber, making them to become negatively charged.
- A small number of the oil drops sprayed into the box above the positively charged plate pass through the hole.
- When there is no electric field between the plates, the drops fall slowly with a steady velocity.
- An individual drop carrying a charge may be brought to rest by applying a voltage across the plates so that its weight ( acting downwards) is exactly balanced by the electrostatic force in it ( acting upwards).
- Millikan varies the voltage so that the oil droplet suspend in the air.
- Then he measured it total charge, by measuring the voltage needed to bring the drop to rest and the rate at which it falls when there is no voltage between the plates.
- Millikan was able to determine that each of the charged particles was some integral multiple of the electronic charge, which he determined to be −1.592 × 10−19 C, a measurement that is fairly close to the modern value for the charge on an electron (−1.60217733 × 10−19 C).
- As a drop could only pick up only whole number of electrons, this indicated that the charge on an individual electron must be -1.6 x 10-19.
- Therefore the value of electron’s charge is -1.602×10-19 C (C stands for coulomb, the SI unit of charge).
- Therefore the mass of the electron m e could be calculated using the electron’s mass; charge ration and the value for the electron’s charge.
The plum pudding model
- Thomson proposed the plum pudding model of the atom, where the atom consisted of one or more of these tiny electrons distributed in a sea of positive charge.
- Thomson thought that the positive charge necessary to counterbalance the negative charges of electrons in a neutral atom was in the form of a cloud.
- According to this model, an atom is spherical in shape and it consist of positive and negative charges equally distributed as shown in Figure 7 .

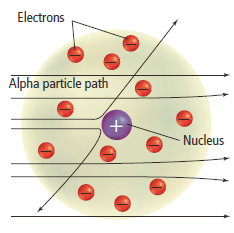
- In 1911, Ernest Rutherford (1871–1937) began to study how positively charged alpha particles interacted with solid matter.
- Rutherford carried out an experiment using a thin gold metal sheet to see if alpha particles would be deflected as they passed through the sheet.
Rutherford’s experiment
- The Rutherford’s gold fold experiment consists of a source of alpha particles, a thin gold sheet and a fluorescent screen. The screen consists of a phosphorescent coating of zinc-sulphide on its interior surface. The screen is circular in shape. The metal foil was mounted at the centre of the apparatus as shown in Figure 10 .
- When an energetic alpha particle struck the phosphorescent screen, a flash of light would be observed. By noting where the flashes occurred, the scientists could determine if the atoms in the gold foil deflected the alpha particles.
- Based on the plum pudding model, where the electrons were evenly dispersed in a sphere of positive charge, Rutherford expected that the heavier alpha particles should be able to pass through the atom with little or no deflections
- The diagram below ( Figure 8 )shows the results Rutherford expected from the experiment.

Rutherford’s model of the atom
- Rutherford demonstrated that the plum pudding model proposed by Thomson was false.
- Based on some calculations, they showed that the diameter of the nucleus was about five orders of magnitude smaller than that of the atom.
- Using this model, Rutherford showed that the nucleus of an atom is of the order of 10 -14 m across compared with the size of an atom which is of the order of 10 -10 m.
- The large angles of scattering for a very small number of particles led Rutherford to propose that the majority of the mass of the atom was concentrated in a minute positively charged region, around which the electrons in the atom circulated.
- When an alpha particle came very close to the nucleus, Rutherford reasoned, the electrostatic repulsion between the two would be sufficient to repel the alpha particle and so produce the large angle of scattering.
- Since the nucleus was small, this scattering would occur for only the few particles which approached the nucleus sufficiently closely.
- Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model is shown in the Figure 10.
Rutherford’s model of the atom conclusion
- Therefore they concluded that matter is mostly empty space, with the very lightweight electrons orbiting around an incredibly dense and positively charged nucleus.
- He also concluded that almost all of the positive charges were contained in a tiny, dense region in the centre of the atom, which he called the nucleus.
- The negatively charged electrons are held within the atom by their attraction to the positively charged nucleus.
Summary of Rutherford’s experiment
The proton and the neutron.
- By 1920, Rutherford had refined the concept of the nucleus and concluded that the nucleus contained positively charged particles called protons.
- A proton is a subatomic particle carrying a charge of 1+.
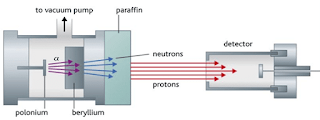
- In 1932, James Chadwick (1891–1974), showed that the nucleus also contained another subatomic neutral particle, called the neutron.
- A neutron is a subatomic particle that has a mass nearly equal to that of a proton, but it carries no electric charge.
- Chadwick’s experiment consists of bombarding a beryllium plate with alpha particle. An uncharged radiation is produced on the opposite side of the sheet. Therefore, he used a solid material containing many hydrogen atoms (paraffin wax) in the path of this radiation caused protons to be knocked out of the wax. He showed that the unknown radiation must consist of uncharged particles with a mass similar to that of the proton.
The Atomic Theory
Structure of the atom.
- An atom is an electrically neutral, spherical entity composed of a positively charged central nucleus surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons.
- All atoms are made up of the three fundamental subatomic particles—the electron, the proton, and the neutron.
- The electrons move rapidly within the available volume, held there by the attraction of the positively charged nucleus.
- An atom’s diameter (≈1×10 -10 m) is about 20,000 times the diameter of its nucleus (≈5×10 -15 m).
- The nucleus, which is composed of neutral neutrons and positively charged protons, contains all of an atom’s positive charge and more than 99.97% of its mass.

