An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know
- Translations |
- Service Centers |
- Pandemic Assistance
Farmers.gov is not optimized for this browser. Please use the latest versions of Chrome, Edge, or Safari for the best experience. Dismiss
Find your state/county's agriculture data and USDA resources on your farmers.gov Local Dashboard !

How to Start a Farm: Plan Your Operation
Think about your operation from the ground up and start planning for your business. A good farm business plan is your roadmap to start-up, profitability, and growth, and provides the foundation for your conversation with USDA about how our programs can complement your operation.
Keep reading about planning your business below, get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey , or jump to a different section of the farmer's journey.
On This Page
Why you need a farm business plan.
A comprehensive business plan is an important first step for any size business, no matter how simple or complex. You should create a strong business plan because it:
- Will help you get organized . It will help you to remember all of the details and make sure you are taking all of the necessary steps.
- Will act as your guide . It will help you to think carefully about why you want to farm or ranch and what you want to achieve in the future. Over time, you can look back at your business plan and determine whether you are achieving your goals.
- Is required to get a loan . In order to get an FSA loan, a guarantee on a loan made by a commercial lender, or a land contract, you need to create a detailed business plan . Lenders look closely at business plans to determine if you can afford to repay the loan.
How USDA Can Help
Whether you need a good get-started guide, have a plan that you would like to verify, or have a plan you’re looking to update for your next growth phase, USDA can help connect you to resources to help your decisions.
Your state's beginning farmer and rancher coordinator can connect you to local resources in your community to help you establish a successful business plan. Reach out to your state's coordinator for one-on-one technical assistance and guidance. They can also connect you with organizations that specifically serve beginning farmers and ranchers.
It is important to know that no single solution fits everyone, and you should research, seek guidance, and make the best decision for your operation according to your own individual priorities.
Build a Farm Business Plan
There are many different styles of business plans. Some are written documents; others may be a set of worksheets that you complete. No matter what format you choose, several key aspects of your operation are important to consider.
Use the guidelines below to draft your business plan. Answering these kinds of questions in detail will help you create and develop your final business plan. Once you have a business plan for your operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center. During your visit, we can help you with the necessary steps to register your business and get access to key USDA programs.
Business History
Are you starting a new farm or ranch, or are you already in business? If you are already in business:
- What products do you produce?
- What is the size of your operation?
- What agricultural production and financial management training or experience do you, your family members, or your business partners have?
- How long have you been in business?
Mission, Vision, and Goals
This is your business. Defining your mission, vision and goals is crucial to the success of your business. These questions will help provide a basis for developing other aspects of your business plan.
- What values are important to you and the operation as a whole?
- What short- and long-term goals do you have for your operation?
- How do you plan to start, expand, or change your operation?
- What plans do you have to make your operation efficient or more profitable ?
- What type of farm or ranch model (conventional, sustainable, organic, or alternative agricultural practices) do you plan to use?
Organization and Management
Starting your own business is no small feat. You will need to determine how your business will be structured and organized, and who will manage (or help manage) your business. You will need to be able to convey this to others who are involved as well.
- What is the legal structure of your business? Will it be a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, trust, limited liability company, or other type of entity?
- What help will you need in operating and managing your farm or ranch?
- What other resources, such as a mentor or community-based organization , do you plan to use?
Marketing is a valuable tool for businesses. It can help your businesses increase brand awareness, engagement and sales. It is important to narrow down your target audience and think about what you are providing that others cannot.
- What are you going to produce ?
- Who is your target consumer ?
- Is there demand for what you are planning to produce?
- What is the cost of production?
- How much will you sell it for and when do you expect to see profit ?
- How will you get your product to consumers ? What are the transportation costs and requirements?
- How will you market your products?
- Do you know the relevant federal, state, and local food safety regulations? What licensing do you need for your operation?
Today there are many types of land, tools, and resources to choose from. You will need to think about what you currently have and what you will need to obtain to achieve your goals.
- What resources do you have or will you need for your business?
- Do you already have access to farmland ? If not, do you plan to lease, rent, or purchase land?
- What equipment do you need?
- Is the equipment and real estate that you own or rent adequate to conduct your operation? If not, how do you plan to address those needs?
- Will you be implementing any conservation practices to sustain your operation?
- What types of workers will you need to operate the farm?
- What additional resources do you need?
Now that you have an idea of what you are going to provide and what you will need to run your operation you will need to consider the finances of your operation.
- How will you finance the business?
- What are your current assets (property or investments you own) and liabilities (debts, loans, or payments you owe)?
- Will the income you generate be sufficient to pay your operating expenses, living expenses, and loan payments?
- What other sources of income are available to supplement your business income?
- What business expenses will you incur?
- What family living expenses do you pay?
- What are some potential risks or challenges you foresee for your operation? How will you manage those risks?
- How will you measure the success of your business?
Farm Business Plan Worksheets
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan.
Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans.
- FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet
- FSA-2037 Instructions
Planning for Conservation and Risk Management
Another key tool is a conservation plan, which determines how you want to improve the health of your land. A conservation plan can help you lay out your plan to address resource needs, costs and schedules.
USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) staff are available at your local USDA Service Center to help you develop a conservation plan for your land based on your goals. NRCS staff can also help you explore conservation programs and initiatives, such as the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) .
Conservation in Agriculture
Crop insurance, whole farm revenue protection and other resources can help you prepare for unforeseen challenges like natural disasters.
Disaster Recovery

Special Considerations
Special considerations for businesses.
There are different types of farm businesses each with their own unique considerations. Determine what applies to your operation.
- Organic Farming has unique considerations. Learn about organic agriculture , organic certification , and the Organic Certification Cost Share Program to see if an organic business is an option for you. NRCS also has resources for organic producers and offers assistance to develop a conservation plan.
- Urban Farming has special opportunities and restrictions. Learn how USDA can help farmers in urban spaces .
- Value-Added Products . The Agricultural Marketing Resource Center (AgMRC) is a national virtual resource center for value-added agricultural groups.
- Cooperative. If you are interested in starting a cooperative, USDA’s Rural Development Agency (RD) has helpful resources to help you begin . State-based Cooperative Development Centers , partially funded by RD, provide technical assistance and education on starting a cooperative.
Special Considerations for Individuals
Historically Underserved Farmers and Ranchers: We offer help for the unique concerns of producers who meet the USDA definition of "historically underserved," which includes farmers who are:
- socially disadvantaged
- limited resource
- military veterans
Women: Learn about specific incentives, priorities, and set asides for women in agriculture within USDA programs.
Heirs' Property Landowners: If you inherited land without a clear title or documented legal ownership, learn how USDA can help Heirs’ Property Landowners gain access to a variety of programs and services
Business Planning
Creating a good business plan takes time and effort. The following are some key resources for planning your business.
- Farm Answers from the University of Minnesota features a library of how-to resources and guidance, a directory of beginning farmer training programs, and other sources of information in agriculture. The library includes business planning guides such as a Guide to Developing a Business Plan for Farms and Rural Businesses and an Example Business Plan .
- The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers information about starting, managing, and transitioning a business.
SCORE is a nonprofit organization with a network of volunteers who have experience in running and managing businesses. The Score Mentorship Program partners with USDA to provide:
- Free, local support and resources, including business planning help, financial guidance, growth strategies.
- Mentorship through one-on-one business coaching -- in-person, online, and by phone.
- Training from subject matter experts with agribusiness experience.
- Online resources and step-by-step outlines for business strategies.
- Learn more about the program through the Score FAQ .
Training Opportunities
Attend field days, workshops, courses, or formal education programs to build necessary skills to ensure you can successfully produce your selected farm products and/or services. Many local and regional agricultural organizations, including USDA and Cooperative Extension, offer training to beginning farmers.
- Cooperative Extension offices address common issues faced by agricultural producers, and conduct workshops and educational events for the agricultural community.
- extension.org is an online community for the Cooperative Extension program where you can find publications and ask experts for advice.
Now that you have a basic plan for your farm operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center.
2. Visit Your USDA Service Center
How to Start a Farm with USDA
Get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey or jump to a specific page below.
Find Your Local Service Center
USDA Service Centers are locations where you can connect with Farm Service Agency, Natural Resources Conservation Service, or Rural Development employees for your business needs. Enter your state and county below to find your local service center and agency offices. If this locator does not work in your browser, please visit offices.usda.gov.
Learn more about our Urban Service Centers . Visit the Risk Management Agency website to find a regional or compliance office or to find an insurance agent near you.
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Produce Farm Business Plan
Start your own produce farm business plan
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens (MGSG) is an exciting new company that meets an unsatiated need for quality salad greens. The close proximity to Eugene ensures a steady flow of customers. MGSG is a start-up grower and distributor of exotic salad greens for restaurants and individual consumers. MGSG is located in Blue River, Oregon and serves the southern Willamette Valley. MGSG’s objectives are to develop a product-based company whose goal is to exceed customer’s expectations, increase production efficiency by 10% a year, and lastly, and develop a sustainable farm business, able to survive off their cash flow.
MGSG will sell a spring mix of salad field greens. These greens will include but are not limited to: red leaf, arugula, radicchio, mustard greens, endive, and chicory. These greens are grown for use in salad mixtures, purchased by the end consumer as well as by restaurants who then serve it to their patrons.
MGSG has decided to target two distinct market segments, individual customers and restaurants. The individual customers will purchase greens from MGSG at the Tuesday and Saturday Farmer’s Market. This segment is growing at 12% and has 12,000 potential customers. The second segment is local restaurants. This market is smaller at only 28 potential customers, but is more consistent in demand throughout the year.
Competitive Edge
MGSG has two competitive edges that will help them maintain strong growth rates, increasing their market penetration. The first edge is quality. MGSG prides themselves on the high quality of exotic salad greens. Greens that do not meet MGSG high standards of quality are rejected as imperfects and go to a not-for-profit food bank. MGSG’s second competitive edge is their flexibility. The entire farm has been set up to allow them to change crops or scale existing crops to meet demand. This is highly unusual as most farms are unable to change crops mid year.
MGSG is led by Heidi Ponic. Heidi initially got her start in growing while working at a greenhouse. After college, Heidi went to work for a large grass seed company. This experience is what solidified Heidi’s desire to continue working in an agricultural capacity. Soon after her experience at the Willamette Seed Company she decided to enroll in Oregon State University’s Master of Horticulture Program. Heidi’s Masters provided her with requisite detail and skills to develop her own farm business.
1.1 Objectives
The objectives for the first three years of operation include:
- To create a product-based company whose goal is to exceed customers’ expectations.
- To increase the efficiency of our production by 10% a year.
- To develop a sustainable farm, surviving off its own cash flow.
1.2 Mission
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ mission is to provide the highest-quality salad greens. We exist to attract and maintain customers. When we adhere to this maxim, everything else will fall in to place. Our services will exceed the expectations of our customers.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens, soon to be located in Blue River, OR, is a grower and seller of exotic salad field greens. MGSG grows a wide variety of field greens including red leaf, arugula, radicchio, mustard greens, endive, and chicory. MGSG sells the greens both at farmer markets as well as direct to restaurants.
The business will be based out of Heidi Ponic’s home. The office will be within her home and the greenhouse will be on her adjoining 20 acres of land.
2.1 Company Ownership
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens will be a sole proprietorship with Heidi Ponic as the founder and owner. Heidi will be funding the business with a $50,000 investment of her own. An additional $10,000 will be invested by family member O.G. Tylthe with exit/repayment initially scheduled for year five.
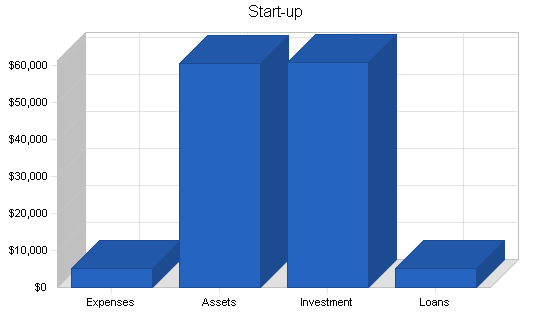
2.2 Start-up Summary
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ start-up costs will include all the equipment needed for the home-based office, the construction of the greenhouse and all the necessary equipment, and other essentials for growing.
The home office equipment will be the largest chunk of the start-up expenses. This equipment includes a computer system, fax machine, office supplies, cellular phone, and pager. The computer should have at least a 500 megahertz Celeron/Pentium processor, 64 megabytes of RAM (preferably 128), 6 gigabyte hard drive, and a rewritable CD-ROM for backing up the system. The home office will also require a few pieces of furniture such as a desk, chair, and book shelf to transform a standard room into an office. Lastly, an additional land phone line will be required.
The greenhouse will need the following equipment: a 25′ x 100′ greenhouse structure made out of poly carbonate, a ventilation system, a heater, a mister system, supplemental lighting, fertilizer injector, pruners, pots, trays, soil, seeds, and assorted chemicals.
Please note that of the $25,300 of long-term assets, $20,000 will be depreciated straight line for 27.5 years (real estate) and the remaining $5,300 will be depreciated on a seven year straight-line schedule.
MGSG will sell a spring mix of salad field greens. These greens will include but are not limited to: red leaf, arugula, radicchio, mustard greens, endive, and chicory. These greens are grown for use in salad mixtures, purchased by the end consumer as well as by restaurants who then serve it to their patrons. While the greens are washed at the farm, they are not certified washed and the patrons are told to wash them an additional time.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
MGSG will be focusing on two distinct users of greens, individual consumers, and restaurants. The consumer market is seasonal so we will have production shifts during the consumer off season and all of the production will go toward wholesale restaurant distribution. During the spring and the summer MGSG will be serving both the consumer markets through farmer market stands and the restaurants through direct distribution.
4.1 Market Segmentation
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens has two distinct customers:
- Individual Consumers . This group of people buy exotic salad greens because they have a more sophisticated pallette. Average Americans have been raised on iceberg lettuce and this is their green of choice (unfortunately). When people from this class get a little “crazy” they might even try romaine lettuce. These people are typically unsophisticated or unadventurous in terms of culinary habits. These are NOT the people MGSG serves. MGSG is going after people that appreciate healthier, tastier alternatives to the standby of iceberg lettuce. This group of consumers is more likely to make their own meals instead of going out, appreciates fine dining, and generally is from a higher socio/economic class. Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ field greens are more expensive than choices like iceberg or romaine, therefore one can conclude that the consumer typically makes more money if they are willing to pay significantly more for their salad greens, and second, people with more sophisticated palates typically are more educated.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Restaurants . Not all restaurants use exotic field greens mixes, generally it is a restaurant of fine dining that serves the finer greens. To be even more specific, it is typically an adventurous American or nouveau cuisine restaurant as opposed to a nicer French or German restaurant that appreciates the exotic field greens mix. For what ever reason (probably attributable to demand of their customers), the French and German restaurants, even the finer ones tend to serve “peasant greens.” The restaurants are a year round customer which is helpful to balance the seasonal demand of individual consumers (group 1 above). Another advantage of having the restaurants as a customer is that even though they get a better price, MGSG has a long term contract with them which helps out in terms of stability.

4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ target market segment strategy is fairly easy. Our two different customer groups purchase from two distinct locations so it is quite easy to target them individually.
Individuals . These customers will be buying MGSG products from the different farmer markets located in Eugene, OR. The main one is “The Farmers Market” held downtown twice a week in the spring, summer, and the early autumn. This market gets quite a bit of traffic because there is a nice selection of different farmers and products and it is in a central location in the heart of Eugene. Additionally, there are several other smaller farmer markets that exist in outlining communities. By setting up a booth in these markets, there is already a steady flow of interested customers. There obviously is a fee to set up a stand, but what you get for the fee is all of your marketing taken care of and a line of customers. In addition to individuals frequenting the farmer markets, some restaurants will go there as well. This occurs when a restaurant needs certain ingredients but did not have the time to order it in advance.
Restaurants . MGSG will target these customers by introducing MGSG and their products to the restaurants through meetings with the buyers at each restaurant. There are about 25-30 different restaurants in Eugene that use field greens in their salad and MGSG intends to approach these to form long-term relationships.
4.3 Industry Analysis
There are three different types of competitors that MGSG faces:
- Supermarkets . These stores sell a salad greens mix to consumers. The advantage of the supermarket is convenience. There are many supermarkets around the city and they are open many hours during the day. Their disadvantage is price and quality. The quality and variety lower than the standards set by the offerings of MGSG and other similar local farmers. The cost is higher, usually 15% more.
- Similar local farmers . These are very similar operations to MGSG, sometimes larger and sometimes smaller. There appears to be room in the market for multiple farmers as most of the farmers sell out their products each day at the farmer markets.
- Large distributors . An example of this would be Food Service of America (FSA) which buys a wide variety of products and quality of produce from farmers and distributes them to restaurants. The produce is not usually local, and is a few more days older from the field compared with the local farmers. The price is comparable and the quality can be comparable, but not necessarily. The disadvantage of a food distributor is the lack of flexibility relative to a local grower when serving local customers.
Buying patterns are based on the customer’s desires. What is meant by this is that lower-end restaurants (or at least restaurants that are less concerned about quality) will not bother to get greens from local farmers, there is no need for them to. This pattern is similar for the individuals. There are some individuals that are content with the offerings from supermarkets. There are others that appreciate the difference in quality and are willing to schedule a trip to the farmers market to meet their weekly needs.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
MGSG will be aggressively courting the farmer markets to ensure the ability to have a booth at the markets. Additionally, MGSG will be aggressive in going after the local restaurants that have a consistent need for the greens. Through an assurance of top-shelf service and superior customer service and reliability, MGSG will continue to grow its number of clients.
5.1 Competitive Edge
Mixed Greens Salad Gardens’ competitive edge has two main aspects: quality and flexibility.
- Quality . While the quality of the other local farmers is quite good, Heidi’s extensive educational background and practical experience provides her with tools to create a superior product. Heidi is a perfectionist and her striving for perfection will lead MGSG to developing a product that will be a notch better than the competition.
- Flexibility . With MGSG being both small and local in nature, it will be able to be flexible in meeting customer’s demands. For instance, if a local restaurant has customers that prefer more arugula in their salad mix, MGSG can rapidly shift production to meet the needs of that customer. Most of the farmers, and all of the distributors, typically have their production schedules set up for maximum yield and are unable to modify crop production very much. Heidi is less concerned about maximizing yield, she is more concerned with pleasing the customer. She believes, rightfully so, that talking care of the customer is the most important thing.
A combination of quality and flexibility will create a sustainable competitive advantage that will allow MGSG to succeed.
5.2 Sales Strategy
MGSG’s sales strategy will be based on visibility, consistency, and strategic relationships.
- Visibility . MGSG will need to generate visibility that sets them apart from the other local farmers that sell at the market. This in part will be done through the use of a colorful, distinct booth set-up that stands out among the other farmers. This visibility will create recognition for MGSG. This is important because the produce of the different farmers appears to be the same. The differences are discovered upon tasting the produce in your home. If MGSG stands out in terms of the booth appearance, the repeat customer will more easily make the connection between the unusual booth and MGSG’s product.
- Consistency . In addition to product consistency, MGSG will have consistency in regards to their presence at the farmer markets. It is much easier to build awareness and loyalty if people can reliably expect to see MGSG every week in the same place.
- Strategic relationships . This will be the key for restaurant sales. As stated before, restaurant sales are a consistent income that help reduce the seasonality of MGSG’s sales. Forming mutually beneficial, strategic partnership will be of upmost importance for building a good revenue base.
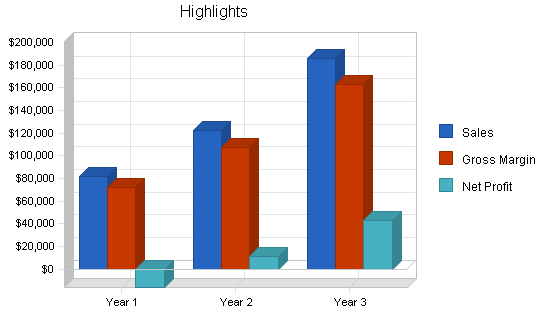
5.2.1 Sales Forecast

5.3 Milestones
MGSG will have several milestones early on:
- The end of the consumer season and the ramping up of the restaurant supply cycle.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Heidi Ponic, founder and owner, first became interested in growing vegetables at the age of five. Heidi pursued her love for plants by obtaining a biology degree at the University of Washington. Throughout her last three years at Washington, she worked in a greenhouse that grew many different types of annuals. Upon graduation, Heidi went to work for a large grass seed manufacturer. Although the growing of grass seed proved to be far less interesting then most other plants, she was determined to get management experience, a skill set that she lacked. After two years at Willamette Seed Company, she enrolled in Oregon State University’s Masters of Horticulture program.
Having gone through the three years of the Masters program, she realized two things, 1) she needed to create a job/company for herself, 2) she should follow her passion and grow vegetables. These realizations were the final catalyst to pursue her lifelong dream of running her own greenhouse operation.
Heidi’s educational training and her passion creates the ideal combination for an owner of a start-up company.
6.1 Personnel Plan
The staff will consist of Heidi working full time. While the bulk of the time Heidi will spend managing the operation, she will always spend a few hours a week tending to the plants. In addition to all of the general management required for the production of the greens, Heidi will be setting up strategic relationships with local restaurants. Mixed Greens Salad Gardens will have hired two full-time gardeners beginning in the middle of the first month, and will hire a part-time helper by month four. The gardeners will be primarily responsible for the raising of the field greens, while the part-time help will be used to help staff the farmers market booth for the consumer selling of the greens.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following sections will outline the important financial information.
7.1 Important Assumptions
The following table highlights some of the important financial assumptions.
7.2 Break-even Analysis
The Break-even Analysis below indicates the monthly sales needed to break even.

7.3 Projected Profit and Loss
The following table will indicate projected profit and loss. Our losses at start-up are evident, as is the turn of the corner in July when we become profitable.

7.4 Projected Cash Flow
The following chart and table will indicate projected cash flow.

7.5 Projected Balance Sheet
The following table will indicate the projected balance sheet.
7.6 Business Ratios
Business ratios for the years of this plan are shown below. Industry profile ratios based on the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code 0161, Lettuce Farms, as part of Vegetables and Melons, Not Elsewhere Classified, are shown for comparison.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
VEGETABLE FARMING BUSINESS PLAN: 2023 Template (Updated)
- by Folakemi Adegbaju
- August 9, 2023
- No comments
- 8 minute read

Table of Contents Hide
Why do i need a vegetable farming business plan, #1. executive summary, #2. company description, #3. market research, #4. competitive analysis, #5. marketing plan, #7. management team, #6. financial plan, #8. explain your funding request, #9. appendix , a vegetable farming business plan template, when do you need a vegetable farming business plan, which vegetable farming method is most profitable, is vegetable farming profitable, how long does managu take to mature, how long does mchicha take to grow, how do you plant mchicha seeds, when can i transplant amaranth, final thought, what is the most profitable type of farming, what crop is in highest demand, what is britain's favourite vegetable.
Have you ever considered starting a vegetable farming business? Will you take advantage of the chance to try it out, or will you believe that this venture won’t be successful? It’s possible that many of us can’t even imagine doing this kind of work or running this kind of business. If you know what you’re doing and have a strong vegetable business plan, this form of business can also be highly lucrative. Those who have done this before will agree that it requires time, patience, money, luck, and, of course, a business plan.
Download the business plan template for your vegetable farming business
What Is a Vegetable Farming Business Plan?
A vegetable farming business plan is a thorough road map for the expansion and development of your small business. It also expresses who you are, what you intend to do, and how you intend to go about doing it. Also, it aids in luring talent and investment.
But keep in mind that a business concept or idea is not the same as a business plan.
It’s important that you know that your business’s growth or development depends on your plan. We’ve listed below some of the reasons why you need a vegetable farming business plan for your vegetable farm.
#1. Clarity
Writing down your business concept and plan will make it easier for you, possible investors, and other stakeholders to see them.
#2. Depth of Knowledge
Writing a vegetable farming business plan necessitates serious consideration of the market and how the company might function there.
#3. Organization
The goals and objectives of your vegetable farming business should be made apparent in a vegetable farming business plan, along with the timelines for achieving them. This will increase the likelihood that the company will stay organized and on course, and it will make it easier for you to evaluate the company’s development.
#4. Forecasting of financial data
When ideas are discussed, they frequently sound good, but when precise budgets and cash flow forecasts are created, this frequently changes.
Indicating profit or loss and what would happen if external conditions changed would be possible with the aid of financial forecasting (sensitivity analysis).
#5. Accountability
Ideas and strategies can be utilized to track progress and hold oneself accountable as the business develops once they have been included in the business plan.
#6. Evaluating
It is possible to evaluate the vegetable farming business plan to determine whether expectations were met or surpassed. By doing this, the strategy in the business plan can be modified and updated.
As you know, vegetable farms that have a written business plan have a far higher chance of success than those that don’t. Your vegetable farming business will also flourish with the support of a solid vegetable farming business plan, which will also enable you to foresee potential obstacles. Why not start planning for your farm by taking a look at our vegetable farming business plan template today?
How to Write a Vegetable Farming Business Plan
The anxiety of starting your vegetable farming business is normal, but do you know how to write a vegetable farming business plan? Writing a perfect business plan is a crucial part of your business. It accelerates the growth of your business. Writing one might seem so confusing and tiring, especially if it’s your first time.
You can get the business plan template for your vegetable farming business or follow these steps to write your plan:
The executive summary condenses all the crucial details about your company into a manageable amount of text. Typically, an executive summary is one page or fewer. It provides a broad overview of everything and summarizes the remaining parts of your vegetable farming business plan. It is, in essence, a summary of your company.
Despite the fact that it is the first section in the plan, write your executive summary last so you can summarize the most important points from the previous sections.
Your company description in a business plan includes the following three components:
- Mission statement
These components provide context for the larger picture in your vegetable farming business plan, allowing investors to understand the driving force behind your organization so that the goals also make sense.
The next stage is to describe your ideal potential consumer and the current and future potential market size. Personas, another name for target markets, identify demographic data.
Here are some of the data you can use for your market research:
For a deeper understanding of your customer’s requirements and wants, you might even map their entire customer journey.
The first step in conducting competitive research is to find other businesses that are already active in the market you wish to enter. It may seem intimidating to set aside enough time to research every prospective rival you may have, yet doing so can be highly beneficial.
After you’ve determined who your biggest competitors are, respond to the following further questions:
- Where do they spend money on marketing?
- What kind of media attention do they receive?
- How effective is their customer support?
- What are their pricing and sales tactics?
Consider what makes you unique for a while. Be prepared to describe the customer pain issues your vegetable farm will address if your idea is actually innovative. If there isn’t any direct competition for your business, look at other organisations that offer comparable goods or services.
Your marketing plan could mean the difference between gaining a lot of business and experiencing explosive growth. Your business plan’s growth tactics are a crucial component.
Here are some ways you can carry out your marketing plan to get people familiar with your vegetable farm:
- Word of mouth
- Reviews and ratings
- Local Google Ads
- Social media
Your vegetable farm’s management team determines how successful it is. Describe each member of your team and why they are important to the realisation or expansion of your business idea. In this section of your vegetable farming business plan, be sure to highlight the credentials and experience of your management team’s top performers.
Your business might not have financial information, financial statements, or thorough reporting if you’re just getting started. You must still create a budget and a financial plan , though.
If you’re looking for investors and your business is established, make sure to include:
- Income statements
- Profit and loss statements
- Cash flow projections
- Balance sheets
Be as realistic as you can when estimating the financial requirements of a small business. If you don’t want to give a specific number, you can give a range of numbers. Include both the best-case and worst-case scenarios, though.
It’s possible that you will sell equity to raise money in the first few years of operation because a new business doesn’t have a history of making profits. Equity denotes ownership; thus, when you sell equity to raise money, you are effectively selling a stake in your business.
Finally, put together an appendix that is well organized with all the information readers will need to complement your plan.
Why not download our vegetable business plan template to help you write an effective business plan for your business? Download here!
A vegetable farming business plan for your company requires not only following the aforementioned steps but also making use of a template checklist. Also, the essence of a checklist is to help you keep track of all the necessary processes you need to achieve while starting your new business.
However, we advise you to download our vegetable farming business plan template to make sure you follow the right steps while writing your vegetable farming business plan. Here is the vegetable farming business plan template checklist:
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market research
- Organisation and management
- Product or service.
- The marketing and sales strategy
- Funding requests
- Financial forecasts
- Appendix
Use a vegetable farming business plan template to create a strong vegetable farming business plan even if you don’t anticipate looking for funding right away. Download our vegetable farming business plan template today!
Your vegetable farming business plan is necessary at every stage of your vegetable farming development. Here are some of the times you might need it:
- Seeking funding, investments, or loans
- Searching for a new partner or co-founder
- Attracting, hiring, and retaining top talent
- Experiencing slow growth and needing a change
There are a lot of vegetables, but not all are profitable. Here are some vegetables that are profitable and you can venture into:
- Microgreens.
- Goji Berries.
Yes, it is. As much as you are determined and put in hard work.
Due to its quick maturation duration of up to 60 days and its good harvest period of up to 4 months, managed farming would be a great addition to your farm. Due to the fact that the majority of urban dwellers regularly eat green vegetables as part of their meals, there is also a ready market there.
While the tall type takes between 70 and 120 days to reach maturity, the short variant does so in 45 to 60 days. They are advised for regions with low and high rainfall. It is attacked by a few pests and diseases and needs little care. It can endure severe drought once it’s established.
From mid-spring to early summer, spread seeds in straight rows, just covering them with earth. Up until the seedlings emerge, keep the soil moist. Till the plants are 4 inches (10 cm) tall, manually weed the area, progressively spacing the plants 18 inches (46 cm) apart. Most summer weeds will be driven out by the plants as they develop.
You can transplant your seedlings once they are about three inches tall and their roots are showing through the rock wool cube. Remember that amaranth will produce at its peak in the broad sun (i.e., at least six hours of direct sunlight).
If you don’t make a plan, you’re planning to fail. A well-thought-out business plan is essential to the success of any company, as it serves as a road map for success, a source of inspiration for personnel, and a tool for reducing financial backers’ concerns and maximizing returns. A well-thought-out vegetable farming business plan will give you peace of mind and put you on the path to success before you even launch your vegetable farm.
Apiculture. As a new business, apiculture is among the top in the agricultural industry. Commercial beekeeping farms have mushroomed around the world as a result of the global increase in demand for honey and its by-products and the global decrease in the supply of natural honey.
Cash crops are valued relative to other commodities, but from an absolute value viewpoint, cannabis is the most lucrative crop in the world. Rice, then corn, and finally wheat come next.
Tomatoes are now more popular than potatoes in Britain. Potato sales fell by roughly 10% in 2022, falling further behind the surging demand for tomatoes.
Related Articles
- Farm Business Tenancy: Guide & Overview
- POULTRY FARM BUSINESS PLAN: Template and Guide
- SMALL FARMING BUSINESS PLAN: Simple Steps to Write One!!!
- FARMING BUSINESS PLAN: Template & Best Start-Up Guide
Folakemi Adegbaju
She is a passionate copywriter and a good listener
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CONSULTING BUSINESS PLAN: 2023 Template & Tips
Property development business plan: 2023 uk template & guide.
We noticed you're visiting from Netherlands. We've updated our prices to Euro for your shopping convenience. Use Pound sterling instead. Dismiss

How To Write a Business Plan for Vegetable Farming in 9 Steps: Checklist
By henry sheykin, resources on vegetables farming.
- Financial Model
- Business Plan
- Value Proposition
- One-Page Business Plan
Are you thinking about starting a vegetable farm? With the increasing demand for locally-sourced, organic produce, the vegetable farming industry has shown steady growth in recent years, with a 5.4% increase from 2015 to 2019.
However, starting a successful vegetable farm requires careful planning and preparation. In this article, we will provide a checklist of 9 essential steps to help you write a successful business plan for your own vegetable farming venture.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your farm is sustainable, efficient, and profitable, while also providing high-quality, healthy produce to your local community. So let's get started!
Research The Market Demand For Vegetables In The Local Area
Before starting a vegetable farming business, it’s important to understand the demand for vegetables in your local area. This research will help you determine the types of vegetables that are in high demand and the best time of year to grow them. The following are important factors to consider when researching the local market demand for vegetables:
- Identify the target market: Conduct research on the types of customers in your area that are most likely to purchase vegetables from a local farm. This may include local restaurants, grocery stores, or individuals who are health-conscious or environmentally conscious.
- Assess the competition: Research other vegetable farms in the area to determine what types of vegetables they are growing and when they are available. This will help you identify gaps in the market or areas where you can differentiate yourself from your competition.
- Analyze trends: Stay up-to-date on food and farming trends in your area, such as an increased focus on organic or sustainably-grown vegetables.
- Understand the seasonality: Determine the best times of the year to grow and sell specific types of vegetables in your local area. This will help you plan crop rotations and ensure that you are providing vegetables when there is high demand.
- Connect with local farmers' markets or community-supported agriculture programs (CSAs) to gauge the interest in locally-sourced vegetables.
- Consider conducting surveys or focus groups with potential customers to gain a deeper understanding of their needs and preferences.
- Use social media and online tools to track conversations and posts related to local food and farming trends.
By thoroughly researching the local market demand for vegetables, you can ensure that your business is well-positioned to meet the needs of your customers, differentiate yourself from your competition, and ultimately succeed in the vegetable farming industry.
Determine The Specific Type Of Vegetables To Be Grown And The Appropriate Season For Each.
After researching the local market demand for vegetables, the next step in starting a vegetable farm is to determine which specific types of vegetables to grow and the appropriate season for each. This is an essential step in creating a business plan and ensuring the success of the farm.
1. Research the demand for specific vegetables. One of the most important factors to consider when choosing which vegetables to grow is whether there is a high demand for them in the local area. Talk to local chefs, restaurateurs, and grocery store owners to get a better idea of what types of vegetables are currently in demand.
2. Consider the climate and soil conditions. Some vegetables grow better in certain types of soil and thrive in specific climates. Research which vegetables will grow well in the local climate and soil conditions to ensure a successful harvest.
3. Determine the appropriate season for each vegetable. Each vegetable has an ideal season for planting and harvesting. Research the planting and harvesting seasons for each vegetable to ensure that the farm produces the highest quality and quantity of each crop.
- Consider planting a variety of vegetables to appeal to a wider customer base.
- Research the nutritional value of each vegetable to educate customers and boost sales.
- Consider partnering with local chefs or restaurants to create a demand for specific vegetables.
By determining the specific type of vegetables to be grown and the appropriate season for each, vegetable farmers can ensure a successful harvest and increased profitability. Doing thorough research and considering the local market demand, climate, soil conditions and the appropriate season for each vegetable can help farmers create a strong business plan and grow their business sustainably.
Identify The Necessary Equipment, Supplies, And Labor Needed To Manage The Farm Effectively.
Starting a vegetable farm will require a variety of equipment, tools, supplies, and labor to manage the operation successfully. Here are some of the essential items and personnel that you will need:
- Tractors and implements: Tractors and implements such as plows, harrows, and cultivators are essential for planting and cultivating the crops. You may also need a mower or a hay baler for cutting hay or straw for mulching or animal feed.
- Hand tools: Hand tools such as hoes, shovels, trowels, and pruners are needed for manual farming tasks such as weeding, planting, pruning, and harvesting.
- Irrigation system: You will need an irrigation system that uses drip or sprinkler technology to water the crops efficiently.
- Greenhouse or cold frames: A greenhouse or cold frames will enable you to extend the growing season and protect the crops from adverse weather conditions, pests, and diseases.
- Farm vehicles: You may need a pickup truck or a van for transporting the crops and supplies to the market or the distributor.
- Fertilizers and pesticides: Organic fertilizers and pesticides are essential for maintaining soil fertility and crop health. You may also need natural predators such as ladybugs or bees to control pest populations.
Labor: The size of your farm will determine how many workers you need and what tasks they perform. You may need:
- Farm manager: A farm manager is responsible for overseeing the daily operations of the farm, managing the workers, and coordinating with the distributor, customer, and regulatory agencies.
- Farm laborers: Farm laborers are responsible for manual tasks such as planting, weeding, harvesting, and packing.
- Specialists: You may also need specialists such as agronomists, soil scientists, pathologists, or entomologists for consultation, research, and advice.
- Interns: Interns or apprentices may be available for training and assistance under academic or vocational programs.
Identifying the necessary equipment, supplies, and labor for your vegetable farm is crucial for estimating the startup costs and creating a budget for the operation. You can research suppliers, brands, and prices online or in person, and evaluate them based on quality, durability, and affordability. You can also plan for the storage, maintenance, and insurance of your assets to ensure their longevity and efficiency.
Assess The Availability And Quality Of Water Sources In The Area.
Water is a crucial resource for Vegetable farming, and assessing its availability and quality in the area is paramount to successful operations. Before venturing into vegetable farming, it is important to: assess the availability of water in the area and ensure that there is an adequate supply to meet the farm's needs throughout the growing season. This should be backed by checking for the irrigational methods available in the area.
Tips to assess water availability:
Consult with local water boards or agricultural extension agencies to investigate the availability of water sources and the existing laws regulating their usage.
Check historical weather patterns, including rainfall and droughts, to gauge the reliability of water sources in the area. It’s important to have back-up sources in case of an unpredictable season.
Consider your options for water storage and retention, including wells, rainwater harvesting, and other methods.
Water quality is another critical factor that every farmer should take into account. It is not only important for the crops but also for the health and safety of consumers. It is, therefore, essential to assess the quality of the water sources in the area. Perform tests to check for impurities and contaminants such as heavy metal residues, nitrates, and pesticides, which may affect crop yield and compromise food safety.
Tips to assess water quality:
Take water samples and have them analyzed by an accredited laboratory to identify any potential contamination.
Monitor the quality of the water sources regularly, especially during the growing season.
Implement appropriate water management practices to minimize the risk of contamination, such as ensuring the use of safe irrigation methods.
Assessing the availability and quality of water sources in an area may be a lengthy and rigorous process, but it is a crucial undertaking. It guarantees a smooth operation of the vegetable farm and ensures fresh, healthy and safe produce for the local market.
Check The Soil Quality And Suitability For Growing The Chosen Vegetables.
Soil quality is one of the most critical factors to consider when starting a vegetable farm. The quality of soil can determine the success of your farm, as well as the health of your plants and vegetables. In order to determine the suitability of the soil for growing your chosen vegetables, there are several factors to consider.
- Before starting, ensure that you understand the nutritional requirements of your chosen vegetables and the specific soil conditions that are necessary for growth.
- Keep in mind that soil nutrient levels can vary depending on the location and previous use of the land, so it may be necessary to test the soil before planting.
- Consider the texture of the soil, as well as the level of compaction, drainage, and permeability to water and air.
The texture of the soil refers to the size and distribution of the soil particles, and can impact drainage and nutrient retention. Sandy soils are well-drained but tend to retain less nutrients, while clay soils are nutrient-rich but can be poorly drained. Loamy soils, which are a balance of sand, silt, and clay, are considered the ideal growing medium for most vegetables.
At the same time, the level of compaction in the soil can affect root growth and water uptake. Highly compacted soils can lead to poor root development, which can compromise the overall health and yield of your vegetables. Similarly, soils that have poor drainage or are susceptible to waterlogging can impede the growth of your crops, leading to reduced yield and poor quality.
The pH level of the soil is another important factor to account for, as it can influence the nutrient uptake and overall health of plants. Ideally, the pH level of soil should be between 6 and 7.5, but this can vary based on the specific requirements of your chosen vegetables.
When checking the soil quality, it is also important to assess its suitability for organic farming. Organic farming requires soil that is free of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, and has good microbial activity. If the soil has been previously used for conventional farming practices, you may need to take steps to restore its natural properties and promote microbial activity.
Overall, checking the soil quality and suitability is critical to the success of your vegetable farm. By assessing the texture, drainage, compaction, pH level, and suitability for organic farming, you can ensure that your soil is well-prepared for planting and that your vegetables have the best possible chance of thriving.
Evaluate The Climate And Weather Patterns In The Local Area And How They May Impact The Farm.
Climate and weather patterns have a significant impact on vegetable farming. Knowing the climate of the local area is crucial to ensure that the crops will thrive, and yield will be optimal. Evaluating the weather patterns helps plan crop cycles and take precautions for potential adverse weather conditions.
Getting Information on the Climate and Weather Patterns: By collecting data on the climate and weather patterns in the local area, farmers can determine if it is suitable for certain crops. This can be done by consulting with the local weather station, agricultural offices, and even fellow farmers in the area.
- Use the data from local sources for accurate climatic information, as weather can vary within short distances.
- Consider factors like temperature, light, humidity, precipitation, and wind patterns.
- Use a spreadsheet or a farming app to keep track of weather patterns to analyze how it can affect crop growth.
Impact of Climate and Weather Patterns: Understanding the local climate and weather patterns can help farmers plan with the appropriate crops for each season. Warmer climates, for example, may be suitable for fast-growing crops like tomatoes and peppers, while cooler climates, with less sunlight, is more ideal for leafy greens.
Additionally, it is essential to consider the potential risks of extreme weather conditions like frost, drought, heavy rain, flooding, or storms. In such situations, farmers must take preventive measures, like investing in climate-control equipment and structure, seeding crops that are drought-resistant, crop rotation, or adjusting plant varieties.
- Plan crop rotations and planting cycles to predict weather patterns and ensure crops will mature before harmful weather conditions.
- Install weather tracking systems and alerts to get real-time notifications for impending weather conditions.
- Consider investing in climate-controlled systems like greenhouses, hydroponics, and drip irrigation systems for consistent and quality yields.
Conclusion: A farmer seeking to cultivate quality produce must evaluate the climate and weather patterns of a local area before starting a vegetable farm. By collecting and analyzing data on the local climate and weather patterns, the farmer can select the right type of crops and invest in crop cycles and preventive measures to avoid potential weather risks.
Research The Federal And State Regulations And Permits Required For Vegetable Farming
Before starting a vegetable farm, it is imperative to be aware of the federal and state regulations and permits required for vegetable farming. These regulations are in place to ensure that farmers follow the guidelines for producing high-quality and safe food for the consumers.
The regulations and permits for vegetable farming vary by state, so it is essential to research and comply with the regulations in the area where the farm is located. The following are some of the regulations and permits to consider:
- The USDA's National Organic Program (NOP) certification: This certification is required to use the organic label on products. Farmers must comply with the NOP standards to be eligible for certification.
- The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): The FSMA regulates the growing, harvesting, packing, and holding of fruits and vegetables. It is essential to be aware of these regulations to ensure the safety of the product.
- The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The EPA regulates the application of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides. Farmers must use these products according to the guidelines to avoid potential health hazards.
- The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): The OSHA regulates the safety of the workers on the farm. It is crucial to provide appropriate safety equipment and training to the workers to avoid any accidents.
- The Department of Agriculture: The department may require permits for water usage, permits for land use, and other permits depending on the state's regulations.
- Attend workshops and seminars to stay up-to-date with the changing regulations.
- Consult with a legal advisor to ensure compliance with regulations and permits.
- Keep accurate records of the farm operations to ensure compliance with regulations.
Not complying with regulations may result in fines, penalties, and damage to the farm's reputation. Therefore, it is essential to be aware of the regulations and permits required for vegetable farming. Complying with these regulations assures consumers of the safety and quality of the products and increases the farm's credibility.
Estimate The Startup Costs And Create A Budget For The Operation.
The first step in starting a vegetable farm is to determine the estimated startup costs and create a budget for the operation. This is crucial to understand the financial requirements of the business and to prepare for potential obstacles that may arise in the future.
Here are some tips to get started:
- Consider all the costs that will be involved in the operation, including land, equipment, seeds, irrigation systems, labor, insurance, and marketing.
- Use tools like farm budget calculators to estimate expenses and determine how much funding you need to acquire before starting the farm.
- Find out if there are any grants or loans available for starting a small business or a farm. The USDA or your local bank may be able to help you with financing.
- Consult with other farmers in the area to get an idea of how much it will cost to run a vegetable farm. You can also join a farmer’s association to get more insight into industry standards and best practices.
Once you have a better understanding of the start-up costs, you can create a budget for the operation. It should include every expense category that you determined in the previous step.
Make sure to allocate funds for unexpected expenses and emergencies . It is important to have a buffer in place to cover any unforeseen costs that may arise, such as equipment breakdowns or natural disasters.
You should also consider your cash flow requirements and how you will finance the operation until it becomes profitable. You may need to secure a loan or line of credit to keep the business running until it starts generating revenue.
Finally, regularly review and update your budget to stay on track and avoid overspending. Keeping track of your expenses and income will help you manage your finances effectively and identify areas for improvement.
Estimating the startup costs and creating a budget for the operation may seem intimidating. However, it is a necessary step in starting a successful vegetable farm. By following these tips, you can better understand the financial requirements and develop a sustainable plan for the future.
Determine The Potential Sources Of Funding Or Financing For The Farm.
Starting an organic vegetable farm requires significant capital investment. Therefore, you must figure out various ways to finance your business idea. Here are some potential sources of funding or financing for your farm:
- Personal savings: The most straightforward approach to financing is to use your own funds. This method eliminates the need for external financing and the associated interest payments. Your personal savings can provide a solid financial foundation for the farm and help you demonstrate to potential investors that you are committed to your venture.
- Friends and family: Another option is to seek financial support from friends and family. This approach can provide you with a more flexible repayment plan than traditional loans. However, to avoid conflicts in personal relationships, ensure that such an arrangement follows established guidelines, including signed contracts and repayment schedules.
- Traditional business loans: Lending institutions offer various business loans to entrepreneurs. However, applying for a business loan requires adequate collateral and a good credit history, which can be challenging for startup companies. Traditional business loans can also come with high interest rates and strict repayment schedules.
- Grants: Grants are an excellent option for startup companies committed to sustainable and environmentally conscientious farming practices. Many non-profit organizations and government agencies offer grants to support sustainable agricultural development.
- Crowdfunding: Crowdfunding platforms have become an increasingly popular way for startups to raise capital. Crowdfunding allows entrepreneurs to solicit contributions from small donors interested in supporting their projects. Crowdfunding offers flexibility since it does not require a personal credit history or significant collateral.
- Investor financing: Finding investors willing to finance your farm is another possibility. In exchange for funding, investors will demand partial ownership of the company and expect a share of the farm's profits. To find investors, consult with trade groups, venture capitalists, or private investors. However, investors will likely require substantial research, planning, and an impressive business plan.
- When exploring financing options, consider seeking advice from financial advisors or attorneys to ensure you make informed decisions.
- Be prepared to articulate the farm's unique selling proposition and demonstrate its potential profitability when seeking funding.
- When establishing an equity relationship with investors, consider the long-term implications of sharing decision-making authority.
- Create a comprehensive business plan to present to potential investors or lenders. A solid business plan should include income and expense projections, market research, funding needs, and an overall business strategy.
In conclusion, start by exploring funding options and understanding each lender or investor's terms and conditions. Choose the most suitable financing or funding source and recognize that your farm's financial stability is an ongoing effort. Managing your cash flow and staying on top of payments can help ensure long-term success.
Starting a vegetable farm requires proper planning and research. By following the checklist of 9 steps, you can create a comprehensive business plan that will help you succeed in the competitive industry of vegetable farming. Remember to prioritize sustainability, quality, and customer service, and educate your local community about the benefits of locally-sourced, organic produce.
- Research market demand
- Determine types of vegetables and appropriate season
- Identify necessary equipment, supplies, and labor
- Assess water sources and soil quality
- Evaluate climate and weather patterns
- Research regulations and permits
- Estimate startup costs and create a budget
- Determine potential funding sources

$169.00 $99.00 Get Template
Related Blogs
- Starting a Business
- KPI Metrics
- Running Expenses
- Startup Costs
- Pitch Deck Example
- Increasing Profitability
- Sales Strategy
- Rising Capital
- Valuing a Business
- How Much Makes
- Sell a Business
- Business Idea
- How To Avoid Mistakes
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published
How to write a business plan for an organic vegetable farm?

Writing a business plan for an organic vegetable farm can be an intimidating task, especially for those just starting.
This in-depth guide is designed to help entrepreneurs like you understand how to create a comprehensive business plan so that you can approach the exercise with method and confidence.
We'll cover: why writing an organic vegetable farm business plan is so important - both when starting up, and when running and growing the business - what information you need to include in your plan, how it should be structured, and what tools you can use to get the job done efficiently.
Let's get started!
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for an organic vegetable farm?
- What information is needed to create a business plan for an organic vegetable farm?
- What goes in the financial forecast for an organic vegetable farm?
- What goes in the written part of an organic vegetable farm business plan?
- What tool can I use to write my organic vegetable farm business plan?
Being clear on the scope and goals of the document will make it easier to understand its structure and content. So before diving into the actual content of the plan, let's have a quick look at the main reasons why you would want to write an organic vegetable farm business plan in the first place.
To have a clear roadmap to grow the business
Small businesses rarely experience a constant and predictable environment. Economic cycles go up and down, while the business landscape is mutating constantly with new regulations, technologies, competitors, and consumer behaviours emerging when we least expect it.
In this dynamic context, it's essential to have a clear roadmap for your organic vegetable farm. Otherwise, you are navigating in the dark which is dangerous given that - as a business owner - your capital is at risk.
That's why crafting a well-thought-out business plan is crucial to ensure the long-term success and sustainability of your venture.
To create an effective business plan, you'll need to take a step-by-step approach. First, you'll have to assess your current position (if you're already in business), and then identify where you'd like your organic vegetable farm to be in the next three to five years.
Once you have a clear destination for your organic vegetable farm, you'll focus on three key areas:
- Resources: you'll determine the human, equipment, and capital resources needed to reach your goals successfully.
- Speed: you'll establish the optimal pace at which your business needs to grow if it is to meet its objectives within the desired timeframe.
- Risks: you'll identify and address potential risks you might encounter along the way.
By going through this process regularly, you'll be able to make informed decisions about resource allocation, paving the way for the long-term success of your business.
To get visibility on future cash flows
If your small organic vegetable farm runs out of cash: it's game over. That's why we often say "cash is king", and it's crucial to have a clear view of your organic vegetable farm's future cash flows.
So, how can you achieve this? It's simple - you need to have an up-to-date financial forecast.
The good news is that your organic vegetable farm business plan already includes a financial forecast (which we'll discuss further in this guide). Your task is to ensure it stays current.
To accomplish this, it's essential to regularly compare your actual financial performance with what was planned in your financial forecast. Based on your business's current trajectory, you can make adjustments to the forecast.
By diligently monitoring your organic vegetable farm's financial health, you'll be able to spot potential financial issues, like unexpected cash shortfalls, early on and take corrective actions. Moreover, this practice will enable you to recognize and capitalize on growth opportunities, such as excess cash flow enabling you to expand to new locations.
To secure financing
Whether you are a startup or an existing business, writing a detailed organic vegetable farm business plan is essential when seeking financing from banks or investors.
This makes sense given what we've just seen: financiers want to ensure you have a clear roadmap and visibility on your future cash flows.
Banks will use the information included in the plan to assess your borrowing capacity (how much debt your business can support) and your ability to repay the loan before deciding whether they will extend credit to your business and on what terms.
Similarly, investors will review your plan carefully to assess if their investment can generate an attractive return on investment.
To do so, they will be looking for evidence that your organic vegetable farm has the potential for healthy growth, profitability, and cash flow generation over time.
Now that you understand why it is important to create a business plan for an organic vegetable farm, let's take a look at what information is needed to create one.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Information needed to create a business plan for an organic vegetable farm
Drafting an organic vegetable farm business plan requires research so that you can project sales, investments and cost accurately in your financial forecast, and convince the reader that there is a viable commercial opportunity to be seized.
Below, we'll focus on three critical pieces of information you should gather before starting to write your plan.
Carrying out market research for an organic vegetable farm
As you consider writing your business plan for an organic vegetable farm, conducting market research becomes a vital step to ensure accurate and realistic financial projections.
Market research provides valuable insights into your target customer base, competitors, pricing strategies, and other key factors that can significantly impact the commercial success of your business.
Through this research, you may uncover trends that could influence your organic vegetable farm.
You may discover that organic vegetable farms are becoming more popular with consumers. This trend could result in your farm having an increased demand for organic produce. Additionally, market research may reveal that there could be a growing interest in locally grown produce. This could potentially create an opportunity for you to expand your customer base by marketing your organic vegetables as locally sourced.
Such market trends play a significant role in forecasting revenue, as they offer valuable data about potential customers' spending habits and preferences.
By incorporating these findings into your financial projections, you can present investors with more accurate information, helping them make informed decisions about investing in your organic vegetable farm.
Developing the sales and marketing plan for an organic vegetable farm
As you embark on creating your organic vegetable farm business plan, it is crucial to budget sales and marketing expenses beforehand.
A well-defined sales and marketing plan should include precise projections of the actions required to acquire and retain customers. It will also outline the necessary workforce to execute these initiatives and the budget required for promotions, advertising, and other marketing efforts.
This approach ensures that the appropriate amount of resources is allocated to these activities, aligning with the sales and growth objectives outlined in your business plan.
The staffing and equipment needs of an organic vegetable farm
As you embark on starting or expanding your organic vegetable farm, having a clear plan for recruitment and capital expenditures (investment in equipment and real estate) is essential for ensuring your business's success.
Both the recruitment and investment plans must align with the timing and level of growth projected in your forecast, and they require appropriate funding.
A vegetable farm might incur staffing costs such as wages for employees, payroll taxes, and insurance. They might also need to cover the cost of equipment such as tractors, harvesting tools, and irrigation systems. Additionally, they may need to invest in organic fertilizers and soil amendments to maintain their organic certification.
To create a realistic financial forecast, you also need to consider other operating expenses associated with the day-to-day running of your business, such as insurance and bookkeeping.
With all the necessary information at hand, you are ready to begin crafting your business plan and developing your financial forecast.
What goes into your organic vegetable farm's financial forecast?
The objective of the financial forecast of your organic vegetable farm's business plan is to show the growth, profitability, funding requirements, and cash generation potential of your business over the next 3 to 5 years.
The four key outputs of a financial forecast for an organic vegetable farm are:
- The profit and loss (P&L) statement ,
- The projected balance sheet ,
- The cash flow forecast ,
- And the sources and uses table .
Let's look at each of these in a bit more detail.
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement for an organic vegetable farm shows how much revenue and profit your business is expected to make in the future.