- An atomic nucleus consists of protons and neutrons (the only exception is the simplest hydrogen nucleus, which is a single proton).
- The proton (p + ) has a positive charge, and the neutron (n 0 ) has no charge; thus, the positive charge of the nucleus results from its protons.
- The magnitudes of the charges possessed by a proton and by an electron (e – ) are equal, but the signs of the charges are opposite.
- Since an atom is electrically neutral, the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom must be exactly equal to the number of electrons.
- The proton number of an atom is also known as the atomic number Z . This represents the number of protons in the nucleus.
- All carbon atoms ( Z= 6) have 6 protons, all oxygen atoms ( Z= 8) have 8 protons, and all uranium atoms ( Z= 92) have 92 protons. There are currently 117 known elements, of which 90 occur in nature and 27 have been synthesized by nuclear scientists.
Atomic number
- The mass number (or nucleon number) A is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Thus, a carbon atom with 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus has a mass number of 12, and a uranium atom with 92 protons and 146 neutrons in its nucleus has a mass number of 238.
Mass number
- An atom with Z protons and N neutrons in represented as shown in Figure 13. The atomic symbol X is based on the element Latin, Greek or English name.
- For example, C for carbon, S for sulfur, and Na for sodium (Latin natrium ). Often written with the symbol are the atomic number ( Z ) as a left sub script and the mass number ( A ) as a left super script.

- Since the mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons, the number of neutrons ( N ) equals the mass number minus the atomic number:
- Isotopes are atoms with the same proton number but different nucleon numbers. They have the same electron arrangement and , therefore, the same chemical properties
- For example, all carbon atoms ( Z =6) have 6 protons and 6 electrons, but only 98.89% of naturally occurring carbon atoms have 6 neutrons ( A= 12). A small percentage (1.11%) have 7 neutrons ( A= 13), and even fewer (less than 0.01%) have 8 ( A= 14). These are carbon’s three naturally occurring isotopes: 12 C, 13 C, and 14 C.
- The chemical properties of an element are primarily determined by the number of electrons, so all isotopes of an element have nearly identical chemical behaviour, even though they have different masses.
Calculation of the atomic mass of chlorine
- To calculate the weighted average atomic mass of chlorine, you first need to calculate the mass contribution of each isotope.

Atomic Masses of the Elements
- The mass of an atom is measured relative to the mass of an atomic standard. The modern standard is the carbon-12 atom, whose mass is defined as exactly 12 atomic mass units. Thus, the atomic mass unit (amu) is 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
- Based on this standard, the 1 H atom has a mass of 1.008 amu; in other words, a 12 C atom has almost 12 times the mass of an 1 H atom.
- The other unit for atomic mass is dalton (Da). Therefore one 12 C atom has a mass of 12 daltons (12 Da, or 12 amu).
- The atomic mass unit is a unit of relative mass, but it has an absolute mass of 1.66054×10 -24 g.
Masses of Subatomic Particles
Mass spectrometry.