A healthy organic vegetable farm's P&L statement should show:
- Sales growing at (minimum) or above (better) inflation
- Stable (minimum) or expanding (better) profit margins
- A healthy level of net profitability
This will of course depend on the stage of your business: numbers for a startup will look different than for an established organic vegetable farm.
The forecasted balance sheet of your organic vegetable farm
The projected balance sheet of your organic vegetable farm will enable the reader of your business plan to assess the overall financial health of your business.
It shows three elements: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: are productive resources owned by the business, such as equipment, cash, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: are debts owed to creditors, lenders, and other entities, such as accounts payable (money owed to suppliers).
- Equity: includes the sums invested by the shareholders or business owners and the profits and losses accumulated by the business to date (which are called retained earnings). It is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.

Analysing your organic vegetable farm projected balance sheet provides an understanding of your organic vegetable farm's working capital structure, investment and financing policies.
In particular, the readers of your plan can compare the level of financial debt on the balance sheet to the equity value to measure the level of financial risk (equity doesn't need to be reimbursed, while financial debt must be repaid, making it riskier).
They can also use your balance sheet to assess your organic vegetable farm's liquidity and solvency:
- A liquidity analysis: focuses on whether or not your business has sufficient cash and short-term assets to cover its liabilities due in the next 12 months.
- A solvency analysis: takes and longer view to assess whether or not your business has the capacity to repay its debts over the medium-term.
The projected cash flow statement
A cash flow forecast for an organic vegetable farm shows how much cash the business is projected to generate or consume.

The cash flow statement is divided into 3 main areas:
- The operating cash flow shows how much cash is generated or consumed by the operations (running the business)
- The investing cash flow shows how much cash is being invested in capital expenditure (equipment, real estate, etc.)
- The financing cash flow shows how much cash is raised or distributed to investors and lenders
Looking at the cash flow forecast helps you to ensure that your business has enough cash to keep running, and can help you anticipate potential cash shortfalls.
It is also a best practice to include a monthly cash flow statement in the appendices of your organic vegetable farm business plan so that the readers can view the impact of seasonality on your business cash position and generation.
The initial financing plan
The initial financing plan - also called a sources and uses table - is an important tool when starting an organic vegetable farm.
It shows where the money needed to set up the business will come from (sources) and how it will be allocated (uses).

Having this table helps understand what costs are involved in setting up the organic vegetable farm, how the risks are distributed between the shareholders and the lenders, and what will be the starting cash position (which needs to be sufficient to sustain operations until the business breaks even).
Now that the financial forecast of an organic vegetable farm business plan is understood, let's focus on what goes into the written part of the plan.
Need inspiration for your business plan?
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of business plan templates that you can use to get a clear idea of what a complete business plan looks like.

The written part of an organic vegetable farm business plan
The written part of an organic vegetable farm business plan plays a key role: it lays out the plan of action you intend to execute to seize the commercial opportunity you've identified on the market and provides the context needed for the reader to decide if they believe your plan to be achievable and your financial forecast to be realistic.
The written part of an organic vegetable farm business plan is composed of 7 main sections:
- The executive summary
- The presentation of the company
- The products and services
- The market analysis
- The strategy
- The operations
- The financial plan
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail!
1. The executive summary
The executive summary, the first section of your organic vegetable farm's business plan, serves as an inviting snapshot of your entire plan, leaving readers eager to know more about your business.
To compose an effective executive summary, start with a concise introduction of your business, covering its name, concept, location, history, and unique aspects. Share insights about the services or products you intend to offer and your target customer base.
Subsequently, provide an overview of your organic vegetable farm's addressable market, highlighting current trends and potential growth opportunities.
Then, present a summary of critical financial figures, such as projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
You should then include a summary of your key financial figures such as projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
Lastly, address any funding needs in the "ask" section of your executive summary.
2. The presentation of the company
The second section in your organic vegetable farm's business plan should focus on the structure and ownership, location, and management team of the company.
The structure and ownership part provides an overview of the legal structure of the business, who the owners are and how much each has invested and owns. If you are seeking financing it is important that the reader gets a clear picture of which legal entity is receiving the funds, and who controls the business.
The location part should give an overview of the premises from which the company is operating, and why that location is of particular interest (catchment area, accessibility, amenities nearby, etc.).
When describing the location of your organic vegetable farm, you could emphasize its potential to reach a wide customer base. It may be located in an area with good access to major roads and highways, making it easy for customers to make the trip to your farm. Additionally, the location could be in a region with a growing population, allowing you to take advantage of a larger customer base. Furthermore, the region could have a favorable climate for organic vegetable farming, making it a great place for your farm to thrive.
Finally, you should introduce the management team. Explain each member's role, background, and experience.
It is also important to emphasize any past successes that the members of the management team have achieved, and how long they've been working together, as this will help potential lenders or investors understand why they should trust in their leadership.
3. The products and services section
The products and services section of your business plan should include a detailed description of the offerings that your company provides to its customers.
For example, your organic vegetable farm could offer a variety of freshly-harvested produce like leafy greens, root vegetables, and herbs to customers; a weekly vegetable subscription box with a selection of seasonal produce; and a CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) program that allows customers to purchase a share of the farm's harvest. This would offer customers the opportunity to enjoy healthy, locally-sourced organic produce while supporting a sustainable farming practice.
When drafting this section, you should be precise about the categories of products or services you sell, the types of customers you are targeting and how customers can buy them.
4. The market analysis
When you present your market analysis in your organic vegetable farm business plan, it's crucial to include detailed information about customers' demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, barriers to entry, and any relevant regulations.
The main objective of this section is to help the reader understand the size and attractiveness of the market while demonstrating your solid understanding of the industry.
Begin with the demographics and segmentation subsection, providing an overview of the addressable market for your organic vegetable farm, the key trends in the marketplace, and introducing different customer segments along with their preferences in terms of purchasing habits and budgets.
Next, focus on your target market, zooming in on the specific customer segments your organic vegetable farm aims to serve and explaining how your products and services fulfil their distinct needs.
For example, your target market might include health-conscious families. These families care deeply about the food they feed their children and seek out organic ingredients when possible. They are likely to purchase organic vegetables in bulk and appreciate the convenience of having their favorite produce delivered to their door.
Then proceed to the competition subsection, where you introduce your main competitors and highlight what sets you apart from them.
Finally, conclude your market analysis with an overview of the key regulations applicable to your organic vegetable farm.
5. The strategy section
When you write the strategy section of your organic vegetable farm business plan, remember to cover key elements such as your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
In the competitive edge subsection, elaborate on what makes your company stand out from competitors. This becomes especially important if you're a startup, aiming to carve a place for yourself amidst established players in the marketplace.
The pricing strategy subsection should demonstrate how you plan to maintain profitability while offering competitive prices to attract customers.
Outline your sales & marketing plan, detailing how you'll reach out to new customers and retain existing ones through loyalty programs or special offers.
For the milestones subsection, outline your company's achievements to date and your main objectives for the future, complete with specific dates to set clear expectations for progress.
Lastly, the risks and mitigants subsection should address the main risks that could affect your plan's execution. Explain the measures you've put in place to minimize these risks, assuring potential investors or lenders.
Your organic vegetable farm may face a variety of risks. One potential risk could be a natural disaster, such as a hurricane or hail storm, which could damage your crops and reduce the amount of produce you are able to harvest. Another risk you could encounter is theft or vandalism of your property or equipment, which could lead to financial losses. In both cases, the risks could have a significant impact on the success of your farm.
6. The operations section
The operations of your organic vegetable farm must be presented in detail in your business plan.
The first thing you should cover in this section is your staffing team, the main roles, and the overall recruitment plan to support the growth expected in your business plan. You should also outline the qualifications and experience necessary to fulfil each role, and how you intend to recruit (using job boards, referrals, or headhunters).
You should then state the operating hours of your organic vegetable farm - so that the reader can check the adequacy of your staffing levels - and any plans for varying opening times during peak season. Additionally, the plan should include details on how you will handle customer queries outside of normal operating hours.
The next part of this section should focus on the key assets and IP required to operate your business. If you depend on any licenses or trademarks, physical structures (equipment or property) or lease agreements, these should all go in there.
You may have key assets such as land and equipment that could be considered intellectual property. Additionally, the farm may have special recipes or techniques for preparing organic vegetables that could be considered intellectual property. These may be closely guarded secrets that could give the farm a competitive advantage.
Finally, you should include a list of suppliers that you plan to work with and a breakdown of their services and main commercial terms (price, payment terms, contract duration, etc.). Investors are always keen to know if there is a particular reason why you have chosen to work with a specific supplier (higher-quality products or past relationships for example).
7. The presentation of the financial plan
The financial plan section is where we will present the financial forecast we talked about earlier in this guide.
Now that you have a clear idea of what goes in your organic vegetable farm business plan, let's look at the solutions you can use to draft yours.
What tool should I use to write my organic vegetable farm's business plan?
There are two main ways of creating your organic vegetable farm business plan:
- Using specialized business planning software,
- Hiring a business plan writer.
Using an online business plan software for your organic vegetable farm's business plan
Using online business planning software is the most efficient and modern way to write an organic vegetable farm business plan.
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can access a library of dozens of complete business plan samples and templates for inspiration
- You get a professional business plan, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try The Business Plan Shop for free by signing up here .
Need a solid financial forecast?
The Business Plan Shop does the maths for you. Simply enter your revenues, costs and investments. Click save and our online tool builds a three-way forecast for you instantly.
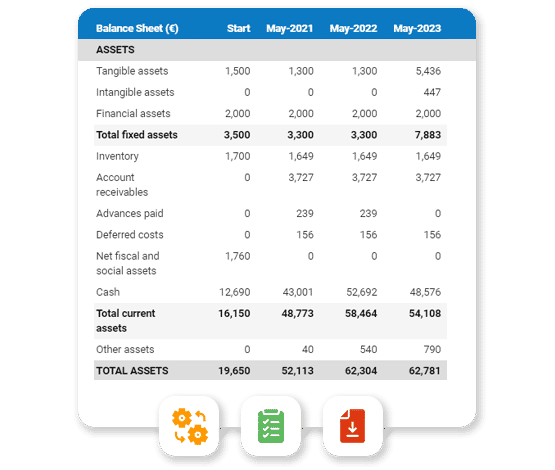
Hiring a business plan writer to write your organic vegetable farm's business plan
Outsourcing your organic vegetable farm business plan to a business plan writer can also be a viable option.
Business plan writers are experienced in writing business plans and adept at creating financial forecasts without errors. Furthermore, hiring a consultant can save you time and allow you to focus on the day-to-day operations of your business.
However, hiring business plan writers is expensive as you are paying for the software used by the consultant, plus their time, and their profit margin of course.
From experience, you need to budget at least £1.5k ($2.0k) excluding tax for a complete business plan, more if you need to make changes after the initial version (which happens frequently after the initial meetings with lenders or investors).
You also need to be careful when seeking investment. Investors want their money to be used to grow the business, not spent on consulting fees. Therefore, the amount you spend on business plan writing services (and other consulting services such as legal services) needs to be negligible relative to the amount raised.
The other drawback is that you usually don't own the business plan itself: you just get the output, while the actual document is saved in the consultant's business plan software - which makes it difficult to maintain the document up to date without hiring the consultant on a retainer.
For these reasons, outsourcing the organic vegetable farm business plan to a business plan writer should be considered carefully, weighing both the advantages and disadvantages of hiring outside help.
Ultimately, it may be the right decision for some businesses, while others may find it beneficial to write their business plan using online software.
Why not create your organic vegetable farm's business plan using Word or Excel?
I must advise against using Microsoft Excel and Word (or their Google, Apple, or open-source equivalents) to write your organic vegetable farm business plan. Let me explain why.
Firstly, creating an accurate and error-free financial forecast on Excel (or any spreadsheet) is highly technical and requires a strong grasp of accounting principles and financial modelling skills. It is, therefore, unlikely that anyone will fully trust your numbers unless you have both a degree in finance and accounting and significant financial modelling experience, like us at The Business Plan Shop.
Secondly, relying on spreadsheets is inefficient. While it may have been the only option in the past, technology has advanced significantly, and software can now perform these tasks much faster and with greater accuracy. With the rise of AI, software can even help us detect mistakes in forecasts and analyze the numbers for better decision-making.
And with the rise of AI, software is also becoming smarter at helping us detect mistakes in our forecasts and helping us analyse the numbers to make better decisions.
Moreover, software makes it easier to compare actuals versus forecasts and maintain up-to-date forecasts to keep visibility on future cash flows, as we discussed earlier in this guide. This task is cumbersome when using spreadsheets.
Now, let's talk about the written part of your organic vegetable farm business plan. While it may be less error-prone, using software can bring tremendous gains in productivity. Word processors, for example, lack instructions and examples for each part of your business plan. They also won't automatically update your numbers when changes occur in your forecast, and they don't handle formatting for you.
Overall, while Word or Excel may seem viable for some entrepreneurs to create a business plan, it's by far becoming an antiquated way of doing things.
- Having an up-to-date business plan is key to maintaining visibility on your future cash flows.
- A business plan has 2 parts: a financial forecast highlighting the expected growth, profitability and cash generation of the business; and a written part which provides the context needed to interpret and assess the quality of the forecast.
- Using business plan software is the modern way of writing and maintaining business plans.
We hope that this guide helped you to better understand how to write the business plan for an organic vegetable farm. If you still have questions, do not hesitate to contact us.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to write a 5 years business plan
- Business plan myths
Know someone who owns or wants to start an organic vegetable farm? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
Sample Vegetable Farming Business Plan
Commercial vegetable farming business plan sample.
Do you have the interest to start a vegetable farm in your community? Vegetables are consumed by so many people daily because of their nutritious value.
Because of this, vegetable farming is one very lucrative agricultural business that any wise entrepreneur should consider venturing into.
If you have not considered the thought of starting a dry season vegetable farming business before, in this post I will be sharing with you how to start a vegetable farm business and become successful in it.
To bring clarity to this discussion, I want to first share with you what a vegetable farm is.
What Is a Vegetable Farm?
A vegetable farm is a type of farm or land where vegetables are cultivated for the consumption of man, either for commercial or private use.
Back then, vegetable cultivation by man was not as easy as it is now. Farmers had to go through manual labor to grow their vegetables.
But as time went on, Animals were used to reduce the hard work of these vegetable cultivators e.g. using those animals to plow the farm for cultivation.
Now, farming processes are fast with the introduction of mechanized equipment, and the usefulness of those animals has reduced greatly.
Types of Commercially Consumable Vegetables
There are lots and lots of vegetables worldwide, if I should start mentioning them one by one, I don’t think this post will have an end. And again, not all of these vegetables are recognized and widely consumed, so starting a farm with such vegetables may not be profitable.
So, with that said, let us check out some of the vegetables known and highly demanded in any market:
I am starting with tomato because it is one of the most consumable vegetables.
Cultivating Tomatoes can be very amazing and profitable, as it requires just 8 hours of sunlight with warm clear weather. And did I forget to say that it is harvested for 3-4 months? Making it awesome for cultivation.
Fluted Pumpkin
This is another most consumed vegetable in any community as it is used to prepare lots of dishes.
Fluted pumpkin is highly valued because of its high nutrient contents when cooked, and also good in blood volume increase when taken raw.
This vegetable is easier to cultivate no matter where you reside because of its tolerance to drought, and also performs well even on poor soils.
This type of vegetable is often consumed raw.
It is also used by cosmetic companies to combat skin problems because it has the same level of hydrogen content as the human skin. So the high demand for cucumber by these cosmetic companies makes cultivating it profitable.
Cultivation of cucumbers should be in rich soil with enough organic matter and steady sunlight.
Watermelons are also regarded as fruits that are consumed by people very well.
Watermelons should be cultivated on warm soil to enhance the growth of the seeds. And watermelons do not take a long time to be harvested, it takes just 3 months to be harvested.
You can’t start a vegetable farm without thinking of planting cabbage on your farm.
Yes! Cabbage is a popular vegetable used in the preparation of Salads, and that makes it popular. People also use it in various ways, some like taking it raw, while others love adding it to dishes, etc.
The only downside about this vegetable is that it is expensive compared to other vegetables. This is because more effort is required to cultivate it. Cabbage performs well in cold climates, is well-drained, and on fertile soil.
Okra is an edible green-pod vegetable with high nutrient content. It contains vitamin A, vitamin K, vitamin C, and vitamin B complex.
In as much as it could be grown on any kind of soil, it does not do well in tight, water-logged soils.
After going through that list above, you may start thinking of how to kick-start your own vegetable farm. But before starting your own vegetable farm, there are some factors you need to consider.
Vegetable Market Development
We all know that vegetables are perishable crops, so after knowing that these vegetables are perishable crops, you need to plan on how to avoid losing them by identifying where you will market this vegetable before there are finally ready for the market.
Site Location
Considering the site location of the farm includes knowing the topography of the soil you intend to use, the soil type, and also find out the availability of water because these vegetables need water to help them grow well.
And also find out how close your farm is to the market.
Disease/Pest Control
As it is known, vegetables are always attacked by pests and seasonal diseases. So, you need to put things in place on how you are going to combat any disease or pest when it comes.
Startup Capital for a Vegetable Farm
You can’t start a vegetable farm without capital. You may want to ask how much it will cost you to start your vegetable farm.
The fact is, there is no written rule as to how much you need to start up a vegetable production business as this greatly depends on how large you want your vegetable farm to be.
Cultivating 1-2 hectares of land varies in cost depending on the location, and also the type of vegetable intended for cultivation. And that should include seedlings, manure, labor, and pesticides.
Here is a sample business plan for starting a vegetable farm.
VEGETABLE FARMING BUSINESS PLAN EXAMPLE
There are several aspects of agriculture that range from crop farming to livestock farming. Each of these requires systematic methods and planning to achieve desired results.
Proper planning is an indispensable requirement of doing business that must not be overlooked, as doing so will be to your own peril. We will focus on an important aspect of agriculture which is crop production with a special focus on the vegetable farming business plan.
As an economic activity, there is a need for proper coordination of all aspects of crop production.
Without the necessary planning, such a venture will hit the rocks, resulting in huge losses of resources as well as time. Let’s get to the details of the vegetable farming business plan, shall we?
Executive Summary
Anyone taking going through your business plan should be able to have a general understanding of your vegetable farming business without having to go through the entire document.
Your executive summary section provides a highly summarized picture of your plan.
Investors, as well as money lenders, are most interested in this section of your business plan. If it is compelling enough, they will like to get into the details to find further information.
If you must attract the attention of your readers, then you need to be very specific as well as concise in your presentations.
It is necessary to give details on the use of funds as lenders will be very interested in knowing the specifics of what the funds will be spent on.
Here, there should also be a clear definition of the loan repayment process as anyone investing in a business will need to know how his/her money will be recouped.
By doing this, you are clearly demonstrating to the investor your capacity to repay any loans as well as interests. The executive summary section is where you pitch your business to investors.
Therefore you need to do a good job here as will also have a telling effect on the general plan.
The Legal Structure
Starting a vegetable farming business requires you to choose the legal structure that best suits your business. Different types of business structures exist to meet specific needs.
Therefore, you should carefully consider your preferred structure, some of which include Sole Proprietorships, Partnerships, Limited Liability Partnerships LLP, Limited Liability Companies LLC, and many more.
After selecting your preferred business structure, you should be able to explain clearly why you chose that particular structure as well as how best it suits your business needs.
After making your choice of a suitable legal structure, all supporting documents should be included in the supporting documents section.
For partnerships, it is necessary to create an exit provision as well as another for business dissolution if the need arises. This helps in significantly reducing unnecessary conflicts that may arise. There should also be provisions for changing the legal structure of the business whenever the need arises in the future.
If you plan on changing the structure of your business at any point in the future, you should clearly state why such change is necessary as well as also providing the timeline when such a change will come into effect.
Business Description
This is where anyone reading your business plan will get to have a clear picture of your services and products.
Here, you will need to also clearly highlight your business assets, inventory, value as well as marketability, and turnover. You need to also provide information on industry trends as well as how your products will be beneficial to the consumer or customers.
There should be some form of projection under this section of where your business should be after some years.
Your Business Location
Where you locate your farm business is important to how your products (in this case vegetable) and other services which may be provided by you will be distributed. This is largely determined by your target market.
Because this is a food crop that is consumed by almost every family, your target market will be very wide. You will need to state the reasons for selecting such a location as well as how it helps/contributes to the growth of your business.
Marketing is very crucial to the success of your vegetable farming business.
Your marketing plan should be such that clearly identifies your target market, as well as providing clear-cut strategies of distributing your agro-products to these targeted customers in the most effective and efficient ways possible.
You need to be clear about the size of your target market as well as how effective your strategies will be towards attracting increased patronage from clients.
Carefully developing a sound marketing plan will go a long way in setting up your business for success.
Your methods of advertising, as well as the pricing of your products, are important considerations to make when writing your business plan. Pricing requires knowing customer behavior which you can use to your advantage in arriving at a fair price where a win-win situation is achieved.
Financial Documentation
Here, a business plan requires sound financial planning.
Important sections that must be included here include a summary of all financial needs such as applying for loans, the budget or cash flow, break-even analysis, a three-year growth projection, as well as actual performance statements among others.
These are very vital towards obtaining loans for your vegetable farming business.
These are some of the requirements for writing your vegetable farming business plan. Without these sections, your business plan is incomplete and will hardly make any meaningful impact at all.
When writing your plan, you should not rush the process as it needs every aspect of the business to be carefully researched if the business is to make a meaningful impact.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Organic Farm Business Plan
Article Index:
2.0 Company Description
3.0 products, 4.0 market analysis, 5.0 marketing strategy and implementation, 6.0 organization and management, 7.0 financial plan, 1.0 executive summary.
Once the humble family vegetable garden, Franks Organic Farm is today a one acre working farm with over 30 varieties of vegetables. When Frank Burns was laid off from his corporate position three years ago, he first he turned to the vegetable garden for money saving / economic reasons. But with the uncertainty of recent events in the Middle East, the energy crisis, the long term effects of reliance on fossil fuels, and his personal philosophies on conservation, Frank Burns and his wife Kathy, turned this family vegetable patch into a thriving certified organic produce business.
Franks Organic Farm is based on the sound principles of conserving natural resources, limiting the carbon footprint, growing, hiring and eating locally grown and prepared foods, and making the world a better place to live in. This unique perspective clearly shows in the quality of the produce, the well cared for gardens, and natural friendliness and ease of its owners.
Franks Organic Farm was created to meet the growing needs of a community that shares these same views and is concerned about what they eat and feed their children. This is a community that is tired of ‘fresh’ tomatoes bought at the local grocery store. When more than likely the “fresh” tomatoes were picked while still unripe, shipped 3,000 miles over several days/weeks, and then artificially “ripened” using ethylene gas, thus robbing it of practically all of its nutritional value.
Franks Organic Farm is a Community Supported Agriculture (“CSA”) Business entity. CSA is both a marketing strategy and a philosophy. The farmers sell shares (subscriptions) in the next season’s produce, usually before the season begins. Each week of the season, the member receives a ‘share’ of produce from the farm. In some cases the members are involved in decision-making of all aspects of the operation; in others the farmer makes all the decisions. Each CSA is as unique to the farmer and the community it serves. Members may pick up their boxes at the farm, at delivery sites, or home delivery may be offered.
The purpose of this business plan is to provide a blueprint for near term and long term goals. The business plan will be utilized as a tool to gauge how well the farm is doing in the future compared to their initial goals and keep them on target. The business plan is also a tool for lenders, explaining the need for initial financing, the source and use of funds, and debt repayment capabilities.
1.1 Business Objectives
Franks Organic Farm has simple objectives: provide healthy and delicious tasting vegetables while simultaneously leaving a minimal carbon footprint. In order to accomplish this, the farm plans to:
- Sell 60 shares by Year 2 and have full-time income or 90 shares sold by Year 3.
- In Year 4, Franks Organic Farm plans to purchase an additional 9 acres for a total of 12 acres. The initial 3 years of operations will provide the excellent credit history and track record necessary for this large purchase.
1.2 Mission Statement
Franks Organic Farm’s mission is to raise the best tasting and finest quality fruits and vegetables for the local community. Franks Organic Farm uses only natural and sustainable farming methods, free from pesticides or fertilizers. Natural foods and natural farming methods leaves a smaller carbon footprint while simultaneously improves the health of its customers and its local community.
1.3 Guiding Principles
Franks Organic Farm’s slogan is simple: “Live life simply and simply live”. The owners also believe in contributing to their community and the planet by:
1. Local Franks Organic Farm believes that in order for the survival of the planet, we must rely on local resources. Buying from local farmers supports the local economy.
2. Sustainable Living By reducing reliance on energy is better for the planet and conserves our natural resources.
3. Satisfied Customers Happy members ensure repeat business and their referrals grow the business.
1.4 Keys to Success
Below are a Franks Organic Farm’s Keys to Success:
- Superlative Communication – Franks Organic Farm keeps its members current on all aspects of the farm – through its weekly newsletters and blog updates on what is happening during the winter months such as new and exciting vegetable offerings being planted in the greenhouse. Additionally, Franks Organic Farm encourages member feedback and input and has its members complete surveys and questionnaires regarding how the farm is doing and what can be done to improve operations.
- Healthier Food Choices – All vegetables are USDA certified organic. The vegetables are pesticide free and chemical free and no preservatives are used.
- Support the Local Economy – Statistically more than 70 percent of the local food supply is grown outside the state. Buying from Franks Organic Farm ensures that its members buy locally and creates jobs that support the local market.
- Offer Personalized Selections – Franks Organic Farm strives to be the leading CSA farm supplier of choice by providing customized offerings to its members. If, say a member wants a cucuzzi fruit – Franks Organic Farm will grow this item if the soil and temperatures can accommodate this item. By providing foods the customers want (and will actually eat) cuts down on waste and makes the planet a better place for everyone.
- Home Delivery – Franks Organic Farm will establish weekly delivery times that are convenient for its customers. This saves customers time and gas money – making everyone happy. Alternatively customers will also have the option to pick up directly at the farm.
Frank and Kathy Burns run, manage, and operate Franks Organic Farm. The company initially sold farm to market then quickly began supporting local restaurants with surplus (waste) sold at the local farmers market. Frank and Kathy are operating the business as a CSA, a business for the first time this year.
The Burns selected the CSA model, in which both the farmer and the members have a mutual interest in the crop. And because the shares are essentially presold prior to planting, the ‘waste’ factor (or excess crops risk) are eliminated. Based on their success at the farmer’s market and local restaurants, the Burns have already sold 100 percent of their 30 shares.
Franks Organic Farm is located on one of three acres located at the Burns’ primary residence in Plymouth, Wisconsin. During the off season, the owners of Franks Organic Farm will actively target and market new members, engage in public speaking events, and complete their forthcoming E Books.