How the Mass Spectrometer Works
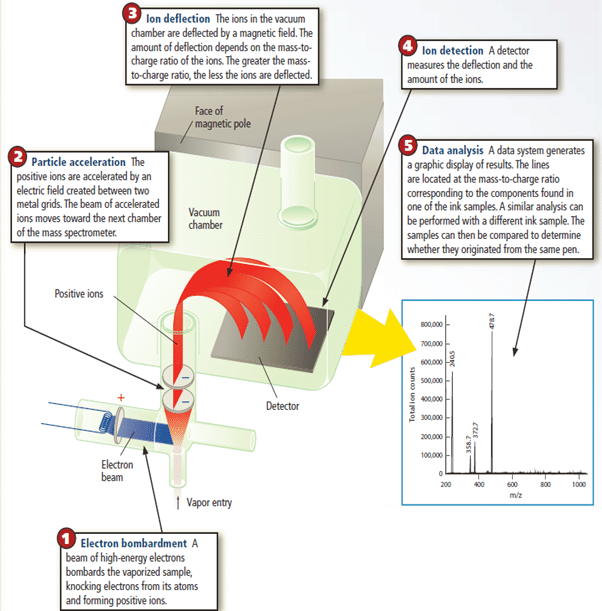
Unstable Nuclei and Radioactive Decay
Radioactivity, nuclear reactions.
- Substances that emitted radiation spontaneously in a process is called radioactivity.
- Radiation s are rays and particles emitted by the radioactive material.
- A nuclear reaction involves a change in the nuclide.
- A nuclear reaction results in the formation of new kinds of atoms.
- Radioactive atoms produce radiation because their nuclei are unstable.
Radioactive decay
- Unstable nuclei disintegrate (break up) and lose energy by emitting radiation such as alpha, beta or gamma radiation. The disintegrated is radioactive decay.
- Unstable atoms disintegrate to form stable atoms, often of a different element.
Types of Radiation
- There are three different types of radiation based on their electric charge.
- An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of electric fields and magnetic on radiation.
- By directing radiation from a radioactive source between two electrically charged plates, As shown in the Figure 17, radiation were deflected toward the negative plate, the positive plate, or not at all.
Alpha radiation
- Alpha particles having a positive charge deflected toward the negatively charged plate were named alpha radiation.
- An alpha particle contains two protons and two neutrons, and thus has a 2+ charge, which explains why alpha particles are attracted to the negatively charged plate as shown in Figure 17.
- An alpha particle is equivalent to a helium-4 nucleus and is represented by α .
- The alpha decay of radioactive radium-226 into radon-222 is shown below.

- The new element, radon (Rn), is created as a result of the alpha decay of the unstable radium-226 nucleus.
- The type of equation shown above is known as a nuclear equation. It shows the atomic numbers and mass numbers of the particles involved. The mass number is conserved in nuclear equations.
Beta radiation
- Beta particles having a negative charge deflected toward the positively charged plate were named beta radiation as shown in Figure 17.
- This radiation consists of fast-moving beta particles.
- Beta particle is an electron with a 1- charge and it represented by the symbol β or e – .
- An example of beta decay of carbon-14 into nitrogen-14 is shown below.

Gamma radiation
- Gamma rays are undeflected since they are electromagnetic and it possessed a high-energy radiation.
- Gamma rays have no mass and are denoted by the symbol γ .
- Gamma ray are neutral, gamma rays are not deflected by electric or magnetic fields.
- They usually accompany alpha and beta radiation, and they account for most of the energy lost during radioactive decays.
- An example gamma rays is shown below:
- Gamma rays are mass less; the emission of gamma rays by themselves cannot result in the formation of a new atom.
Nuclear Stability – Atomic Structure Notes
- The primary factor in determining an atom’s stability is its ratio of neutrons to protons. Atoms that contain either too many or too few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus.
- They emit alpha and beta particles and these emissions affect the neutron-to-proton ratio of the newly created nucleus.
- Radioactive atoms undergo enough radioactive decay to form stable, non-radioactive atoms.
Buy Atomic Structure Books
- Reactions of Aromatic Compounds (Part 2) – BSc Chemistry Notes
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution – Reaction of Aromatic Compounds (Part 1)
- Solid State Chemistry – BSc Chemistry Notes
- MSc Chemistry Notes Iron Metalloporphyrin Complexes in Bioinorganic Molecules
- Zinc Metalloenzymes BSc Chemistry Notes
- B.Sc. Chemistry Notes - Atomic Structure
- University Chemistry Notes Thermodynamics
- Graduation Chemistry Notes - Electromagnetic spectrum UV and Visible Spectroscopy
- College Chemistry of Elements of First Transition Series
You might like
Our website uses cookies to improve your experience. Privacy Policy WhatsApp
- Practical Files
- Notes & Updates