2.1 Ownership
Franks Organic Farm is a C-Corporation formed in the State of Wisconsin and is wholly owned by Frank and Kathy Burns.
Frank Burns, a former Human Resources Director at Sargento Cheese, was recently downsized. Not desiring to re-enter corporate America, and concerned about the environment, global issues and the state of the economy, Frank began expanding his family garden. What began as a way for the family to save some money and reduce the carbon foot print, today has grown from its small ¼ acre plot to over 1+ acre with plans for expansion to 12+ acres. A shrewd businessman and well known in the community, Frank initially approached colleagues and friends in the local restaurant community. These connections marked the beginning of business for the startup farm and as word of mouth spread, Franks Organic Farm attracted ten other additional restaurants. All surplus was sold at the local farmer’s market.
Kathy Burns is an elementary school teacher for the Sheboygan Area School District. A graduate of Marquette University in Milwaukee, Kathy has been teaching fifth grade Science for over ten years. Raised on a family dairy farm, Kathy’s family also had a small fruit and vegetable farm and she loved helping the family grow and harvest the crop. Mrs. Burn’s summer schedule is flexible and helps the family maintain the garden during the busy summer growth season.
2.2 Legal Form
Franks Organic Farm is C-Corporation formed in the State of Wisconsin. The entity is wholly owned by Frank and Kathy Burns.
2.3 Start-Up Summary
The Burns have been managing the family farm successfully for the last fifteen years. Recently the owners installed a greenhouse with warming lights for early starts. They also invested in a pickup truck (2005 Ford F150) for delivering vegetables to the members. Most recently they purchased a tractor and borrowed their neighbor’s attachments as needed for harvest.
Last year, Franks Organic Farm passed the stringent requirements needed to qualify as certified organic as deemed by the USDA. This allows them to market all produce as organic and can also bring higher margins when surplus produce is sold outside the CSA or to restaurants or market stands. The Burns realized that although consumers may not understand all the requirements associated with the organic label (such as pesticide control and fertilizers), the consumer is comfortable with the label. This, is one of the keys, they believe which will set Franks Organic Farm apart from its peers.
All pre-harvest and harvest supplies have been paid for out-of-pocket. The owners have already spent in excess of $40,000 to start their farm business.
When the owners announced they were becoming a CSA, the news traveled fast and demand for their products was so great that they have already presold 100 percent of their shares for the upcoming growing season. In order to meet these demands and meet the opportunity for growth, the owners are seeking an operating loan from the USDA’s Farm Service Agency, Insurance Company or private investor.
The credit facility will be used to meet operating and cash flow needs for the pre harvest and harvest season. The $14,500 credit facility will be secured by a first lien position on the 3 acre plot of land, all buildings and improvements (a greenhouse). The land is valued at $30,000 and is currently owned free and clear by the Burns. The land is adjacent to the Burn’s primary residence.
2.4 Location and Facilities
Franks Organic Farm is located in Plymouth, Wisconsin, located in Sheboygan County Wisconsin. Sheboygan County is located in east-central Wisconsin. Sheboygan County is a one-hour drive to Milwaukee and Green Bay, and less than a 3 hour trip Chicago. Interstate 43 and State Highways 23 and 57 make are the main highways.
Sheboygan County’s population is 117,566. It has grown 4.4 percent between 2000 and 2009. The County is expected to continue to grow by a similar rate until 2015 when it reaches a population of 123,209. Major employers include: Kohler Company, Bemis Manufacturing, Aurora Health Care, Johnsonville Sausage, Rockline Industries, and Sargento Foods. The City of Plymouth is located in west-central Sheboygan County along State Highways 23, 57, and 67. It is the second largest municipality in Sheboygan County and one of the fastest growing in the County. (Sheboygan County Economic Development Corporation).
3.1 Products/Services Descriptions
Franks Organic Farm’s growing season will start in early May and end in October with the goal of 20 weeks. Shares will be comprised approximately 10-15 different crops every 8 weeks of in-season produce. Here is an example of types of produce throughout the season:
Spring: Beets, Broccoli, Cabbage, Carrots, Garlic, Green Onions, Kale, Lettuce (several varieties), Radishes, Peas, Spinach.
Summer: Beans, Carrots, Cucumbers, Eggplant, Green Onions, Leeks, Melons, Onions, Sweet Peppers, Summer Squash, Tomatoes, Zucchini.
Fall: Beans, Beets, Broccoli, Cauliflower, Cucumbers, Chard, Lettuce (several varieties), Potatoes, Red Onions, Spinach, Winter Squash.
All share sales are sold in advance.
A Full Share will provide a family of four vegetables for a week. (estimate). Likewise, a Half Share provides a week of vegetables for two people. Full Shares are $750 and Half Shares are $375 for the season. (The owners are currently only considering the sale of Full Shares at this time).
The Burns will utilize a detailed planting schedule which historically has helped immensely especially in the hectic summer planting season. The detailed guide begins with the plantings that tolerate the coldest spring and these are started in their greenhouse. Summer crops will be shaded with cloths if necessary (like spinach for instance). The farmers will plant many tomatoes (which are very popular) and only some eggplant which is less popular. Other considerations that are detailed in the planting calendar will be the amount of produce that is needed. One way to plant more is to plant smaller amounts more often. Examples include broccoli, carrots, scallions, and summer squash. The Burns have learned that planting these items two or three times during the growing season yields more crop and the surplus can readily be sold at the farmers market. Picking peas is difficult at harvest time, so the Burns always plan to plant surplus to make harvest time worthwhile. It is expected that any surplus can be sold at the farmers market.
3.2 Competitive Comparison
Plymouth, Wisconsin, reports six CSA entities, of which three represent direct competition for the subject.
3.3 Product/Service Sourcing
All produce will be grown on Franks Organic Farm. Frank and Kathy Burns will both actively work and manage the farm.
Distribution At Franks Organic Farm, members have the option for home delivery or to travel to the farm on the scheduled pickup day.
The home delivery choice is what most members prefer and allows the Burns to deliver the farm fresh produce directly. This distribution method has the least carbon footprint, with one driver and one truck. It is obviously the most intensive for the Burns and with busy summer season, this can be too time consuming for them. Items are delivered in reusable boxes. This distribution method represents any easy way to deal with any shortfalls in produce the Burns will simply ‘mix and match’ items for the members.
Alternatively, the members have the option to pick up the produce directly at the farm. The Burns enjoy this option especially during the busy season, because it frees up some of their time. This option requires that the driveway be easily accessible to the members and that the farm appears in good condition at all times. This onsite setup allows members to view firsthand what is growing, the condition of the plants and soil. The members will also be aware of any draught issues for example, and what remediation efforts the farmers are taking to care for the crops. On pickup day, the Burns have setup a stand and a ‘buffet-style’ layout in which members can pick and choose up to a specific limit of produce for that week. This option creates a ‘festive’ environment on the farm in which members can interact with each other, the farmers, and exchange recipes. If any shortfalls exist, this mix and match buffet style provides the solution. Just like home delivery, members are given a one box to fill and refill weekly with their selections for the duration of the growing season.
3.4 Inventory Management
N/A. The CSA farm concept is all about freshness. The produce is delivered immediately from the farm to the (member’s) table.
3.5 Warehousing and Fulfillment
3.6 future products/services.
- The owners of the farm have plans to introduce honey bees the following season and offer honey as another organic product.
- On occasion, Franks Organic Farm partners with its neighboring dairy farm and an organic bakery in town. From time to time members will find fresh cheeses and organic breads in their weekly selection boxes. Franks Organic Farm owners are currently considering joining forces with a local orchard company as well. The orchard will supply apple butter and jams.
- Within one year, Franks Organic Farm plans to utilize an additional acre and add 30 more families to their growing share program. They plan to add 30 more families (shares) by Year Three.
- Franks Organic Farm has long term plans to purchase an additional 9 acres or a total of 360 shares. To support the farm, they will hire apprentice farmers, part-time delivery drivers and a bookkeeper. The Burns would then be able to focus their efforts on crop research, marketing trends and their members. Part of the focus of organic growing is returning back to the community. All employees will earn fair wages for work performed.
- Other future plans include accessing the internet to increase awareness and the importance of local and community farming. Kathy Burns is compiling a recipe E-book which will supplement cash flow during non-productive months. In his spare time, Frank Burns is also compiling an E-Book to sell on Franks Organic Farm website. The book will focus on modern organic farming techniques for the novice farmer. A second book is forthcoming dealing with environmental concerns and social responsibility.
- Additionally, Franks Organic Farm will publish a weekly newsletter to be included in the member’s box as well as the website. The newsletter will identify what is in the weekly box, what is happening on the farm and recipes. The newsletter will educate members to seasonal eating and sustainable principles.
- Franks Organic Farm has future plans for constructing a vegetable processing area with electricity and water. The facility will have a walk in cooler, a washing and grading area, stainless steel tables and two scales. Additional capital expenditures will be for the purchase of a newer (used) pickup truck and attachments for their tractor. (Currently they borrow their neighbor’s).
Sheboygan County’s cost of living is lower than the national average and housing costs are much lower than the national average. At the same time, Sheboygan County personal income is greater than the national average. In other words, this community not only has a high demand for organic items, but it can afford them as well.
4.1 Industry Analysis
This analysis is based on the North American Industry Classification System (“NAICS”) 111998: Agriculture – All Other Miscellaneous Crop Farming. The US crop production industry includes about 1 million farms with combined annual revenue of about $205 billion. Major companies include Dole Food Company, Chiquita Brands International, and Sunkist Growers. Crop farming is the growing and harvesting of field crops such as grain, oilseeds, tobacco, dry beans, potatoes, vegetables and melons, fruits and nuts, and floriculture.
Global crop production revenue exceeds $1 trillion. The US and China are among the top crop producers. Large companies outside the US include Fresh Del Monte Produce (headquartered in Cayman Islands); Total Produce (Ireland); and Amaggi Exportação e Importação (Brazil).
Demand is driven by federal agricultural policy programs, food consumption trends, and the grain and oilseed export market. The profitability of individual companies depends on maximizing crop yield and minimizing disease risk. Large companies have advantages in highly automated technologies and access to the latest in seed and crop technologies. Small operations can compete effectively by harvesting heirloom, non-genetically modified (GM), or specialty products. The industry is capital-intensive: average annual revenue per employee is about $390,000. (First Research)
The CSA makes the following generalizations/guidelines regarding its industry:
- New entrants should practice farming 2 years prior to making a commitment to the challenge of CSA farming
- In general, 20-30 shares per acre is possible
- 30 shares per farmer or laborer is possible
- To earn full time income 80-100 shares may be necessary
- The share price ranges from $300-$800 per share annually ($15-$40 per share weekly) (CSA – Michigan 2012)
4.1.1 Market Size
The US crop production industry includes about 1 million farms with combined annual revenue of about $205 billion. (First Research)
Although the USDA does not have official statistics on U.S. organic retail sales, information is available from industry sources. U.S. sales of organic products were $21.1 billion in 2008–over 3 percent of total food sales and were expected to reach $23.0 billion in 2009. (Nutrition Business Journal)
4.1.2 Industry Participants
Major participants include Dole Food Company, Chiquita Brands International, and Sunkist Growers. (First Research)
4.1.3 Main Competitors
Plymouth, Wisconsin reports six CSA entities, of which three represent direct competition for the subject.
Backyard Bounty W4873 County Hwy U Plymouth, WI 53073 http://ljcomerford.wordpress.com/
This is a 22 acre family owned farm and has been operating as a CSA for several years. In addition to its offerings of organic fruits and vegetables this farm also sells organic poultry and eggs. The farm had mixed reviews by its members.
Eilert’s Acres N5575 County Road ZZ Plymouth, WI 53073 http://www.eilertsacres.com/
Owned by Edward and Kay Eilert, this farm began business as a CSA in 2011. The farm provides many of the same vegetables as the subject as well as providing farm to door delivery service.
Springdale Farms W7065 Silver Spring Lane Plymouth, WI 53073 http://www.springdalefarmcsa.org/
This CSA farm is the most established in the direct market and has been in existence 20+ years. Springdale Farm has various pick up sites in the greater Sheboygan MSA. Based on the farm’s website, members are not given the option to select specialty vegetables and instead members are encouraged to ‘trade-in’ any unwanted produce back to the community to share and thus avoid waste. This has not proven to be a deterrent for the farm’s following. For the most recent growing season, the farm has a waiting list.
The following are CSA businesses that compete indirectly with the subject:
Old Plank Farm W6028 County Road C Plymouth, WI 53073 http://www.oldplankfarm.com/
This entity only sells its goods at a local farm stand; it does not sell shares. In addition, this indirect competitor sells organic eggs at its farm stand. Based on its limited selection and differing offerings, this indirect competitor attracts individuals who are only seeking small, specialty quantities of produce, but do not want to commit to purchasing shares for a full season.
Log Cabin Orchard N4797 County Rd E Plymouth, WI 53073 www.logcabinorchard.com
This indirect competitor is a fruit orchard selling apples, pears, plums, honey, apple and maple syrup, fresh apple cider and apple butter. In the fall, this CSA generally offers U-Pick apples options. Due its differing selection of products, this entity is not a direct competitor.
Red Twig Farm http://redtwigfarm.wordpress.com/
This entity only sells to Goodside Co-op and Trust Local Foods; because this CSA farm differs in its target client, it is does not represent a direct competitor for the subject.
4.1.4 Market Segments
2008, Sheboygan County’s median household in-come was $51,681 and the mean household income was estimated to be $61,889.
Nearly 72 percent of Sheboygan County’s housing units are owner-occupied. The median housing value in Sheboygan County is estimated to be $149,700, which is $43,000 less than the United States estimated median home value. At the same time, Sheboygan County income is higher than the national average, which is the reason for high home ownership rates.
Franks Organic Farm is targeting the households with incomes above $50,000. The target market represents approximately 51.5 percent of the total population, which should easily absorb Franks Organic Farm’s entrance.
Sheboygan County’s population is 117,566. It grew 4.4 percent between 2000 and 2009. The County is expected to continue to grow by a similar rate until 2015 when it reaches a population of 123,209.
4.2 Market Tests
While selling produce to local restaurants, Mr. Burns realized that the CSA option could potentially come to fruition. Historically the restaurant patrons always asked the source of the beautiful and delicate lettuces and quality tomatoes. Realizing the popularity of his produce, Mr. Burns, while continuing on a quest for global carbon footprint reduction, began researching the possibility of beginning a CSA effort. With the help of his restaurant partners, Mr. Burns posted fliers and brochures in their lobbies. By the end of the summer, Franks Organic Farm had presold 100 percent of the shares for the upcoming growing season.
4.3 Target Market Segment Strategy
Franks Organic Farm is targeting households with earnings in excess of $50,000 in the greater Sheboygan County. Approximately 51 percent of the population resides in this category. Other farmers have missed this target by focusing on traditional farming methods while Franks Organic Farm has obtained the Certified Organic stamp of approval. Additionally, Franks Organic Farm will focus its energies primarily on its members and provide services exceeding expectations by offering farm to door delivery service, providing supplemental local organic products and by providing a festive like atmosphere at the farm – especially on harvest day and other special occasions.
The following chart depicts the target market:
4.3.1 Market Needs
According to a USDA survey of market managers (Organic Produce, Price Premiums, and Eco-Labeling in U.S. Farmers’ Markets, April 2004) found that demand for organic products was strong or moderate in most of the farmers’ markets surveyed around the country, and that the managers felt more organic farmers were needed to meet consumer demand in many states. (USDA updated 06/19/12)
As demonstrated on the national map Sheboygan County represents a strong demand for organic produce.
“Organically” grown’ is the key. The term “organic” is now legally defined and can only be used to describe produce that is grown in accordance with the USDA rules and is certified as such by an independent agency.
4.3.2 Market Trends
While consumers may not understand all the requirements associated with being certified organic, they are comfortable with the label. Which is why Franks Organic Farm sought the services of the independent certification agency and has earned the distinction to be labeled an organic farm. Comparatively their CSA counterparts that continue to operate by traditional farming methods, Franks Organic Farm holds itself to a higher standard, which in time, they believe will attract and keep new members.
4.3.3 Market Growth
U.S. sales of organic products were $21.1 billion in 2008 – over 3 percent of total food sales- and were expected to reach $23.0 billion in 2009 (Nutrition Business Journal).
4.4 Positioning
Franks Organic Farm is aware that its members are crucial to its survival and growth. The owners will make certain each member feels that Franks Organic Farm is indeed his/her farm! After all, they do own a portion of the farm! The Burns will encourage its members to stop by to see operations. In addition the owners will host an open house at harvest time to celebrate the season’s bounty.
To further ensure its members are satisfied and encourage retention, the owners will use surveys and questionnaires as tools to gauge member satisfaction. The surveys/questionnaires will allow members to express feedback and also represent additional opportunities to communicate with Franks Organic Farm.
Franks Organic Farm is targeting households with earnings in excess of $50,000 in the greater Sheboygan County. Other farmers have missed this target by focusing on traditional farming methods while Franks Organic Farm has obtained the Certified Organic stamp of approval. Additionally, Franks Organic Farm will focus its energies primarily on its members and provide services exceeding expectations by offering farm to door delivery service, providing supplemental local organic products and by providing a festive like atmosphere at the farm – especially on harvest day and other special occasions.
5.1 SWOT Analysis
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The following is the SWOT analysis for Franks Organic Farm.
5.1.1 Strengths
- Franks Organic Farm receives share proceeds prior to start of the season which helps to pay for seeds, supplies and inputs
- During the off-season the owners of Franks Organic Farm can market and recruit new members and complete their E Books
- Franks Organic Farm will establish long term relationships with its members lasting at least one season
- Members share in the financial risks of the farm
- Low capital requirements, relatively inexpensive startup business
5.1.2 Weaknesses
- As many as 30 or more different crops must be grown to provide diversity to members throughout the season
- Location-if the farm is not close to its customers, it becomes burdensome for the farmer to make deliveries
- Labor intensive – during the season, crops are continually being planted, harvested, cleaned, sorted and packed – leaving little extra time for the farmer
- Member retention is key – if the member is not happy the likelihood of returning next season or providing a good recommendation is not good.
5.1.3 Opportunities
- The greater Sheboygan County is a prime location for organic produce with an historically high demand.
- Because many farmers still utilize traditional farming methods (pesticide and herbicide applications) Franks Organic Farm stands out from the crowd with its Certified Organic stamp of approval
5.1.4 Threats
- New entrants to the market pose a threat. Partially mitigating this risk is the recommended 2-3 year trial farming period – which would give Franks Organic Farm the necessary ‘heads-up’ to go against (said) competitors.
- Weather, storms, pests – can damage or even destroy crops.
- The farm is economically tied, and in inflationary times, consumers could revert back to traditional methods of buying fruits and vegetables at the local grocery store.
5.2 Strategy Pyramid
Strategy Create awareness that Franks Organic Farm delivers a wide variety of quality wholesome and healthy vegetables on a consistent basis.
Tactics Create a specific, detailed planting guide, planting several times over the growing season.
Programs Post fliers and brochures at local restaurants, and locally owned and operated organic/natural item stores in town.
Strategy Create a community of awareness to think globally, act locally.
Tactics Constant communication with members will foster the awareness who in turn will relate these ideals to the local community.
Programs Host open house events at Franks Organic Farm for special events such as Harvest Time and Earth Day.
5.3 Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Kathy and Frank Burns stand out from the competition: They are experienced operators and have demonstrated ability to grow large quantities of many different vegetables. They have demonstrated their ability to manage the crops, harvest, pack and deliver to their customers. They are doing business as a CSA. And unlike their conventional farming peers, Franks Organic Farm has met the stringent requirements to be designated Certified Organic.
5.4 Competitive Edge
CSA farming differs greatly from traditional farming due to the fact that members have ownership shares in the farm. Bearing this in mind, Franks Organic Farm will wholeheartedly focus on this vital aspect to retain members. The owners will constantly stay in touch with their members and encourage them to come and visit ‘their’ farm.
Unlike its traditional farm stand competitors, Franks Organic Farm will offer a variety of selections – up to 30 different types of produce during season. It should be noted that variety is a double edged sword: Many members will join a CSA because of the variety of offerings. It is important to have plenty of the basics like green beans, tomatoes and carrots. Conversely, too little a selection will be disappointing. To meet this balance, the Burns have created a questionnaire asking members what they prefer.
The Burns also provide weekly recipes and meal planning tips to coincide with the weekly boxes. Customers like the convenience of knowing how to prepare the items they are picking up from ‘their’ farm.
5.5 Marketing Strategy and Positioning
Franks Organic Farm will utilize product differentiation to stand apart from the competition. By growing wholesome organic produce, offering farm to door service, and actively engaging with its members, Franks Organic Farm will go above and beyond to maintain and grow its member base.
5.5.1 Positioning Statement
Franks Organic Farm will be the premier organic CSA in the greater Sheboygan County by offering at least 30 of the most delicious and mouth watering organic vegetables available in the local growing area and by providing exceptional relationships with its members, its community and the planet.
5.5.2 Pricing Strategy
Franks Organic Farm will utilize a fair price for a fair value. Some research suggests that the CSA farm is usually lower in price than organically grown food from local markets and is often less than foods from the supermarket. This could be a selling point for attracting new members, however, it also important to note this in not about cheap food.
5.5.3 Promotion and Advertising Strategy
The best strategy is word of mouth advertising. When people are happy with their shares they tell friends.
Franks Organic Farm will place brochures with other CSA businesses such as the local organic bakery and neighboring dairy farm.
Franks Organic Farm’s website will provide additional marketing information. In addition to its map and location, Franks Organic Farm will be listed with other CSA organizations such as national CSA and the USDA.
In the off season, the Frank Burns will provide lectures to civic and environmental groups.
During harvest time, the farm will be open to the public to browse and purchase surplus from the harvest bounty. They will also host special events such as Earth Day.
5.5.4 Website
Franks Organic Farm’s website will be a vital key in marketing. In addition to providing its history, location and contact information, the site will also have links to its CSA affiliations, the USDA website and current organic industry topics. The website will also have links to the current weekly newsletter (during season) and off season the owners will maintain a blog of what items are currently going to seedlings in the greenhouse and what new and exciting produce will be available in the upcoming season.
Additionally, the site will have links to Kathy and Frank’s forthcoming E-books which will provide additional cash flow during the non-production months.
The site will also take advantage of social media and have a Facebook link as well.
5.5.5 Marketing Programs
Franks Organic Farm will actively work to engage its members and local community by:
- Creating fliers and brochures and posting in community gathering places such as churches, community centers, farmers markets and other environmentally centric business.
- Franks Organic Farm’s website with emphasis on its USDA Certified Organic stamp of approval; the website will also have links to the USDA website and the national CSA website.
- Word of Mouth will play an important role
5.6 Sales Strategy
Franks Organic Farm has already sold all 30 of its shares for the upcoming season with future plans to sell 60 shares in Year Two and 90 shares in Year Three. In order to meet these goals, the farmers will continue to rely on advertising fliers, its online presence and most importantly word of mouth. The word of mouth recommendation from a satisfied member not only generates an opportunity for repeat business, but also is beneficial in recruiting new members.
5.6.1 Sales Forecast
The following table represents the annual sales forecast for the initial three years of operations:
Table 5.6.1 Annual Sales Forecast
5.6.2 Sales Programs
Franks Organic Farm’s primary sales program is the sale of shares. Additional sales programs will come from the sale of their forthcoming books. Honey production is expected to come online by Year Three.
During the slow winter months, both Frank and Kathy Burns will actively market their Franks Organic Farm, by providing speaking engagements at local events, becoming involved in the local community primarily its environmental issues, and writing and publishing papers supporting locally grown businesses. This slower time will also be utilized to create the weekly newsletter templates which coincide with the weekly deliveries. Historically the members love the newsletters – which facilitate additional contact between farmer and member. The weekly newsletter summarizes what is included in the weekly delivery, offers recipes and cooking suggestions, and summarizes what activities are transpiring at the farm. (This will be helpful especially during the busy summer months when there is little time available to write the weekly newsletters).
Franks Organic Farm is a C-Corporation doing business in the State of Wisconsin.
5.8 Milestones
The following chart depicts the Milestones Franks Organic Farm anticipates achieving:
Table 5.8 Milestones
5.9 Exit Strategy
In the event that Franks Organic Farm will cease operations, all assets (farm equipment, tools, scales) will be sold at auction. Proceeds from the sale will be first be used to pay off the financial obligation to the operating capital loan and the remaining proceeds will be paid to the members (if any obligations remain).
6.1 Organizational Structure
Franks Organic Farm will be wholly owned and operated by Frank and Kathy Burns. Mr. Burns will perform all office and accounting functions such as calculating the initial garden costs, seed costs and planting times. Both owners will harvest the crop. Franks Organic Farm will hire one apprentice farmer for each additional acre that is cultivated. Over time, they have plans to hire part-time delivery drivers as well as bookkeeper.
6.2 Management Team
Frank Burns, will actively manage the farm. Farm management duties will include the creation of a detailed planting guide and building a living soil. Only sustainable and organic farming methods will be used with no reliance on off-farm inputs and chemical pesticides/fertilizers. Growing methods include crop rotation, planting cover crops, applying finished compost and mulches, and encouraging beneficial insects, weed management, irrigation and harvesting. Mr. Burns will also be responsibility for preparing detailed accounting records for their tax accountant.
Kathy Burns will also actively participate in managing the crop during the busy summer months. During the slower winter months, both will work to complete their E-books which will be sold on line and supplement revenue. They will also actively market Franks Organic Farm by speaking to local civic groups, providing tours of the farm, and drafting the weekly newsletters.
6.3 Management Team Gaps
Franks Organic Farm will rely on its Tax Accountant to assist with tax reporting.
6.4 Personnel Plan
The following is a summary of Franks Organic Farm’s Personnel Plan.
Table 6.4 Personnel Plan
6.5 Board of Directors
The financial plan will cover the following:
- Required Cost of Start-Up
- Profit and Loss
- Balance Sheet
- Financial Ratios
7.1 Important Assumptions
- Revenues increase 50% Year One and 33% Year Two
- The following variable expenses are tied to volumes and will increase the same amount as revenue: salaries, fuel charges, postage, repairs and maintenance and supplies
- The loan example is based on traditional lending – with a collateralized working capital loan, fully amortizing with a three year pay down.
- The loan interest rate is based on the Prime Lending Rate plus 4.00%; Wall Street Journal Prime at this writing is 3.25%
7.2 Start-Up Costs
The following chart summarizes start-up expenses:
Table 7.2 Start-Up Costs
7.3 Source and Use of Funds
To date, the owners have come out of pocket approximately $40,600 or 74 percent of the project’s total costs. The following chart summarizes the source and use of funds:
7.4 Break-Even Analysis
Total fixed costs are estimated to be $18,437. The variable costs (salaries, fuel charges, postage, repairs and maintenance, and supplies) are estimated to be $109.74 per unit (full share). Units are considered full shares for analysis purposes and do not consider half shares. Based on the assumption of $750 as the average share price, the breakeven revenue then is $21,597 or 4 units (shares). This is further depicted in the Table Below and the Graph that follows:
7.5 Projections
7.5.1 projected profit and loss.
Franks Organic Farm’s estimated profit and loss for the initial three years of operations is reflected below:
Table 7.5.1 Pro Forma Profit and Loss
7.5.2 Projected Cash Flow
The statement of cash flow shows the incoming and outgoing cash of Franks Organic Farm:
Table 7.5.2 Pro Forma Cash Flow
7.5.3 Projected Balance Sheet
The following chart depicts the proforma balance sheet:
7.6 Business Ratios
The following ratios are based on the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) code 111998– All Other Miscellaneous Crop Farming. The ratio analysis compares the subject to industry peers based on similar asset size and revenues.
Table 7.6 Ratio Analysis
- Agriculture Farming
- Livestock Farming
Project Reports
- Hydroponics
- Best Fertilizers
- Vertical Farming
- Sheep Farming
- Goat Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Fish Farming
- Pig Farming
- Dairy Farming
- Rabbit Farming
- Success Stories of Farmers
- Boost Fruit Yield
- District Wise Crop Production
- Schemes & Subsidies
- Agriculture Colleges
- Farm Insurance
- Disease Control And Management
Agriculture
Aquaculture
Horticulture
Agri Business
Vegetable Farming Business Plan for High Yield and Profits
Table of contents, things to consider in starting a vegetable farming business, production factors and techniques for vegetable farming business, marketing strategies used in a small vegetable farming business plan , importance of vegetable production, factors that determine successful vegetable production, production techniques of quality vegetables, production plan of a vegetable farming business, some of the important high yield vegetable crops, the conclusion of a vegetable farming business plan.
Introduction to vegetable farming business plan
Vegetables are very important sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants providing human health benefits. Vegetable farming business is a profitable business and this not only for a big farmer. It is also profitable for small and marginal farmers. A small-scale vegetable farming has the earning potential throughout the year. If you are planning for commercial vegetable production for maximum profits, you must have a proper vegetable farming business plan.
A step by step guide to vegetable farming business plan
Growing vegetable crops is the perfect way to turn your gardening skills and knowledge into extra income. Business planning is the key to success when you’re ready to invest in starting a vegetable-production business . Poor management and lack of planning are, in many cases, the main causes of business failure. Vegetable farming is a type of crop production intended mainly for human consumption of the crop’s edible parts such as the shoot, leaves, fruits, and roots. According to the consuming part of the crop, vegetables are mainly divided into the following groups;
- Leafy vegetables (lettuce, cabbage, spinach)
- Fruit vegetables (pepper, cucumber, tomato)
- Root vegetables (carrot, radish, sweet potato)
- Bulb vegetables (garlic, onion, fennel)
- Flower vegetables (artichoke, cauliflower, broccoli)