BSc 1st Year Geology- Full Course & Notes

- Category 1st Year
- Last Update 03 Nov, 2023
About The Course
To pay the fee of the course please whatsapp on 9840842566 or click here.
The BSc 1st Year Geology course is designed for BSc 1st Year Geology Group Students. The BSc 1st year Geology Course Includes Complete Classes, Complete Notes along with the Recorded as well as Live sessions.
The Geology of BSc 1st Year seems Tough as it has a huge syllabus. Don’t worry this course is designed such that all Important Questions along with TU solutions of Past Year Questions are Available on the course.
You can Preview Some of the Lectures from the Curriculum Section or If you don’t know how To View Demo Classes go through the Following Links:
To Watch Demo Videos from Mobile: Click Here
To Watch Demo Video from Laptop/Computer: Click Here
BSc 1st Year Geology Course Includes:
- Complete Live Sessions Recordings(2080 Batch)
- Complete Chapter Notes
- Each Chapter Recorded Session
- Practical Exam Tips
- TU Solutions
- Model Questions
- Assignments Included
If you have Any Queries mail [email protected] or contact at 9840842566 .
What Will You Learn?
You Will Learn About BSc 1st Year Geology.
The Course Curriculam
Rapid revision classes, introduction + minerals + rocks, rapid revision day 2, day 4: crystallography, introduction to geology, minerals & rocks, earth’s interior, introduction to plate tectonics & isostasy, weathering & mass wasting, geological work of running water, groundwater & its geological activity, glaciers & glaciations, geological work of sea & ocean, geological work of wind, introduction to crystallography, internal order in crystal, crystal system & classes, crystal growth & twining, introduction to mineralogy & its physical properties, crystal chemistry of minerals, chemical properties of minerals, introduction to optical mineralogy, mineral genesis & mineral classification, introduction to structural geology, geological map & cross section, stereographic projection, stress & strain, unconformity, intrusive contacts, primary structures, foliation & lineation, concept of field geology.
Dipendra Chaulagain
Insert/edit link.
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
BSc 1st year consists of two semesters, i.e. Semester I and Semester II. In this post, I have provided the download links of Chemistry notes for BSc Sem I as well as Sem II. In our recent post, we have also shared physics & botany notes for BSc 1st year. This is all about our previous similar posts for BSc 1st Year Students. Let us discuss the ...
The syllabus of BSc 1st year is distributed into two semesters. The first semester comprises books like Elementary Algebra, Matrices, Trigonometry, Differential Calculus & Vector Analysis. Likewise, the syllabus for the second semester comprises Group Theory, Integral Calculus & Analytical Geometry. The detailed syllabus of both the semesters ...
Below are the Notes of BSc 1st Year Chemistry, Chapter 1 Atomic Structure. On average 4 - 10 Marks for Short Questions and sometimes Long Questions can be asked from this Chapter. Atomic Structure Topics Below are Some Important Topics that can be. Explore Complete Bsc 1st Year Chemistry Notes of all Chapters & Download PDF.
3. The paired electrons of the valence shell does not take part in the bond formation. 4. A covalent bond is formed by the overlapping of two half filled valence atomic orbitals of two different atoms. 5. The electrons in the overlapping orbitals get paired and confined between the nuclei of two atoms. 6.
Downloading BSc botany notes is quite easy. All you have to do is to simply scroll down and click on the "Download" link beside each subject. Download Links. Semester I Notes: Semester II Notes: I hope you are able to download Botany notes for BSc 1st year using the above links.
4.9 BSc Chemistry First Year Syllabus. 4.10 BSc Physics First Year Syllabus. 4.11 BSc Nautical Science First Year Syllabus. 4.12 BSc Forestry First Year Syllabus. 4.13 BSc Mathematics First Year Syllabus. 4.14 BSc Zoology First Year Syllabus. 4.15 BSc Botany First Year Syllabus. 4.16 BSc Optometry First Year Syllabus.
View BSc First Year Assignment Booklet.pdf from BSC 511 at Richfield Graduate Institute of Technology (Pty) Ltd - Pretoria. Reg. No. : 2000/000752/07 MAIN CAMPUS 292 SMITH STREET DURBAN 4000 FACULTY ... BSc First Years Assignments - Copy.pdf. Solutions Available. Ujamaa School. POL1AA1 202. final exam.pdf. Solutions Available. University of the ...