Vegetable farming business demands proper planning, investment, adequate knowledge, and marketing. However, here we have discussed some of the main essentials;
- First of all, a solid vegetable farming business plan is very important.
- In starting, figure out how must land area you have for vegetable farming.
- According to the agro-climatic condition choose the vegetable for farming.
- You must consider the local market because vegetables are hugely perishable items.
- Also, cultivate the scope of export.
- Select the right species.
- Furthermore, you must arrange the proper irrigation for your vegetable farm.
- Plan for harvesting storage.
- Calculate the entire working capital cost.
- Finally, you must arrange the required finance.
Vegetable farming business requires attention to all production operations, including insect, disease, and weed control and efficient marketing. The kind of vegetable grown is determined by consumer demands, which can be defined in terms of vegetable variety, size, tenderness, flavor, and type of pack. Though, effective management involves the adoption of methods resulting in a steady flow of the desired amount of produce over the whole of the natural growing season of the vegetable crop. Many vegetable plants can be grown throughout the year in some climates, while yield per acre for a given kind of vegetable varies based on the growing season and region where the crop is produced.
Climate – Climate involves the temperature level, moisture, daylight, and wind conditions of a specific region. Climatic factors strongly affect all stages and processes of vegetable plant growth
Temperature – Temperature requirements are mainly based on the minimum, optimum, and maximum temperatures during both day and night throughout plant growth.
Moisture – The amount and annual distribution of rainfall in a region, particularly during certain periods of development, affects local crops.
Daylight – Light is the source of energy for vegetable plants. The response of plants to light is mainly dependent upon light intensity, quality, and daily duration.
Site – The choice of a site involves such factors as soil and climatic regions.
Soil preparation and management – Soil preparation and management for vegetable growing involves many of the usual operations required for other crops. Good drainage is important for early vegetables because of wet soil retards development.
Propagation – Propagation of vegetable plants, involving the formation and development of new individuals in the establishment of new plantings, is accomplished by the use of either seeds or the vegetative parts of plants.
Planting – Vegetable crops are planted in the field where they are to grow to maturity. A few kinds are commonly started in a seedbed, established in the greenhouse or the open, and transplanted as seedlings.
Cultivation – Vegetable cultivation refers to stirring the soil between rows of vegetable plants.
Irrigation – Vegetable farming requires irrigation in arid and semi-arid regions, and irrigation is frequently used as insurance against drought in more humid regions.
Disease and insect control – The vegetable production of satisfactory crops requires rigorous disease- and insect-control measures. Crop yield can be lowered by disease or insect attack, and when plants are attacked at an early stage of growth the entire crop may be lost. Reduction in the quality of crops may also be caused by diseases and insects.
Harvesting – The development stage of vegetables when harvested affects the quality of the product reaching the consumer.
Marketing strategy to the small vegetable growing farmer can be;
- Collective approaches, no individual side marketing
- Growing quality vegetables.
- Collection through cooperative or committee.
- Standardization of the product.
- Sale in the outlet by cooperative or Malls.
- Welfare strategy for farmers in profit distribution.
- Government subsidy to the collective approach.
In case if you miss this: Growing Medicinal Plants Hydroponically .

Vegetables are vital to the general good health of human beings, and providing necessary vitamins and minerals, and reducing risk from dangerous diseases and other medical conditions. First, of course, you would need a piece of land to start vegetable farming and try at least an acre for commercial vegetable growing. Then you would require equipment, which you can buy, lease or borrow, such as a tractor, tiller, plow, disc, cultivator, and planter. Lower your production cost as much as possible by spending on equipment only when required. Unnecessary expenses on equipment can eat away potential profits.
Vegetable production provides a promising economic opportunity for reducing rural poverty and unemployment in developing countries and is the main component of farm diversification strategies. Vegetables are mankind’s most affordable source of vitamins and minerals required for good health.
Importance of vegetable production is;
- Importance in human nutrition
- Vegetables are a very important source of farm income
- Vegetables have aesthetic value
- Vegetable production for medicinal purpose
- Roll of vegetables in the national economy
- Flexibility in plant production program-unlike the fruits with vegetables the production program can be adjusted and changed for better profits according to needs. With fruits, it is a difficult time taking and expensive to change the production program if it turns out to be unprofitable.
Whether the growth of vegetables is intended for fresh consumption, processing, and seed production, it can be a profitable vegetable business . However, there are a few factors that can influence the profitability of vegetable production from its early beginnings;
- Seed quality; the sowing of quality, clean, labeled, graded to size, viable, and healthy seed can make all the difference between success and failure in vegetable farming.
- Optimal time of sowing and planting; depends on the climate and environmental conditions of the specific area, as well as requirements of each crop.
- Method of planting; the secret to successful vegetable farming lies in the managing of optimal plant requirements, by combining the production of transplants in the greenhouses with planting in the field.
- Finally, considering effective farm management is the first step in creating profitable vegetable production . In essence, farming of these colorful plants can be a profitable business.
- Some plants have high labor requirements to grow. Before selecting a vegetable to raise, know first the extent at which some plants need tending. Then, determine whether you have the time to invest to grow and market it. For example, if you expect to be unable to get your products sold immediately, avoid easily perishable crops such as asparagus, sweet corn, peas and grow potatoes and onions instead.
- Some plants are difficult to grow and need special attention from the farmer for optimum results. Your choice of the crop must consider whether you have the knowledge and experience in growing such crops and whether you are willing to learn from available resources. Also, some plants would need special equipment. Select those you won’t need to buy the equipment to grow.
You should not miss this: Chilli Seed Germination, Time, Temperature, Procedure .
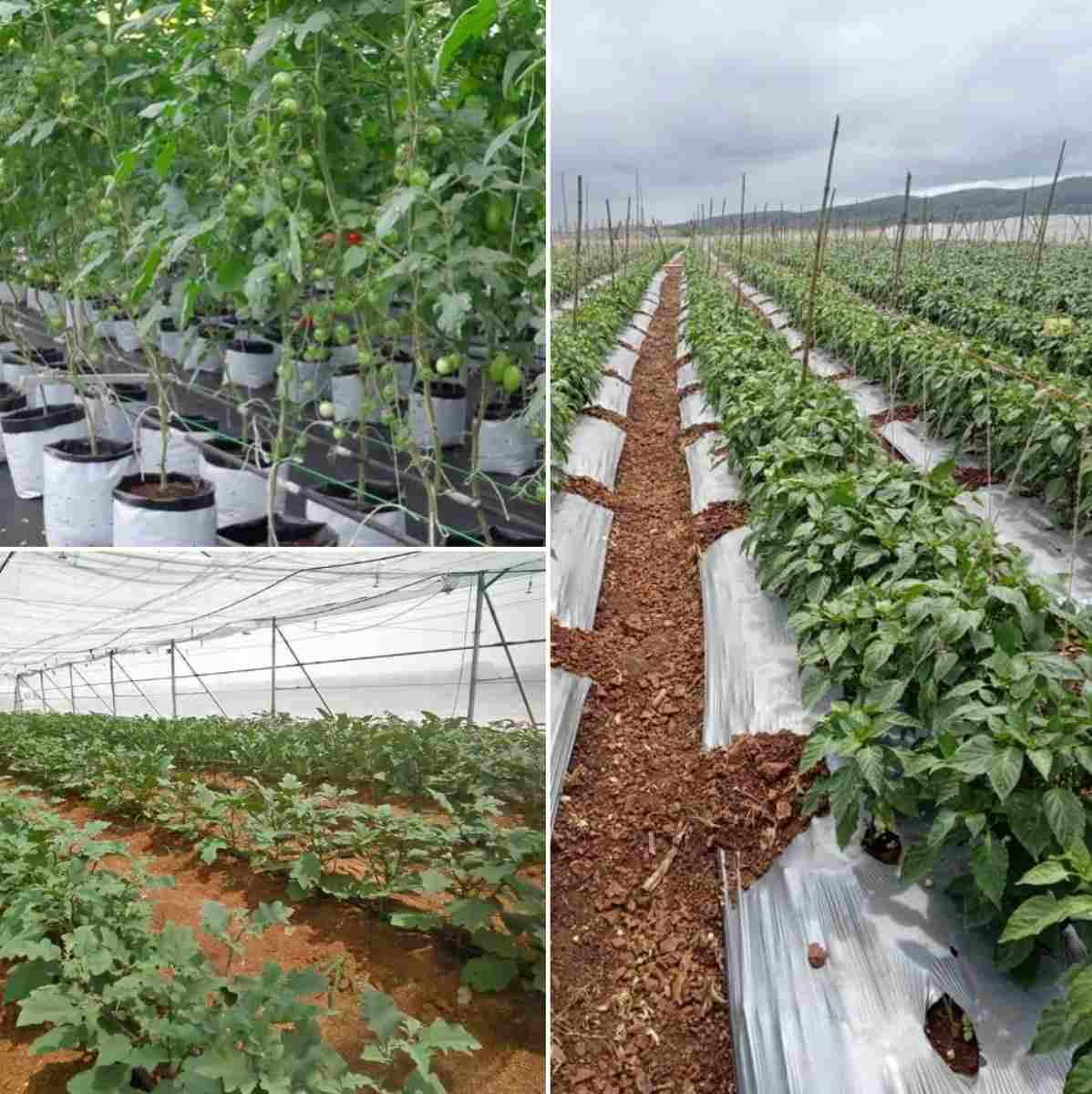

The quality of vegetables mainly depends on the horticultural production systems, environmental factors, and management practices used. Climatic conditions such as temperature and light intensity have a strong influence on the nutritional quality of vegetables. Hydroponic cultivation technique ensures the production of quality vegetables, and in this culture system, both plant nutrition and environmental conditions are artificially managed according to the plant need. Growing quality vegetables is easier and safer in hydroponic compared to conventional soil culture. The advantages of this system are that plant roots are visible and the root zone environment can be easily monitored. In this system of cultivation, the yield of the vegetable crop can be maximized through the efficient use of all resources, and it is believed to be the intensive form of agricultural enterprises for commercial production of greenhouse vegetable plants .
Soilless culture of vegetables uses inert organic or inorganic substrate through the hydroponic nutrient application. This culture has been reported to practice in the greenhouse as an alternative to conventional filed cultivation of many high-value vegetable crops. Under these protected cultivation systems, weather factors, the amount and composition of nutrient solution, and the growing medium can be managed successfully. Therefore, the quality of vegetable crops grown through soilless culture improves significantly compared to conventional soil culture. Many researchers found better taste, uniformity, color, texture, and higher nutritional value in fruits grown in soilless culture than in soil cultivation methods.
Once you have a clear idea of what you want your vegetable farm business to look like, what you want to produce, and where you will sell your product, you need to establish a production plan. Some factors to consider are listed below;
Capital needs – Identify the investment and cash operating needs and how much you will need to borrow.
Infrastructure and equipment – Identify what equipment you need for the vegetable crops you will produce. Also, depending on the packaging and also handling requirements identify what type of infrastructure will be needed.
Management – Identify the production, management, and marketing skills essential to make your enterprise successful. If you do not have those skills, identify ways to acquire them, which can include hiring additional labor.
Planting and harvesting schedule – Plan the best timing for planting and harvesting your vegetable crops, based on plant varieties and availability of labor. Remember to plan planting dates based on your harvest schedule (e.g., customer demand).
Post-harvest and sanitation – Post-harvesting needs (sanitation, handling, and cooling) are very important aspects that need careful thought. Cooling is essential to delay produce spoilage and keep it fresh. When the product is not sold and delivered immediately after harvest, a cold storage option can be needed.
Enterprise analysis – Keep good plant production and financial records to help you make good decisions in the future. Use records to identify problems that need to be solved and to identify what practices and crops are profitable for your business.
List of high yield vegetable crops can be given below;
Cucumbers – In an acre area, around 12000 cucumber plants are planted (3 plants per square meter) and each plant yields an average of about 5 to 7 kg per cycle. This will yield about 8,400 to 10,500 plants per acre.
Squash – In general, each squash plant produces about 5 to 25 pounds of yellow squash during the growing season. A 10-foot row of yellow squash averages about 20 to 80 pounds of squash.
Beans – The average yield is about 100 to 120 quintals of green pods per hectare can be expected.
Tomatoes – The average tomato crop yield per acre in India is 10 tonnes although the yield varies from 15 to 20 tonnes per acre in case of irrigated crops.
Peanuts – Grown mainly through age-old farming techniques, peanut yield in India is about 700 to 900 kg per hectares.
Potatoes – During the first year of cultivating potatoes, a good yield can be about 10 tons per acre. Experienced farmers after years of practice can achieve yields 16 to 28 tons per acre.
Peppers – The yield per acre of pepper is about 0.39 tonnes per hectare. This indicates a plant population of 10,250 plants per acre, thus the average yield per plant is 3.6 pounds.
Beetroot – The beetroot crop yields about 20–25 tonnes/hectare in 120 days.
Radishes – It yields about 200 to 250 quintals fresh radish per hectare.
Lettuce – The average yield of lettuce is about 80 to 120 quintals per hectare.
The above information may also be used for Polyhouse vegetable farming, Greenhouse vegetable farming, and even vegetable farming at home. In case if you are interested in this: How to Make Money from a Vegetable Farming .
10 COMMENTS
Thanks for ur information it’s very useful to me..
insightful information for beginners like me. How can I get this information handy for referral purposes during my start up farming carrer
I would like to set a agriculture business in 100 Acre land in Gujarat. I need prepare a business plan which should include crop name, it production detail per year and estimed income. I also need to have deails of other related investmenet like equipments, storage facility, labour cost , water cost , fertiliser cost etc
I want to be a farming business man
The content is important for a small scale farmer who is not in a position to get extension services from agricultural officers. It help me acquire some knowledge in writing a proposal for my vegetable project.
Good information for me to start my vegetable project to feed my country I would like to receive more information through my email as a guide for my project Thank you
Thanks for the Info, I am planning to start the farming can I get more info about the farming with Advance Technology how we built the prototype model first.
This is a great insight into vegetable farming. I wanna develop a business plan for vegetable production on campus. How can I start and what kind of marketing strategy plan do I have to implement
Thank you for the information. Also I would like to receive more information.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf...
Revolutionizing citrus preservation: towards a healthier, greener future, natural solutions for peony leaf and flower problems: 100% effective..., maximizing profits with avocado contract farming in india: a comprehensive..., natural solutions for hydrangea problems: 100% effective remedies for leaf..., the ultimate guide to choosing the perfect foliage friend: bringing..., from sunlight to sustainability: 15 ways to use solar technology..., the ultimate guide to dong tao chicken: exploring from history..., the eco-friendly makeover: how to convert your unused swimming pool..., mastering the art of delaware chicken farming: essentials for healthy..., 20 best homemade fertilizers for money plant: diy recipes and..., how to craft a comprehensive free-range chicken farming business plan, brighten your flock: raising easter egger chickens for beauty and..., how to optimize your poultry egg farm business plan with..., subsidy for spirulina cultivation: how indian government schemes encouraging spirulina..., ultimate guide to raising dominique chickens: breeding, feeding, egg-production, and..., mastering the art of raising jersey giant chickens: care, feeding,..., ultimate guide to raising legbar chickens: breeding, farming practices, diet,..., how to raise welsummer chickens: a comprehensive guide for beginners, how to protect indoor plants in winter: a comprehensive guide, borewell drilling cost, pump price, and pipe cost, polyhouse subsidy, cost, profit, project report, tractor subsidy, bank loan, eligibility, schemes, process, malabar neem project report details guide, cold storage project report, cost and subsidy, mushroom farming project report, cost and profit analysis.

- Agriculture
Livestock Farming
Aquaculture
Poultry Farming

How to start vegetable farming in South Africa
Commercial vegetable farming in South Africa is viable for those with suitable land, climate, and infrastructure. The industry is worth an estimated R4 billion per year, with the top commercial vegetable growers in the country earning between R30 million and R50 million annually. To start a commercial vegetable farm in South Africa, you will need access to suitable land, water, and agricultural infrastructure.
The climate in South Africa is favorable for growing a wide range of vegetables, from leafy greens to root crops. Before starting your farm, it is important to develop a business plan considering the cost of inputs, labor, and other overhead expenses. It is also essential to consider your target market and what price point you will need to sell your produce to make a profit. With proper planning and execution, commercial vegetable farming can be a profitable enterprise in South Africa.
South Africa has a rapidly growing population and an ever-increasing demand for food. This has created a need for more farms and agricultural businesses, including vegetable farms. While many different vegetables are in high demand in South Africa, some of the most popular include potatoes, carrots, tomatoes, onions, and cabbage. Potato farming is one of the most common types of vegetable farming in South Africa.
The country is home to over 200 potato growers producing over 1 million tons of potatoes yearly. Most South African potato farmers grow their crops on small family farms. However, there is an increasing number of larger commercial operations as well. Carrots are another popular vegetable in high demand in South Africa. The country is the world’s second-largest producer of carrots, behind only China.
In case you missed it: Terrace Gardening ideas for Home in India: For Vegetables, Fruits, Flowers, and Herbs

Carrot production has been rising recently due to increasing health consciousness among South Africans. Carrots are typically grown on larger commercial farms but can also be successfully grown on smaller-scale operations. Tomatoes are another staple vegetable in high demand across South Africa.
Tomato farming is typically done on a larger scale than other vegetables due to the high yield potential of the crop. However, tomato farmers must be mindful of market conditions and carefully plan their production to maximize profits. Onions and cabbage are other vegetables widely consumed in South Africa. Onion farming is typically done on a smaller scale than other vegetables due to the lower demand.
Commercial vegetable farming in South Africa is a profitable business. However, to start a successful vegetable farming business, you must have a well-thought-out business plan. This vegetable farming guide will outline everything you need to know about starting a commercial vegetable farm in South Africa, from the initial costs and planning requirements to the day-to-day running of the farm and the potential profits you can make.
The first step in starting a commercial vegetable farm is to develop a business plan. This should include an analysis of the local market for vegetables, an assessment of your potential customer base, and a production plan outlining how you will grow and sell your vegetables. The business plan should also include financial projections for your first few years of operation.
Once you have developed your business plan, you must obtain the necessary financing. This can be done through loans from banks or other financial institutions, private investors, or government grants. In South Africa, several government initiatives provide funding for small businesses, including agricultural businesses.
After securing financing, you will need to purchase or lease land to grow your vegetables. The farm size will depend on the scale of production you are planning. Once you have procured the land, you will need to prepare it for planting by clearing any existing vegetation and preparing the soil. This process can be done manually or with the help of machinery. Once the land is prepared, you can start planting your vegetables.
If you plan to start a vegetable farm in South Africa, there are certain things that you need to take into consideration. The first is the climate. South Africa has a temperate climate, which is ideal for growing vegetables. However, you will need to choose the right location for your farm. The second is the soil type. South Africa has a variety of soil types, from sandy to clayey. You must choose the right type of soil for your vegetable farm.
In case you missed it: Liquid Fertilizer Guide for Plants: How to Apply, Homemade, Types, Vegetables, Herbs, Lawn, Potted Plants, and Indoors

The third is the water supply. South Africa has an abundant water supply, but you will need to ensure that your farm has access to a reliable water source. The fourth is the market for your vegetables. There are many options for selling your vegetables in South Africa, from farmers’ markets to online retailers. You will need to research to find the best option for your business.
The cost is the last thing you need to consider when starting a vegetable farm in South Africa. Vegetable farming can be an expensive business, but there are ways to cut down on costs. One way is to use recycled materials for your farming equipment and buildings. Another way to reduce costs is using organic farming methods, such as composting and crop rotation. Starting a vegetable farm can be a profitable business venture if you are willing to work.
Assuming you would like to start a small-scale commercial vegetable farm in South Africa, the amount of land you need would certainly vary. A rough estimate would be between 1 and 5 hectares; however, this greatly depends on the specific vegetables you plan to grow and your farming method. For example, if you wanted to grow only potatoes, less land would be required than if you wanted to grow a variety of vegetables.
The type of farming method also makes a difference. Using traditional methods requires more land as crops are grown further apart to allow for manual weeding, etc. However, using more intensive methods such as hydroponics or aeroponics, less land is required as crops can be grown closer together, and automated systems take care of tasks such as watering and fertilizing. Regarding cost, purchasing farmland in South Africa can vary widely depending on location and size.
In rural areas, it is possible to find plots of land for sale for around R50,000 per hectare, while in more urban areas, prices can be closer to R1 million per hectare. It is important to research and speak to local farmers before making any decisions. Once you know how much land you need and what it will cost to purchase, you can start planning your vegetable farm! Consider water availability, soil quality, and market access when choosing your location; with careful planning and execution, start a vegetable farm in South Africa.
Vegetable farming in South Africa is a rapidly growing industry with great potential for commercial success. There are many different methods of vegetable farming, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods of vegetable farming in South Africa are described below.
1. Conventional Farming : Conventional farming is the most common type of vegetable farming in South Africa. It involves growing vegetables in open fields using pesticides and fertilizers. This type of farming is comparatively cheap and easy to set up, but it can damage the environment if not managed properly.
2. Organic Farming : Organic farming is a type of vegetable farming that does not use synthetic pesticides or fertilizers. This farming method is more expensive and time-consuming than conventional farming but is more environmentally friendly.
3. Hydroponic Farming : Hydroponic farming is a type of vegetable farming that uses nutrient-rich water solution instead of soil to grow plants. This gardening method is very efficient and does not require pesticides or fertilizers, but it can be expensive.
In case you missed it: High Yield Hybrid Vegetable Varieties in India: For Winter (Rabi), Summer, and Rainy Season (Kharif)

4. Aquaponics Farming : Aquaponics farming combines hydroponic gardening with fish husbandry to create a self-sustaining system where the waste from the fish provides nutrients for the vegetable plants, and the vegetable plants filter the water for the fish. This type of agriculture is highly efficient and environmentally friendly, but it is expensive to set up and maintain.
Regarding farming in South Africa, a number of different vegetables can be grown profitably. However, some vegetables are more profitable than others. The most profitable vegetable to farm in South Africa is potatoes. Here are a few reasons why:
- Potatoes are a relatively easy crop to grow and don’t require a lot of expensive inputs.
- There is always demand for potatoes from local consumers and businesses such as restaurants and food processors.
- Potatoes have a relatively long shelf life, meaning they can be stored and sold throughout the year.
- Potatoes are versatile vegetables used in a wide range of dishes, making them popular with home cooks and professional chefs. If you’re considering starting a vegetable farm in South Africa, potatoes should be at the top of your list!
Many types of vegetables are grown in South Africa. Some of the most common and popular vegetables to grow in South Africa include:
Each type of vegetable has different growing requirements, so it is required to do your own research before deciding which vegetables you would like to grow. Once you have decided on the types of vegetables you would like to grow, you will need to develop a commercial business plan and determine your venture’s cost and profit potential.
Tunnel vegetable farming in South Africa is a popular option for those looking to start their commercial vegetable farm. The climatic conditions in South Africa are ideal for growing a wide variety of vegetables, and the country has a large market for fresh produce. Tunnel farming allows farmers to control the environment where their crops are grown, making it possible to produce high-quality vegetables year-round.
In case you missed it: How to Grow Vegetables in Aquaponic Systems: Types, Methods, Requirements, and Disadvantages

Starting a tunnel farm in South Africa requires a significant investment of capital and a thorough understanding of the business. This guide will provide an overview of what it takes to start a tunnel farm in South Africa, including the cost and profit potential.
Vegetable farming on a small scale in South Africa is a viable option for those with limited land and water resources. With the right business plan and cost-effective production strategies, small-scale farmers can profit from vegetable farming. The ideal location for small-scale vegetable farming in South Africa is in the country’s semi-arid regions, where reliable rainfall and irrigation infrastructure is available. These conditions are necessary to ensure a consistent supply of water for crops.
To be successful, small-scale vegetable farmers must clearly understand their target market and what consumers are willing to pay for their produce. They must also effectively manage their costs, including labor, inputs, and transportation. Finally, small-scale vegetable farmers need a sound marketing strategy to sell their products. This may include selling direct to consumers or through wholesale channels.
Hydroponic vegetable farming is a system where crops are grown in nutrient-rich water instead of soil. This farming method allows for a higher yield of vegetables per square meter and requires less water than traditional farming methods. Hydroponic vegetable farming is becoming increasingly popular in South Africa as the country looks for ways to become more self-sufficient in food production.
The South African government has been investing in hydroponic farms and training farmers in this type of agriculture. There are many benefits to hydroponic vegetable farming, including the following:
- Higher yields of vegetables per square meter
- Less water consumption
- Reduced need for pesticides and herbicides
- No soil erosion
- Faster crop turnaround time
If you plan to start your own hydroponic farm, there are a few things you need to know. First, you’ll need to choose the right location for your farm. Hydroponic farms can be set up indoors or outdoors, but it’s important to ensure that your chosen location has access to sunlight and adequate ventilation. You’ll also need to invest in basic equipment, like grow lights, fans, and pumps. Once you have everything in place (setup), you can start growing your crops!
The cost of starting a vegetable farm in South Africa will vary depending on the size and type of farm you want to start. However, some basics are required for all commercial vegetable farms. These include:
- Land : Buying or leasing land can be the most expensive part of starting a vegetable farm. The land price will depend on your desired farm’s location and size.
- Buildings and Infrastructure : You will need to construct or purchase appropriate buildings and infrastructure for your vegetable farms, such as greenhouses, storage sheds, and irrigation systems. These costs can vary significantly depending on the scale of your operation.
- Equipment : You will need to purchase or lease farming equipment, such as tractors, planting, harvesting equipment, etc. Prices for this equipment can also vary widely depending on your needs.
- Seeds and Plants : You will need to buy seeds or plants for your crops. The cost of these will depend on the types of crops you want to grow.
- Labor : If you do not plan to do all the work yourself, you will need to hire workers for your farm. The labor cost will again depend on the size and scope of your operation.

The average vegetable farm owner in South Africa makes about R45,000 per month. However, this profit can vary depending on the size of the operation and location of the farm, as well as the type of vegetables grown. For example, owners of larger farms located in more rural areas tend to make more money than those with smaller farms in more urban areas. Additionally, farmers who grow more popular vegetables, such as tomatoes and potatoes, usually make more money than those who grow less popular vegetables.
If you’re considering starting a vegetable farming business in South Africa, this article is for you. We’ve included everything you need to know about starting vegetable farming in South Africa, from writing a business plan to calculating start-up costs and estimating profits. So what are you waiting for? Get out there and start growing your own success.
Eco-Friendly Gardening: How to Make Liquid Fertilizer from Kitchen Waste
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Anise in Pots: Explore Seed Propagation to Harvesting
- Guide to Raising Chester White Pigs: Discover Breed Facts to Growth Management
- Mastering the Elegance: The Ultimate Guide to Weeping Cherry Tree Care, Planting, and Maintenance
- Ultimate Guide to Planting Garlic in Grow Bags: Growing Strategies for Beginners
- How to Fix Spider Plant Leaf-Related Problems: Natural and Organic Remedies
- 10 Reasons Why Your Tulsi Plant is Shedding Leaves: Home Remedies and Solutions
- Optimizing Growth and Yield: The Advantages of Palm Bunch Ash Fertilizer
Utilizing Neem Oil Extract as a Natural Pesticide for Hydrangea
- From Soil to Harvest: Various Ways in Which Farmers Can Use AI Tools
Steps to Encourage and Induce Citrus Flowers: A Comprehensive Guide
- How to Fix Snake Plant Leaf-Related Issues: Natural and Organic Remedies
- Transform Your Garden into a Fragrant Oasis with Raat Ki Rani (Night Blooming Jasmine)
Discover the Ideal Chicken Breeds for Philippine Farms
- How to Create a Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan for Profits
- Grow Lemon Cucumbers Like a Pro: Insider Techniques for Bountiful Yields
- Ultimate Guide to Caring for Your Pink Princess Philodendron: Tips for Thriving Variegation
- Areca Nut Profit Per Acre: Calculating Yield and Cost of Cultivation
- How Kaveri Chicken is Becoming a More Profitable Breed in Indian Backyards
- Transform Your Barn: 9 Steps to Convert a Horse Stall into a Chicken Coop
- Exploring Suffolk Sheep Disadvantages with Limitations and Challenges
- Guide to Solving Potted Lemon Tree Problems: How to Revive Lemon Tree in Containers
- Steps to Encourage Female Pumpkin Flowers: Best Strategies for More Flowers and High Yields
- Ultimate Guide to Yellow Raspberries: Exploring from Planting to Care
- Ultimate Guide to Planting Ginger in Grow Bags: Growing Strategies for Beginners
- Ultimate Guide to Growing Red Creeping Thyme: Propagation, Planting, Pruning, and Care
- Top 10 Common Peacock Plant Problems and How to Fix Them
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Naked Neck Chickens: Feeding, Egg-Production, Breeding, and Care
- Unlocking Green Growth: The Surprising Benefits of Himalayan Pink Salt for Plants
- Step-By-Step Guide to Planting Carrots in Grow Bags for a Bountiful Yield
- Nourish Naturally: 10 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Meyer Lemon Tree
- How to Successfully Grow Potatoes in Grow Bags: A Comprehensive Planting Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Planting Tomatoes in Grow Bags: Growing Tips for a Bountiful Harvest
- 10 Best Natural Pesticides for Fruit Trees: 100% Effective to Kill Bugs on Fruit Plants
- 10 Best Natural Pesticides for Weed Plants: 100% Effective to Kill Weeds
- 10 Reasons Why Your Succulents Not Blooming: Remedies and Treatment
I am so interested on Agricultural farming especially on producing a vegetables but due to lack of Capital to kickstart I am unable to opperate, I am still begging anyone or any sponcer or partnership for intervieneance.i sn owning a piece of Land which is 25 to 30 Hector’s vacant to be used.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Ultimate Guide to Grow Anise in Pots: Explore Seed Propagation...
Guide to raising chester white pigs: discover breed facts to..., mastering the elegance: the ultimate guide to weeping cherry tree..., ultimate guide to planting garlic in grow bags: growing strategies..., how to fix spider plant leaf-related problems: natural and organic..., 10 reasons why your tulsi plant is shedding leaves: home..., optimizing growth and yield: the advantages of palm bunch ash..., from soil to harvest: various ways in which farmers can..., how to fix snake plant leaf-related issues: natural and organic..., transform your garden into a fragrant oasis with raat ki..., how to create a poultry egg farm business plan for..., grow lemon cucumbers like a pro: insider techniques for bountiful..., ultimate guide to caring for your pink princess philodendron: tips..., areca nut profit per acre: calculating yield and cost of..., how kaveri chicken is becoming a more profitable breed in..., transform your barn: 9 steps to convert a horse stall..., rice production in myanmar; paddy farming in myanmar, banana farming information guide, growing oats information for beginners, contract goat farming in india: how to earn an extra income from this long-term investment, chilli cultivation information guide, how to start and succeed with microgreens business plan.

Fruit and Vegetable Store Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans » Wholesale & Retail

Are you about starting a fruit and vegetable store? If YES, here is a complete sample fruit and vegetable retail business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE.
If you are considering starting a fruit and vegetable retail store business, the good news is that you can’t get it wrong because various types of vegetables and fruits are consumed all over the globe.
Starting a vegetable and fruit retail business comes with its own fair share of challenges, but that does not rule out the fact that it is indeed a profitable business, especially if you locate the business in good location and you know how to source for fresh fruits and vegetables that are consumed in the location where you have your retail outlet.
A Sample Fruit & Vegetable Store Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
Fruit and vegetable store is a subset of the overall grocery store cum retail industry and fruits and vegetable retail stores are outlets that primarily retail fruits and vegetables.
If you are a close observer of the fruits and vegetables retail line of business, you will agree that the industry is anticipated to increase due to increasing consumer health consciousness, which has led to increasing demand for fresh produce.
While per capita fruit and vegetable consumption has remained stable in recent time, the price of vegetables has increased as consumers demand premium, fresh vegetables.
The supermarket and grocery store industry that fruit and vegetable retail store is a part of is a major sector of the economy of the united states which generates over 2 billion annually from more than 42,539 outlets scattered all around the United States of America.
The industry is responsible for the employment of over 2,624,650 people. Experts project the Supermarket and grocery industry to grow at a 1.4 percent annual rate.
It is a fact that an estimated two-thirds of the United States’ gross domestic product (GDP) comes from retail consumption of which the supermarket and grocery stores industry contributes greatly. This is why the United States of America’s economy is measured with the yardstick of how well the retailing business is fairing in the U.S.
In essence, when there is an unstable economy, purchasing power drops and it impacts the retailing industry negatively which may result in the closure of some grocery stores.
The retail landscape has seen tremendous changes in the last 20 years; it has grown from the usual mom and pop outlets to a more organized and far reaching venture. The introduction of franchise and online stores make it easier for a retailer to reach out to a larger market far beyond the areas where his physical store is located.
It is interesting to note that more grocery shops (fruit and vegetable retail stores inclusive) especially lager retail outlets have started to include self-serve checkout lanes in their stores. It creates shorter lines that appeal to consumers; the average customer would not want to stay longer on a queue.
Over and above, starting a fruit and vegetable retail store business in the United States is a profitable business and it is open for any aspiring entrepreneur to come in and establish his or her business; you can choose to start on a small scale in a street corner like the average mom and pop business or you can choose to start on a large scale with several outlets in key cities all across the United States of America.
2. Executive Summary
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruit & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. is a registered Grocery Store business that will be located in downtown Atlanta – Georgia. Our retail outlet is a standard facility in one of the most ideal locations for a fruit and vegetable retail store.
We will retail a wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables to a wide range of customers. We are aware that there are several supermarket/grocery store outlets all around Atlanta – Georgia that also retail fruits and vegetables, which is why we spent time and resources to conduct our feasibility studies and market survey so as to offer much more than our competitors will be offering.
We have self – service and delivery options for our customers and our outlet is secured with the various payment of options. We know that our customers are the reason why we are in business which is why we will go the extra mile to get them satisfied when they visit our store.
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. will ensure that all our customers are given first class treatment whenever they visit our grocery store.
We have a CRM software that will enable us manage a one on one relationship with our customers no matter how large they are. We will ensure that we get our customers involved in the selection of the fruits and vegetables that will be on our racks.
We are aware of the trend in the retail industry and we are not only going to operate a system where our customers would have to come to our store to make purchase but we will also operate an online store and our customers can order our produce online and they will get it delivered to their houses or any location they want us to deliver the goods within Atlanta – Georgia.
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. is a family business that is owned by Mrs. Dorothy Nightingale and her immediate family members. Dorothy Nightingale has a B.Sc. in Business Administration from the University of Georgia, with over 5 years’ experience in the retailing industry, working for some of the leading brands in the United States of America.
Although the business is launching out with just one outlet in Atlanta – Georgia, but there are plans to open other outlets all around Georgia.
3. Our Products and Services
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. is in the industry to establish a fresh fruits and vegetables one stop retail store and we will ensure we go all the way to make available a wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables in the United States.
Our product offerings are listed below;
- Fresh vegetables such as; cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilies, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress, basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries
- Fresh fruits such as; Banana, Pineapple, Papaya, Strawberry, Blueberry, Raspberry, Plum, Mango, Apple, Cucumber, Dragon Fruits, Oranges, Grapes, Limes, Avocado and a host of other fruits
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to make available a wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables to a wide range of customers in the locations where we have fruits and vegetable retail stores.
- Our mission is to build a fresh fruit and vegetable retail business that will become the leader in our line of business; we want to set up a one stop fruit and vegetable retail store and also in the nearest future run a standard fruit and vegetable farm.
Our Business Structure
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruit & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. intends to build a standard business from the onset hence the need to follow due process when it comes to setting up a structure for the business. We will ensure that we put the right structure in place that will support the kind of growth that we have in mind.
We will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, honest, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all our stakeholders. As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our senior management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of 8 years or more.
In view of that, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Executive Officer (Owner)
- Store Manager
- Human Resources and Admin Manager
Merchandize Manager
Sales and Marketing Manager
Information Technologist
- Accountant/Cashiers
- Customer Service Executive
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results; developing incentives; developing a climate for offering information and opinions.
- Creates, communicates and implements the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
Admin and HR Manager
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Maintains office supplies by checking stocks
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance; calling for repairs
- Enhances department and organization reputation by accepting ownership for accomplishing new and different requests; exploring opportunities to add value to job accomplishments.
- Defines job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carries out induction of new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
Store Manager:
- Responsible for managing the daily activities in the store
- Ensures that proper records of goods are kept and our racks and warehouse does not run out of products
- Ensure that the store facility is in tip top shape and goods are properly arranged and easy to locate
- Controls goods distribution and supply inventory
- Supervises the workforce in the grocery sales floor.
- Manages vendor relations, farm visits, market visits, and the ongoing education and development of the organizations’ buying teams
- Responsible for the purchase of fresh fruits and vegetables for the organization
- Responsible for planning sales, monitoring inventory, selecting the merchandise, and writing and pricing orders to vendors
- Identifies, prioritizes, and reaches out to new partners, and business opportunities
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Develops, executes and evaluates new plans for increasing sales
- Represents the company in strategic meetings
- Helps to increase sales and growth for the company
- Manages the organization website
- Handles ecommerce aspect of the business
- Responsible for installing and maintenance of computer software and hardware for the organization
- Manage logistics and supply chain software, Web servers, e-commerce software and POS (point of sale) systems
- Manage the organization’s CCTV
- Handles any other technological and IT related duties.
Accountant/Cashier:
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensures compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the organization
- Serves as internal auditor for the organization
Client Service Executive
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with customers on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products and services
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the human resources and admin manager in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the organizations’ products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to customers when they make enquiries
- Responsible for cleaning the store facility at all times
- Ensures that toiletries and supplies don’t run out of stock
- Handles any other duty as assigned by the store manager.
6. SWOT Analysis
We decided to open just one store outlet in Atlanta – Georgia in order to test run the business for a period of 3 to 6 years to know if we will invest more money, expand the business and then open other outlets in Georgia.
We are quite aware that there are a several fruits and vegetable retail stores and of course several supermarket and grocery stores all over Atlanta – Georgia and even in the same location where we intend locating ours who also engage in the retailing of fresh fruits and vegetables, which is why we are following the due process of establishing a new business.
We know that if a proper SWOT analysis is conducted for our business, we will be able to position our business to maximize our strength, leverage on the opportunities that will be available to us, mitigate our risks and be equipped to confront our threats.
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. employed the services of an expert HR and Business Analyst with bias in retailing to help us conduct a thorough SWOT analysis and to help us create a Business model that will help us achieve our business goals and objectives.
This is the summary of the SWOT analysis that was conducted for Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc.;
Part of what is going to count as a positive for us is the fact that we are centrally located. The business model we will be operating on, varieties of payment options, wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables and our excellent customer service culture will definitely count as a strong strength for Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc.
From our findings, one major weakness that may count against us is the fact that we are a new fruits and vegetables store and we don’t have the financial capacity to compete with multi – million dollar supermarket and grocery store outlets that also retail fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Opportunities:
The fact that we are going to be operating our fruits and vegetable retail store in one of the most populated cities in Georgia provides us with unlimited opportunities to sell our fresh fruits and vegetables to a large number of people especially vegetarians.
We have been able to conduct thorough feasibility studies and market survey and we know what our potential clients will be looking for when they visit our store; we are well positioned to take on the opportunities that will come our way.
We are aware that one of the major threats that we are likely going to face is economic downturn. Another threat that may likely confront us is the arrival of a new fruit and vegetable store, supermarket, grocery store or retail outlet who would want to engage in the sale of fruits and vegetables in same location where ours is located.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
It is important to state that any trend that is applicable to business in the supermarket and grocery store industry is applicable to fruit and vegetable retail stores.
Supermarket and grocery store business has been in existence for as long as human started trading goods, but one thing is certain, the supermarket and grocery store industry that fruits and vegetables retail store business is a part of is still evolving.
The introduction of technology and subsequently online retail store has indeed helped in reshaping the industry. It is now a common phenomenon for supermarkets and grocery outlets to leverage on technology to effectively predict consumer demand patterns and to strategically position their shops to meet their needs.
If you are a close observer of the trends in the vegetable and fruits retail line of business, you will agree that the vegetable and fruits sale is anticipated to increase due to increasing consumer health consciousness. While per capita fruit and vegetable consumption has remained stable over in recent time, the price of vegetables has increased as consumers demand premium, fresh vegetables.
So also, the number of outlets retailing fruits and vegetables has been increasing. Small, local vegetable and fruits retail outlets are benefiting from the organic, local movement, while large, commercial farms are improving labor efficiency. Going forward, players in the vegetable and fruits line of business will continue to increase revenue generation for their business.
8. Our Target Market
Those who are the end consumers of fresh vegetable and fruits is all encompassing; it is far – reaching. Every household consumes fresh vegetables, so a fresh vegetable and fruit retail store should be able to sell his or her produce to as many people as possible.
Our Competitive Advantage
A recent study conducted on the supermarket and grocery store industry reveals that the market has become much more intensely competitive over the last decade. As a matter of fact, you have to be highly creative, customer centric and proactive if you must survive in this industry.
We are aware of the stiff competition and we are prepared to compete favorably with other leading stores in and around Atlanta – Georgia.
One thing is certain; we will ensure that we have a wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables available in our store at all times. It will be difficult for customers to visit our store and not see the type of fruits or vegetables that they are looking for.
Our excellent customer service culture, online store, various payment options and highly secured facility will serve as a competitive advantage for us.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category in the industry meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. is in business to retail a wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables to the residents of Atlanta – Georgia. We are in the industry to maximize profits and we are going to go all the way out to ensure that we achieve or business goals and objectives.
Our source of income will be the retailing of;
- Fresh vegetables such as cucumbers, shallots, tomatoes, lettuce, chilies, capsicum, red salad onions and snow peas, Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, roses, tomatoes, okra, cantaloupe and bell peppers, watercress, basil, coriander, parsley, lemongrass, sage, beans, peas, kohlrabi, taro, radishes, strawberries, melons, onions, turnips, parsnips, mushroom, carrot, melon, sweet potato, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and eggplant as well as the choys that are used for stir fries
10. Sales Forecast
One thing is certain in this business, if your store is stocked with a wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables and centrally positioned, you will always attract customers cum sales and that will sure translate to increase in revenue generation for the business.
We are well positioned to take on the available market in Atlanta – Georgia and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income from the first six months of operation and grow the business and our clientele base.
We have been able to examine the supermarket and grocery industry, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast. The sales projections are based on information gathered on the field and some assumptions that are peculiar to startups in Atlanta – Georgia.
- First Fiscal Year: $150,000
- Second Fiscal Year: $350,000
- Third Fiscal Year: $550,000
N.B : This projection was done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and there won’t be any major competitor offering same products and customer care services as we do within same location. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
Before choosing a location for Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. we conducted a thorough market survey and feasibility studies in order for us to be able to penetrate the available market and become the preferred choice for residents of Atlanta – Georgia.
We have detailed information and data that we were able to utilize to structure our business to attract the number of customers we want to attract per time.
We hired experts who have good understanding of the supermarket and grocery industry to help us develop marketing strategies that will help us achieve our business goal of winning a larger percentage of the available market in Atlanta – Georgia.
In summary, Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. will adopt the following sales and marketing approach to win customers over;
- Open our fresh fruits and vegetables store in a grand style with a party for all.
- Introduce our fresh fruits and vegetable retail store by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to vegetarians, small scale smoothie and juice shops, households and key stake holders in and around Atlanta – Georgia
- Ensure that we have a wide range of fresh vegetables and fruits in our shelves at all times.
- Print out fliers and business cards and strategically drop them in offices, libraries, public facilities and train stations et al.
- Use friends and family to spread word about our fruits and vegetable retail store
- Place a small or classified advertisement in the newspaper, or local publication about our store
- Make use of attractive hand bills to create awareness and also to give direction to our store
- Position our signage/flexi banners at strategic places around Atlanta – Georgia
- Position our greeters to welcome and direct potential customers
- Create a loyalty plan that will enable us reward our regular customers
- Engage in roadshows within our neighborhood to create awareness for our fruit and vegetable store.
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
Even though our store is well located, we will still go ahead to intensify publicity for the business. Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. has a long term plan of opening outlets in various locations all around Georgia which is why we will deliberately build our brand to be well accepted in Atlanta before venturing out.
As a matter of fact, our publicity and advertising strategy is not solely for winning customers over but to effectively communicate our brand. Here are the platforms we intend leveraging on to promote and advertise Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc.
- Place adverts on community based newspapers, radio and TV stations.
- Encourage the use of word of mouth publicity from our loyal customers
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like YouTube, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Snapchat, Google+ and other platforms to promote our store.
- Ensure that our we position our banners and billboards in strategic positions all around Atlanta – Georgia
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas in and around our neighborhood
- Advertise our fresh fruits and vegetable store business in our official website and employ strategies that will help us pull traffic to the site
- Brand all our official cars and vans and ensure that all our staff members wear our branded shirt or cap at regular intervals.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Pricing is one of the key factors that gives leverage to supermarkets and grocery stores and a fruit and vegetable store is not an exception, it is normal for consumers to go to places where they can get fresh fruits and vegetables at cheaper prices which is why big players in the industry attract loads of consumers.
We know we don’t have the capacity to compete with multi – million dollar grocery stores but we will ensure that the prices of all the products that are available in our store are competitive with what is obtainable amongst fresh vegetables and fruits retail stores within our level.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, is all inclusive because we are aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. will make available to her clients;
- Payment with cash
- Payment via credit cards/Point of Sale Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via mobile money transfer
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our clients make payment for fresh fruits and vegetables purchased without any stress on their part. Our bank account numbers will be made available on our website and promotional materials to clients who may want to deposit cash or make online transfer for our produce.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
From our market survey and feasibility studies, we have been able to come up with a detailed budget on how to achieve a standard fruit and vegetable store and here are the key areas we will spend our startup capital;
- The total fee for registering the business in the United States of America – $750.
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services (software, P.O.S machines and other software) – $3,300.
- Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580.
- The cost for hiring business consultant – $2,500.
- Insurance (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $2,400.
- The cost for payment of rent for 12 months at $1.76 per square feet in the total amount of $75,300.
- The cost for facility remodeling (construction of racks and shelves) – $10,000.
- Other start-up expenses including stationery ( $500 ) and phone and utility deposits ( $2,500 ).
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $60,000
- The cost for start-up inventory (stocking with a wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables) – $150,000
- The cost for store equipment (cash register, security, ventilation, signage) – $13,750
- The cost of purchase and installation of CCTVs – $5,000
- The cost for the purchase of furniture and gadgets (Computers, Printers, Telephone, TVs, Sound System, tables and chairs et al) – $4,000.
- The cost of launching a website – $600
- The cost for our opening party – $5,000
- Miscellaneous – $5,000
We would need an estimate of $200,000 to successfully set up our fresh fruits and vegetable store in Atlanta – Georgia.
Generating Startup Capital for Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc.
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store, Inc. is a family business that is owned and financed by Dorothy Nightingale and her immediate family. They do not intend to welcome any external business partners which is why she has decided to restrict the sourcing of the startup capital to 3 major sources.
These are the areas we intend generating our startup capital;
- Generate part of the startup capital from personal savings
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from the bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $50,000 ( Personal savings $30,000 and soft loan from family members $20,000 ) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $100,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited with the amount.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
It is an established fact that the future of a business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of the employees, their investment strategy and the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business, then it won’t be too long before the business closes shop.
One of our goals of starting this business is to build a business that will survive off its cash flow without injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running.
We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to retail our fresh fruits and vegetables a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Dorothy Nightingale® Fruits & Vegetable Retail Store will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner.
We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Registration: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Securing Point of Sales (POS) Machines: Completed
- Opening Mobile Money Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of facility and remodeling the shop: In Progress
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Generating capital from family members: Completed
- Applications for Loan from the bank: In Progress
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents and other relevant Legal Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Printing of Packaging and Promotional Materials: In Progress
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of furniture, racks, shelves, computers, electronic appliances, office appliances and CCTV: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business both online and around the community: In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement (License): Secured
- Opening party planning: In Progress
- Compilation of our list of fresh fruits and vegetables that will be available in our store: Completed
- Establishing business relationship with fruits and vegetable farmers – suppliers of fresh fruits and vegetables: In Progress
Related Posts:
- Retail Store Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Breathalyzer Vending Machine Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Rice Retail Store Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Ice Vending Machine Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Mall Kiosk Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
They Grow Your Berries and Peaches, but Often Lack One Item: Insurance
Farmers of fruits and vegetables say coverage has become unavailable or unaffordable as drought and floods increasingly threaten their crops.