Welcome to IndianChemistry website. We started this site to provide contents such as study materials, Mock tests, UGC-NET, GATE, TIFR, BARC, ISRO Previous Year Papers and their solutions, free video lectures, Best Books Recommendations for preparation for the CSIR-UGC NET, GATE and Other Competitive Exams to the ASPIRANTS who want to pursue their career in the field of Chemistry.
BSc 1st Year Zoology Course Includes: Complete Live Sessions Recordings (2080 Batch) Complete Chapter Notes. Each Chapter Recorded Session. Practical Exam Tips. TU Solutions. Model Questions. Assignments Included. If you have Any Queries mail [email protected] or contact at 9840842566.
"ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND PERIODIC PROPERTIES" Inorganic Chemistry,BSc.1st Year Complete Handwritten Notes In English- https://kanhaiyapatel.myinstamojo.com/prod...
3. The force of attraction between the nucleus and the electron is equal to centrifugal force of the moving electron. Force of attraction towards nucleus = centrifugal forcebr. 4. An electron can move only in those permissive orbits in which the angular momentum (mvr) of the electron is an integral multiple of h/2π.
BSc 1st Year Botany Course Includes: Complete Live Sessions Recordings (2080 Batch) Complete Chapter Notes. Each Chapter Recorded Session. Practical Exam Tips. TU Solutions. Model Questions. Assignments Included. If you have Any Queries mail [email protected] or contact at 9840842566.
Organic compounds of nitrogen: Classification, nomenclature and structure of amines. Preparation and properties of aliphatic amines. Separation and identification of 1° , 2° and 3° amines. Preparation, properties and estimation of urea. B.Sc. First Part Chemistry MCQs. Class Timing: 6 AM. Topic: Physical Chemistry.
Mechanism of organic reactions Bsc 1st year organic chemistry || Bsc 1st semester || Bsc 1st year organic chemistry Chapter : 2 by ChemBoost : Bsc Chemistry
BSc 1st Year Physics Subjects. There are two semester in BSc Physics & each of these semester consists of two theory subjects along with lab experiments. The semester I is composed of Mathematical Physics & Mechanics whereas Electricity, Magnetism, Waves & Optics are covered in Semester II. Semester I. Semester II.
The BSc Physics 1st year syllabus is divided into two semesters consisting of both theory and practical subjects. BSc Physics 1st semester syllabus aims at imparting a strong foundation in physics with subjects such as Mechanics and Wave Motion, Circuit Fundamentals and Basic Electronics, Electricity, Magnetism, Electrostatics, etc., whereas the BSc Physics 2nd semester subjects include ...
In these free Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding notes pdf, we will study the atom, which is a necessary pre-requisite in understanding the nature of chemical bonding in compounds. It provides basic knowledge about ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding and explains that chemical bonding is best regarded as a continuum between the three cases.
IGNOU BSc Assignments 2024- IGNOU BSc Assignment Question Paper has been uploaded by the university for its current session 2024. The students of the BSc program can now download the Assignment Questions from this page. ... Sir bsc 1st year assignment ke answer. Reply. Y.K.BADOLA says: August 19, 2021 at 11:03 am. Sir/Madam, please provided ...
BSc 1st Year Statistics Course Includes: Complete Live Sessions Recordings (2080 Batch) Complete Chapter Notes. Each Chapter Recorded Session. Practical Exam Tips. TU Solutions. Model Questions. Assignments Included. If you have Any Queries mail [email protected] or contact at 9840842566.
Downloading BSc 1st year Physics notes is quick & easy. All you have to do is to follow the below steps: Step 1: Click here to go to the download links. Step 2: Click on the download links beside each subject & the pdf file will be downloaded in your system. Step 3: For opening these pdf files, you should have proper application installed on ...
The modern standard is the carbon-12 atom, whose mass is defined as exactly 12 atomic mass units. Thus, the atomic mass unit (amu) is 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Based on this standard, the 1 H atom has a mass of 1.008 amu; in other words, a 12 C atom has almost 12 times the mass of an 1 H atom.
View ASSIGNMENT BOOKLET 2018-BSc (1st Year).pdf from MICT 621 at Richfield Graduate Ins... ASSIGNMENT BOOKLET 2019 1ST YEAR (DIT 3 Year).pdf Richfield Graduate Institute of Technology (Pty) Ltd - Durban
BSc 1st Year Geology Course Includes: Complete Live Sessions Recordings (2080 Batch) Complete Chapter Notes. Each Chapter Recorded Session. Practical Exam Tips. TU Solutions. Model Questions. Assignments Included. If you have Any Queries mail [email protected] or contact at 9840842566.