By Patrick Cooley
Farmers who grow fresh fruits and vegetables are often finding crop insurance prohibitively expensive — or even unavailable — as climate change escalates the likelihood of drought and floods capable of decimating harvests.
Their predicament has left some small farmers questioning their future on the land.
Efforts to increase the availability and affordability of crop insurance are being considered in Congress as part of the next farm bill, but divisions between the interests of big and small farmers loom over the debate.
The threat to farms from climate change is not hypothetical. A 2021 study from researchers at Stanford University found that rising temperatures were responsible for 19 percent of the $27 billion in crop insurance payouts from 1991 to 2017 and concluded that additional warming substantially increases the likelihood of future crop losses.
About 85 percent of the nation’s commodity crops — which include row crops like corn, soybeans and wheat — are insured, according to the National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition, a nonprofit promoting environmentally friendly food production.
In contrast, barely half the land devoted to specialty crops — supermarket staples like strawberries, apples, asparagus and peaches — was insured in 2022, federal statistics show.
Among those going without insurance is Bernie Smiarowski, who farms potatoes on 700 acres in western Massachusetts, along with 12 acres for strawberries. His soil is considered some of the nation’s most fertile. The trade-off is the proximity to the Connecticut River, a bargain that grows more tenuous as a warming world heightens the likelihood of flooding.
Mr. Smiarowski lost nearly $1.25 million worth of potatoes to floods last year, when heavy rains pummeled the area and water from the river seeped into his fields. It was the third straight year of challenging weather.
“We had two extremely wet years, sandwiched around one of the driest years I’ve ever seen,” he said. “We can’t sustain another year like last year.”
Even in an ordinary year, his expenses of $2,000 an acre yield returns ranging from a 20 percent profit to just breaking even. Mr. Smiarowski said the least expensive plans quoted to him — around $170 an acre annually — would be a significant outlay but would cover only 60 percent of the potatoes’ wholesale price.
He sees the case for insurance, but for now, he’s simply hoping for the best.
And specialty farmers say few agents will work with them. “I know of only one in the state,” said Mike Koeppl, who grows strawberries on seven acres near Oshkosh, Wis.
Their reluctance is financial, experts say. Agents make more money insuring vast tracts of corn and soybeans. The average American farm is 445 acres, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, but the average specialty farm is considerably smaller.
And most insurance plans cover a single crop, meaning specialty farmers growing a variety of fruits and vegetables need to buy multiple policies.
Companies offering crop insurance stress that their plans must offer payouts that roughly equal the insurance premiums taken in.
Kristen Ward, regional vice president for crop insurance for Farm Credit Mid-America, said that her company worked with farmers in six states, covering crops from barley to grapes, but that it could not do so in places where conditions were not conducive to specialty fruits and vegetables.
Premiums offered to farmers are based on risk, “which is rated accordingly for where the crop is grown,” she said. “That may look different in different parts of the country.”
Products to fill such gaps have emerged, including whole farm revenue protection, a comprehensive insurance policy for farms growing multiple crops.
More than 220,000 American farms grow specialty crops, according to the American Farm Bureau Federation, a trade group. But only 18,659 whole farm revenue plans have been sold in the decade they have been offered, federal statistics show.
Advocates for the small specialty farmers are looking to Washington for relief.
The federal crop insurance program was born during the Great Depression, when the Dust Bowl ravaged the farm belt. Under the $18 billion program, the government pays half a farmer’s crop insurance premium to guarantee a secure food supply.
In December, Congress extended the current farm bill through 2024, but lawmakers have been unable to agree on what will follow.
The National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition recently released a set of recommendations including easing access to whole farm revenue insurance and expanding disaster relief.
“Floods, drought and hurricanes are all becoming more frequent and strong,” said Billy Hackett, a policy specialist for the coalition. “That’s why it’s important to have a safety net.”
Senator Debbie Stabenow, a Michigan Democrat, has proposed language in the farm bill giving specialty farmers access to highly subsidized insurance policies and streamlining the application process for products like whole farm revenue coverage. “I will always fight to make sure that specialty crops are a central part of farm policy,” Ms. Stabenow said in a statement.
A stand-alone bill, whose co-sponsors include Senator Cory Booker, Democrat of New Jersey, provides incentives for insurance agents to work with small and specialty crop farmers. The bill bases subsidies on the complexity of an insurance plan, rather than the size of the premium.
But commodity farmers are wary of modifications to the crop insurance program.
Growers of corn, soybeans and wheat worry about “changing how the program functions broadly in a way that sets everyone back rather than helping to fill the gaps that exist for certain crops,” said Danny Munch, an economist for the American Farm Bureau Federation.
Some lawmakers oppose changes because of those concerns.
“For years, Iowa farmers have told me to leave crop insurance alone in the next farm bill,” Senator Charles E. Grassley, Republican of Iowa — a state heavily dependent on commodity crops like corn and soybeans — said in a statement. “There’s no need to fiddle with something that’s not broken.”
The impasse has led some farmers to pursue other sorts of assistance.
After Mr. Smiarowski’s Massachusetts crop was ruined last year, he and other farmers affected by the flood appealed to Gov. Maura Healey for help, which came in the form of disaster relief. Mr. Smiarowski was grateful, but he said his share covered only about 20 percent of his losses.
The support was also temporary, leaving him with no option but to wish for more favorable weather in the future.
“When times are bad, you get what you can and you hope for a better year next year,” he said.
Explore Our Business Coverage
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping the world of business..
Phoenix Housing Crunch: A swelling population coupled with development restrictions have contributed to a dire shortage of affordable housing in the biggest city in Arizona , one of the six states likely to determine the U.S. presidential election.
A Billionaire Online Warrior: Bill Ackman, an obstinate hedge-funder who loves a public crusade, has used X to push himself into a new realm of celebrity .
Cancel Smartphones: The N.Y.U. professor Jonathan Haidt became a favorite in Silicon Valley for his work on what he called the “coddling” of young people. Now, he has an idea for fixing Gen Z .
Landline Pride: Traditional phones may seem like relics in the iPhone era, but a recent AT&T cellular service outage had some landline lovers extolling their virtues.
C.E.O. Dreams: Fresh business school graduates are raising “search funds” from willing investors to buy companies they can lead.
Nelson Peltz Wants Respect: The longtime corporate agitator feels misunderstood . Maybe his fight with Disney could change that.

Plant Your Own Vegetable Patch: A Step-by-Step Guide
Posted: May 3, 2023 | Last updated: July 17, 2023

Get your fruit and veg patch off to a flying start with these tips

Why grow your own?
Growing your own crops does take a little time and effort and initial investment, but the rewards are many. There’s nothing quite like having a regular supply of fresh and tasty fruit and vegetables direct from your yard to your table, plus gardening is good for the body and soul . Getting regular exercise can relieve stress and anxiety and boost energy, while a daily dose of sunshine produces Vitamin D, essential for healthy bones and teeth.

Environmental benefits
Long-distance transportation of produce relies heavily on fossil fuels so you are immediately cutting down your carbon emissions , which contribute to climate change, by growing your own. Plus, you are in control, so you can ditch those nasty chemicals and pesticides that are routinely used in commercial farming, which contaminate the environment and harm wildlife. But where do you start? Read on...

Where should you put your vegetable garden?
When planning your vegetable garden , the first thing to consider is light. Most vegetables and fruits will grow best in full sunshine. Choose a spot that receives at least six, preferably eight hours of full sunshine every day. Some vegetables like cabbage, spinach and radishes can be grown in part shade but no crops will thrive in deep shade. Make sure you pick an area that’s level as this makes watering evenly easier.

Tending your garden
Your garden will need regular attention so ideally position it close to the house for easy access, like the folk at Suburban Existence , where it won’t be ‘out of sight and out of mind’. Try to site it close to a water tap too or place some barrels nearby where water can be collected to make the task easy.

How big should my vegetable garden be?
How big should a vegetable garden be? Well, it all depends on how much time you have at your disposal. Tending a vegetable garden takes time so start small, maybe ten-foot-by-ten-foot. You can always build up, depending on how well you take to your new hobby. You don’t want to be overwhelmed. Mark the area with some gardening string and think carefully about those first seedlings.

Prepare your soil
Preparation is everything, so start by digging out weeds, stems and roots and remove as many stones on your patch as possible. Then feed your soil with well-rotted compost or manure, which should be raked level. Add organic matter like composted leaves or shredded aged bark to the surface of the soil when you can and at least once a year to build up long-term soil health, and if you need a quick fix, try an organic fertilizer.
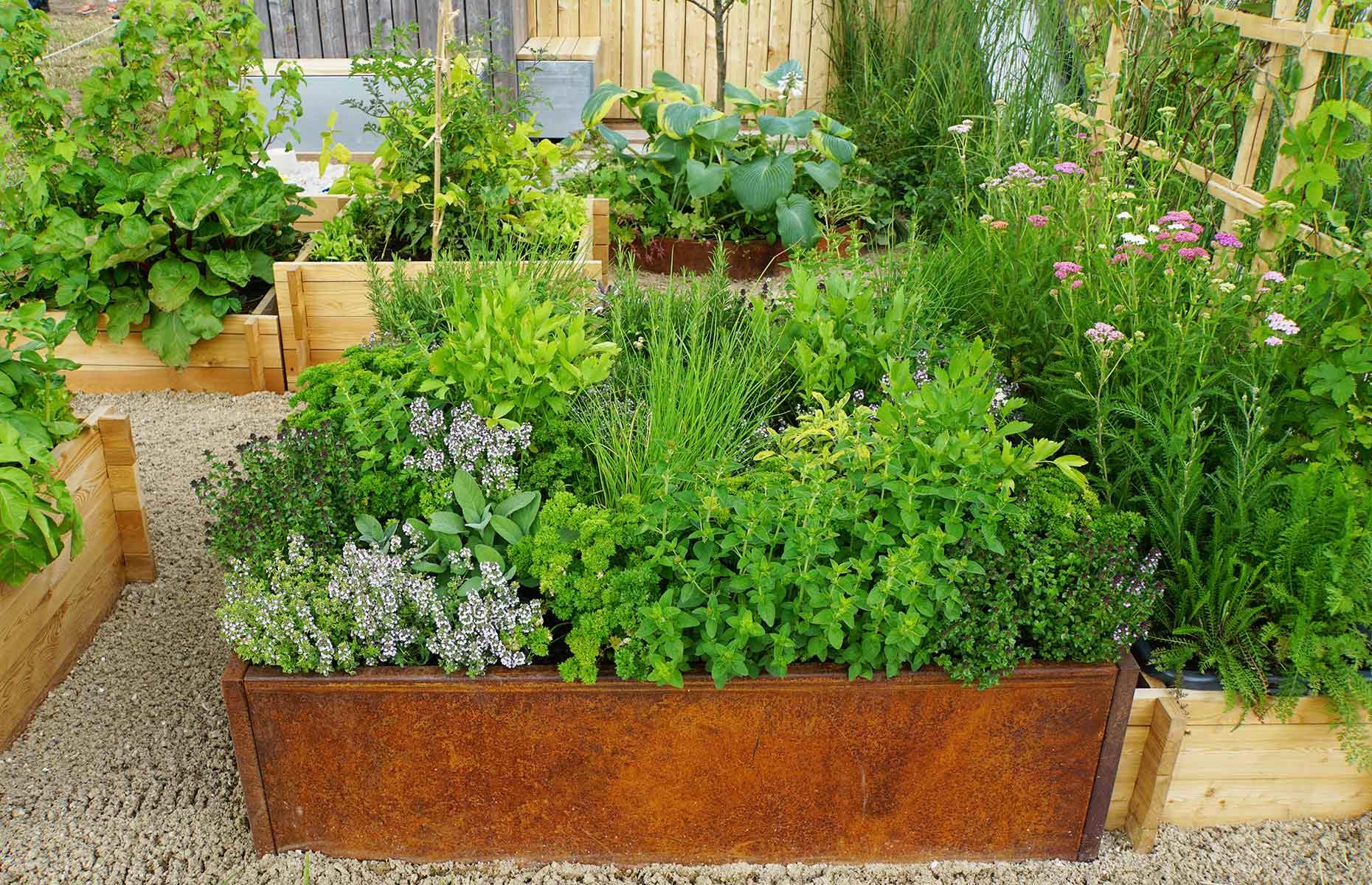

Using raised beds
You might think about growing your vegetables in raised beds if you have clay soil which suffers poor drainage. Raised beds allow the soil to drain faster and warm more quickly in the spring, meaning plants will start to grow earlier in the season. They are great for beginners because you can control the quality of the soil by adding nutrient-rich soil and compost from the outset, ensuring success. They are also attractive and easier to maintain.
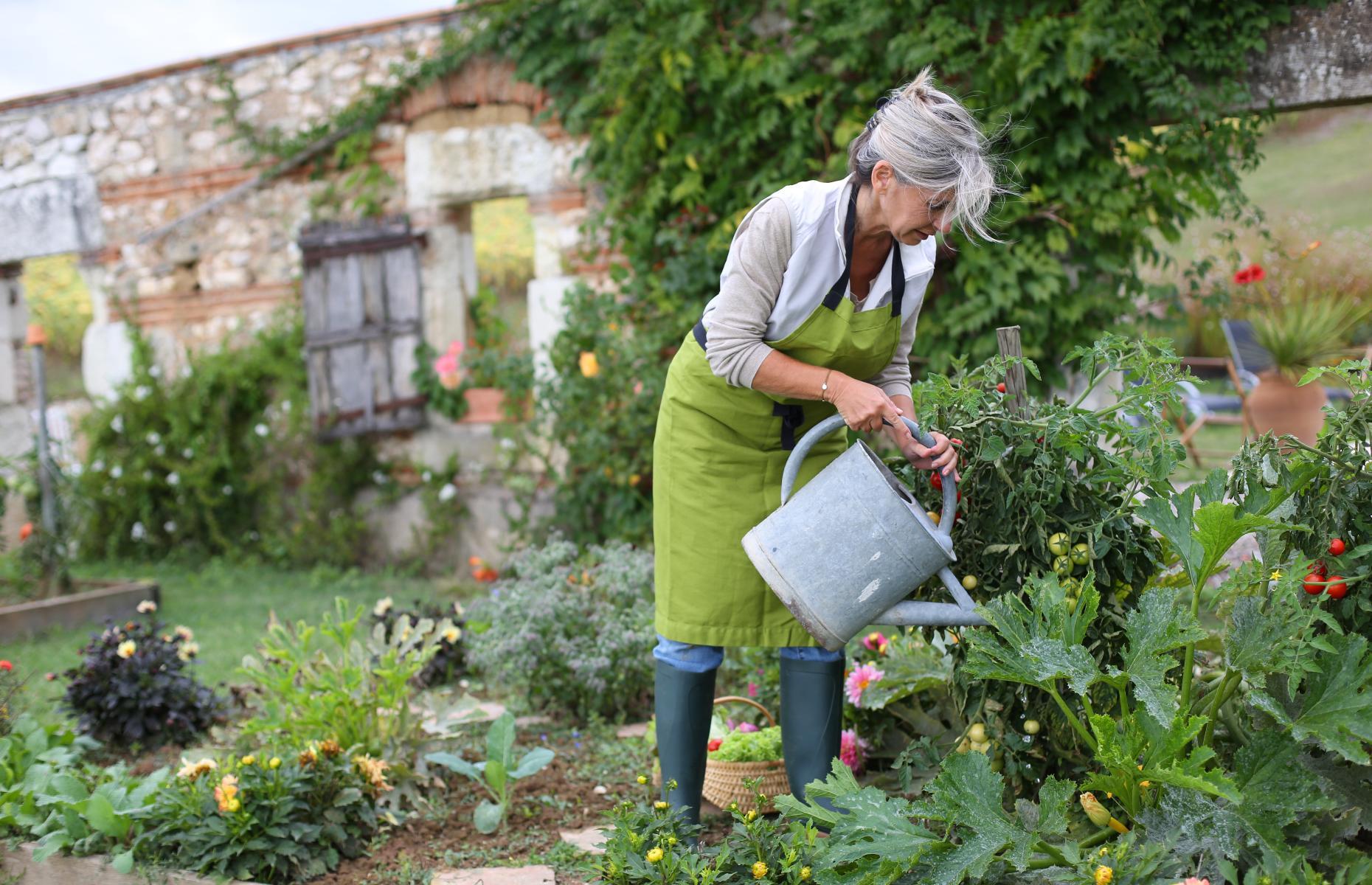

Timing is everything
Spring and autumn are generally the best times to start a vegetable garden as the temperatures are neither too hot or cold. However, plant too early in spring and tender plants will be caught out by sudden frost or fail to thrive. Check your local area's weather patterns and plan accordingly.
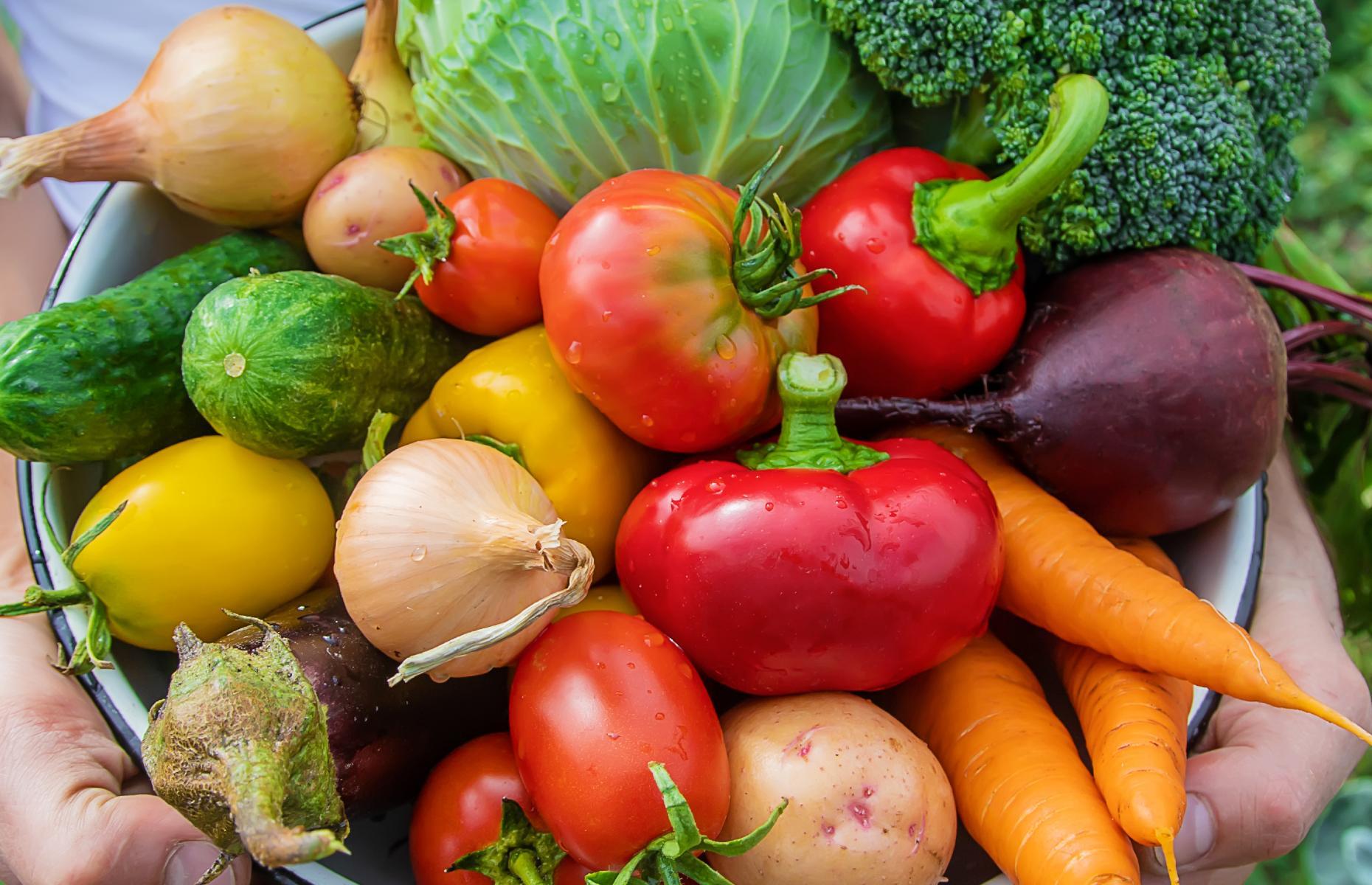

Deciding what to grow
It makes sense to grow your favorite fruit and vegetables, but you might also consider those that are most costly in the shops so you can save money as well. Some varieties are easier to grow than others. If you’re a beginner, your best bet is to choose easy-to-grow crops first like zucchini, potatoes, beans, snow peas, strawberries, cucumbers and carrots, which are ready to harvest within a short time and suffer few pests and diseases .

Plan your vegetable garden layout
If you want a range of crops to harvest, plant three-foot or six-foot rows of different crops: a three-foot row of salad leaves, radishes and coriander for example and a six-foot row of dwarf beans, Swiss chard and carrots. That way you always have a variety of produce available and you can avoid gluts (where all of the produce ripens at the same time and you have more than you can eat). Check out these layout examples and the RHS vegetable planner to help you decide what to plant when.
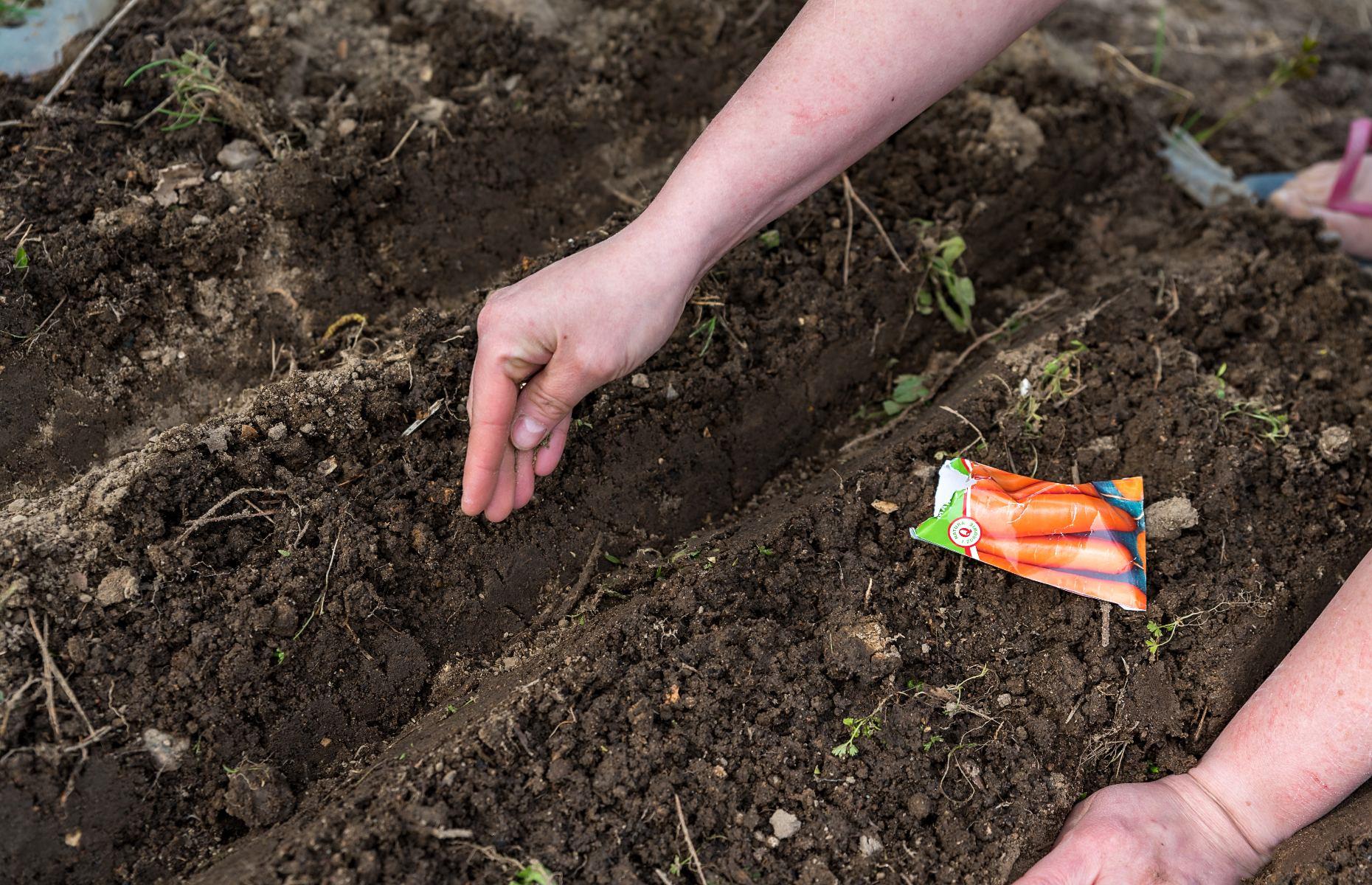

Sowing the seeds of success
Before you get busy in the garden, you need to consider how your seeds should be sown. Some can be sown directly into the soil, where they will grow where they are planted, while others are sown in a seed bed and then transplanted to their final growing position. Others need to be sown indoors in pots of compost where it is warmer. You can sow tomatoes, lettuces and cucumbers into small pots or trays of compost, water well and cover with cling film or place them on a warm windowsill to get them germinating before you can transfer them out to the garden.
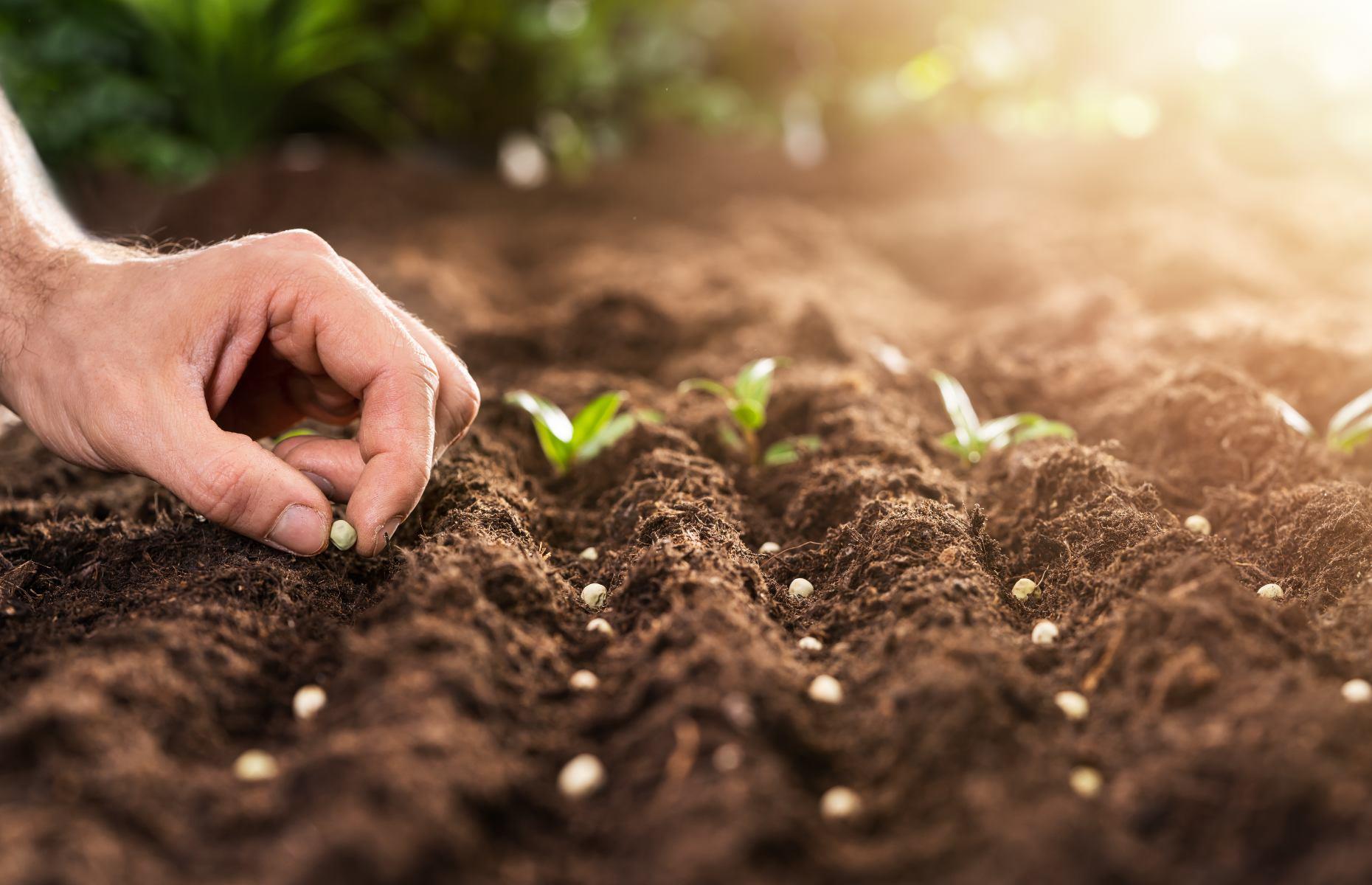

Direct sowing
Most vegetables can be sown directly into the soil. Start by making a shallow trench with a bamboo cane or trowel and insert the seed at intervals before covering with soil and lightly firming down. Then water the soil after sowing. Onions, shallots, garlic and broad beans can be sown from March, as can hardy vegetables such as carrots, beets and spinach, if you lay cloches or plastic sheeting over the beds for a few weeks first to warm them.
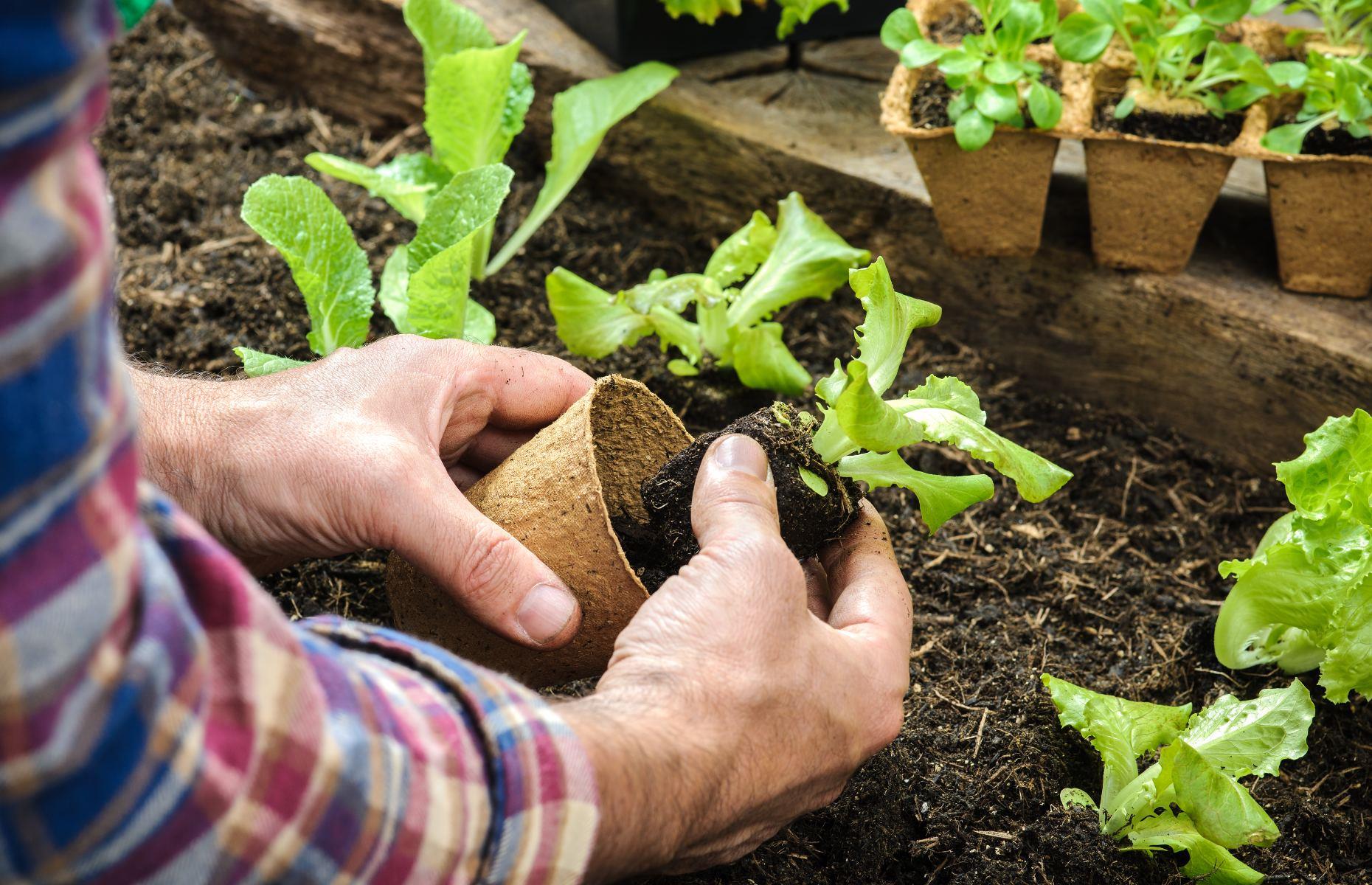

Give plants the best start
If possible, start off vulnerable plants, such as salad leaves and courgettes, indoors in pots and plant them outside when they are big enough to withstand cold and attack from garden pests. Before you plant them outdoors, seedlings will need to be hardened off, say the RHS , so that they acclimatize to the temperature. Move them first to a warm sheltered position outside during the day, bringing them in at night, before gradually moving them outside over a period of about ten days.

How to grow tomatoes
Tomatoes are a good example of a crop that benefits from starting off indoors . All you need is some seed compost, a seed container and propagator, if you have one, a sunny window ledge if you don’t. Sow your seeds at two-inch intervals, cover with a layer of compost and water well. Transfer the seedlings to pots and when they’re bigger and the weather is warmer, you can plant them outside in the ground.

How to water properly

How to stay on top of weeds
Remove weeds as soon as you see them so that they don’t have the opportunity to produce seeds and spread. Weed by hand or use a hoe, keeping the blade edge sharp to sever the weeds so that they can be left to wither where they fall. Mulching with organic matter , leaving it on the surface of the soil, is a good way to stop new weeds from popping up.

Pest control
Before you reach for the insecticide, try some lower-impact methods first. Picking off large insects and caterpillars by hand and dropping them into a bucket of soapy water is a safe, effective way of dealing with limited infestations. Regular weeding can help too and if you have to resort to insecticides, try to go for an eco-friendly pesticide to protect pollinators.

Keep picking and producing

Do I need a greenhouse?
You don’t need a greenhouse to grow your own fruit and vegetables, but it sure helps. Having a greenhouse allows you to grow more crops for longer. You’ll be able to start crops earlier on in the season and extend harvest time, producing a much greater yield. It also allows you to produce more crops from seed, which is much cheaper than buying established plants.

Gardening tools of the trade
If you want to give your new hobby a decent chance of success, it’s worth investing in the right tools . Whether you’re tending a few patio pots or an entire walled vegetable garden, you’ll need a pair of gardening gloves to protect your hands. Secateurs or pruning shears are next, along with a hand trowel for weeding, planting and sowing seeds, and garden classic, a watering can. For bigger jobs, you’ll need a hoe, spade, fork, rake and hose.

What can I grow on a balcony or patio?
There are lots of fruit and vegetable varieties that can be grown in pots or containers on a balcony or patio if you’re short on space. Use pots of different heights to add visual interest and think vertically too. You can fix growing systems, like trellis or shelves to walls and hanging baskets are great for small varieties of tomatoes. Combine flowers and edibles in pots for a display that tastes as good as it looks.

Getting the children involved
Growing vegetables is a great way to get the whole family involved in gardening. Children quickly see the fruits of their labor. It’s also ideal for teaching them about where their food comes and the environment in general. Fast and tasty crops to consider are strawberries, peas and mini carrots as well as cherry tomatoes.
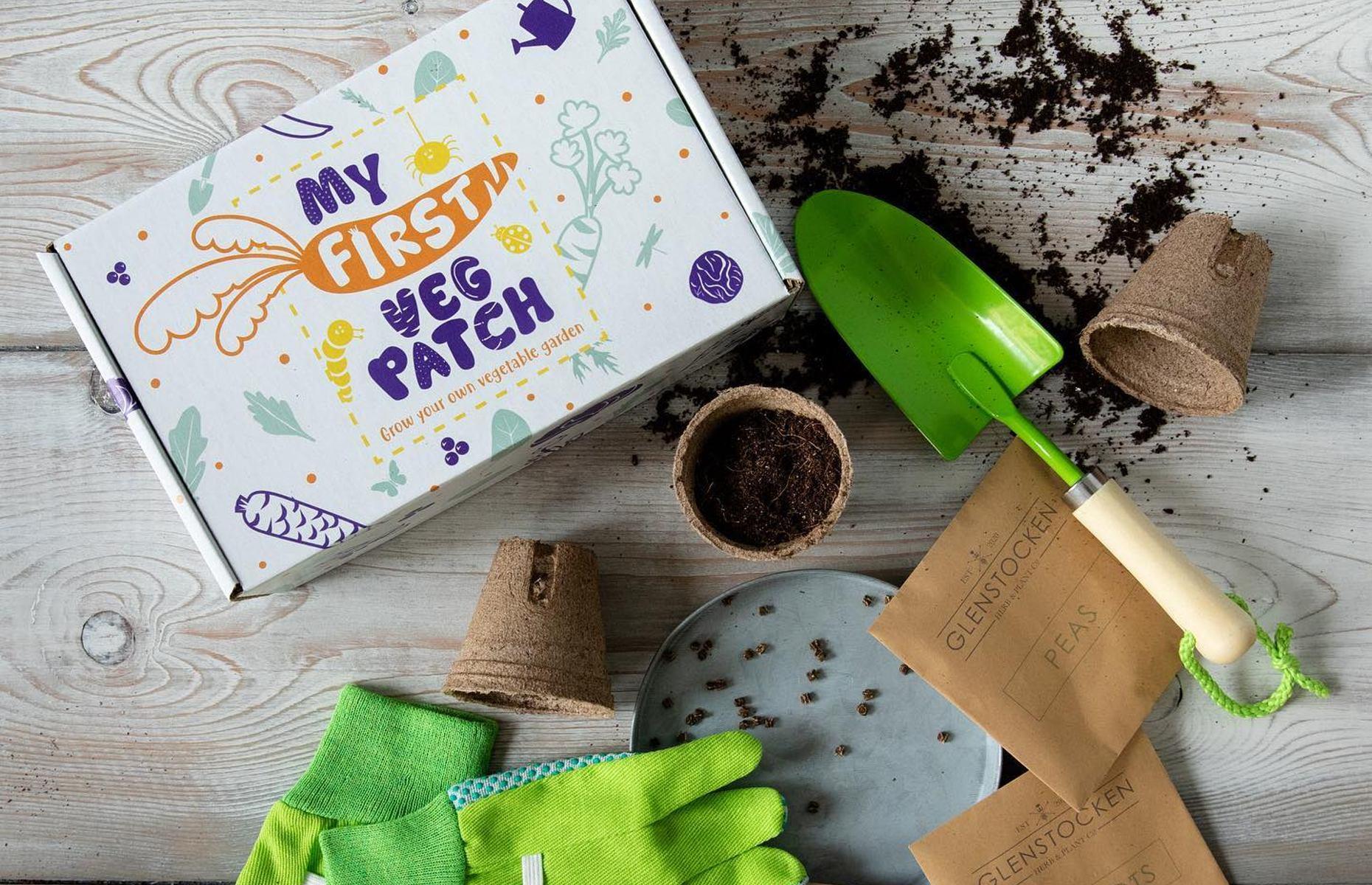

Gardening for kids
There are heaps of gardening paraphernalia out there to encourage your child to get their hands dirty outside in the fresh air from cute gardening tool sets to this fabulous Kids Grow Your Own Veg Patch Kit , which might even inspire them to eat their greens. Gardening helps stimulate your child’s senses of sight, sound, taste and smell which is central to their development.

Gardening for all ages and abilities
Long associated with retirement, there’s a reason so many people gravitate towards gardening in their later life. As well as being an enjoyable form of exercise which improves the blood flow to the brain, gardening encourages the use of all motor skills and improves a sense of well-being. It has even been shown to help reduce the risk of dementia by up to 20% according to studies . And then there are the nutritious vegetables, which are a good source of vitamins and fiber for all ages.

Tidy up … but not too much
It’s a good idea to have a tidy up at the end of every season but don’t overdo it. Leaving plants in the soil to decompose naturally improves the quality of the soil by adding nutrients. Old seed heads can help feed birds over the winter, grasses can add texture to the soil and fallen leaves can be used on compost heaps. Here’s vegetable grower extraordinaire Huw Richards getting the beds ready for winter.

Hydroponic systems
If you really can’t face all that digging and getting your hands dirty but want freshly grown herbs and tomatoes on hand, you might consider one of the impressive hydroponic systems currently on the market, which require only water, light and oxygen, along with smart technology, to produce a wide range of produce in urban spaces. Super easy to use and stylish in design, you can have your greens at the flick of a switch…

Keep a track
Once you’re up and running, keep notes on what works best and which pests have become a problem. Record when you have sown seeds, harvested and which crops you have rotated where. You’ll be an expert in no time and meanwhile you’ll be feasting on fresh fruit and vegetables throughout the year.
Loved this? Discover more gardening advice and tips on our Facebook page
More for You
McDonald’s brings beloved breakfast sandwich back to select locations
Air Force One experiencing ‘rampant thievery’ from White House reporters traveling with president: Politico
Can You Use A Cast Iron Skillet On An Electric Stove?
These Are the 16 Smells Rats Hate the Most
The sequels of 50 iconic movies that made fans wait for decades
You Shouldn’t Be Able to Pay With Cash OR a Card at a National Park. They Should Be Free.
Dramatic video appearing to show a flaming Russian Su-27 jet crashing into the Black Sea shot down by own side, Ukraine says
Have a Bunch of Old Pillows? Here Are 7 Things You Can Do With Them
The Best Way To Keep Bananas From Turning Brown Too Fast
16 Coolest Small Towns in the U.S. You’ve Never Heard Of
The Most Expensive Dog Breeds Money Can Buy in 2024
24 Popular TV Shows That Would Never Be Made Today
Joe Biden Faces 'Clear' Evidence He Lied in Impeachment Probe—Attorney
Lost cities hidden for thousands of years discovered under forest
Instead Of Tossing Old Tortillas In The Garbage, Fire Up The Oven
What happens after your student loans are forgiven? This is what you must know
How to get rid of stink bugs, according to an entomologist
Netflix Drama: 25 Gripping Series That Will Keep You on the Edge of Your Seat
Indian Navy rescues Iranian fishing vessel hijacked by pirates
Chance Perdomo Dies: ‘Gen V' Star Was 27

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Use of Funds. The company is seeking to raise of $830,000 for the purpose of financing the acquisition of the Green Acres Vegetable Farm and Mobile Farmers Vegetable Farm, facilities modifications, equipment, and funding operating expenses. Another $1,000,000 will be invested in the company by its four co-owners.
The fruit farm business plan will include all the elements of a successful business, like Executive Summary, management summary, operating plan, marketing plan, and financial projections. Download Business Plan for an Agriculture Fruit Farm Sample in PDF. OGScapital writer specializes business plan themes such as fountain pepper farm business ...
Here is how you can deal with each challenge: 1. High Initial Investment. As explained in our fruit and vegetable business plan, starting a farming business requires significant capital. According to a report by Starter Story, the average startup costs for a vegetable farm in 2024 are $19,815. Primary startup costs for starting a vegetable farm ...
The amount required for purchase of the first set of fruits seedlings et al - $50,000. The amount required to set up a standard fruit juice processing plant within the farm facility - $ 100,000. Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) - $40,000.
It serves as a roadmap, outlining the vision, goals, and strategies necessary to establish and grow the business. This comprehensive business plan aims to provide Agrolearners.com with a detailed framework for entering the fruit and vegetable industry, addressing key areas such as market analysis, competitive positioning, marketing strategies ...
Download this free agriculture fruit farm business plan template, with pre-filled examples, to create your own plan. Download Now Or plan with professional support in LivePlan. Save 50% today . Available formats: What you get with this template. A complete business plan. Text and financials are already filled out and ready for you to update. ...
It can be used to create a vegetable farm business plan, fruit farm business plan, agriculture farm business plans or many other types of rural businesses. Sample Business Plan For Farms & Agricultural Businesses. Executive Summary - The Executive Summary is the most important part of your business plan. It is a brief description of your farm ...
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan. Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans. FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet. FSA-2037 Instructions.
Explore a real-world produce farm business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan. ... code 0161, Lettuce Farms, as part of Vegetables and Melons, Not Elsewhere Classified, are shown for comparison. Ratio Analysis: Year 1: Year 2: Year 3: Industry Profile: Sales Growth: 0.00% : 49 ...
It can be used to create a vegetable farm business plan, or a dairy farm, produce farm, fruit farm, agriculture farm and more. ... Fruit Farm: this type of farm primarily grows fruits. Hay and Crop Farm: More than half of these types of farms grow hay, while a small number grow sugar beets. A variety of other crops, such as hops and herbs, are ...
The amount required for the purchase of the first set of vegetables and fruits seedlings et al - $50,000. The amount required to set up a standard vegetable processing plant within the farm facility - $100,000. Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) - $40,000.
Describe your farming operations in detail, including the types of vegetables you plan to grow, the cultivation methods, and the size of your farm. Discuss the equipment and technology you will use, as well as the labor requirements. Address any environmental considerations, such as sustainable farming practices or organic certification.
You can get the business plan template for your vegetable farming business or follow these steps to write your plan: #1. Executive Summary. The executive summary condenses all the crucial details about your company into a manageable amount of text. Typically, an executive summary is one page or fewer. It provides a broad overview of everything ...
After researching the local market demand for vegetables, the next step in starting a vegetable farm is to determine which specific types of vegetables to grow and the appropriate season for each. This is an essential step in creating a business plan and ensuring the success of the farm. 1. Research the demand for specific vegetables.
In conclusion, starting a small vegetable farm requires careful planning and execution. By developing a comprehensive business plan, conducting thorough market research, and implementing sustainable practices, you can increase the likelihood of success. Remember, flexibility and adaptability are key in the ever-evolving agricultural industry.
The written part of an organic vegetable farm business plan. The written part of an organic vegetable farm business plan plays a key role: it lays out the plan of action you intend to execute to seize the commercial opportunity you've identified on the market and provides the context needed for the reader to decide if they believe your plan to be achievable and your financial forecast to be ...
Cultivating 1-2 hectares of land varies in cost depending on the location, and also the type of vegetable intended for cultivation. And that should include seedlings, manure, labor, and pesticides. Here is a sample business plan for starting a vegetable farm.
1.1 Business Objectives. Franks Organic Farm has simple objectives: provide healthy and delicious tasting vegetables while simultaneously leaving a minimal carbon footprint. In order to accomplish this, the farm plans to: Sell 60 shares by Year 2 and have full-time income or 90 shares sold by Year 3.
A vegetable farming business plan is a type of strategic plan that caters to the business of vegetable farming. This business plan helps by giving you a variety of ways to help make your vegetable farming business a success. In addition to that, a vegetable farming business plan is a road map to help you avoid any risks that always go along ...
Some of the important high yield vegetable crops. List of high yield vegetable crops can be given below; Cucumbers - In an acre area, around 12000 cucumber plants are planted (3 plants per square meter) and each plant yields an average of about 5 to 7 kg per cycle. This will yield about 8,400 to 10,500 plants per acre.
This vegetable farming guide will outline everything you need to know about starting a commercial vegetable farm in South Africa, from the initial costs and planning requirements to the day-to-day running of the farm and the potential profits you can make. The first step in starting a commercial vegetable farm is to develop a business plan.
What is Climate Smart Agriculture? I think Climate Smart is really about soil and water management. It's interesting being here in Southern California, which right now is in the middle of an atmospheric river.That is one of those symptoms of our climate challenges.
Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) - $60,000. The cost for start-up inventory (stocking with a wide range of fresh fruits and vegetables) - $150,000. The cost for store equipment (cash register, security, ventilation, signage) - $13,750.
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Spinach Farming Docx Crop Selection and Production Techniques. Choosing the right crops and implementing appropriate production techniques are critical factors in vegetable farming.Evaluate the suitability of different vegetables for South African conditions and outline the production methods you will employ. . Consider factors such as crop rotation ...
More than 220,000 American farms grow specialty crops, according to the American Farm Bureau Federation, a trade group. But only 18,659 whole farm revenue plans have been sold in the decade they ...
When planning your vegetable garden, the first thing to consider is light.Most vegetables and fruits will grow best in full sunshine. Choose a spot that receives at least six, preferably eight ...